Materials occupy center stage in modern human civilization and are all around us. The metal in automotive and wires, the plastic in packaging, and the variety of fabrics in clothes are a few common materials. However, many raw materials are either depleting fast or pollute the environment, either directly or indirectly in any of the processing steps. Startups now develop sustainable and cost-effective materials that often offer improved physical properties as well. Examples include biodegradable plastics, thermally adaptive fabric, and flexible displays. Innovations and new challenges in manufacturing, such as additive manufacturing, also lead to the development of advanced materials. Due to the obvious need for manufacturing to produce literally anything, novel materials also impact other industries such as energy, automotive, construction, and textiles.
Top 5 Global Startup Hubs: Materials
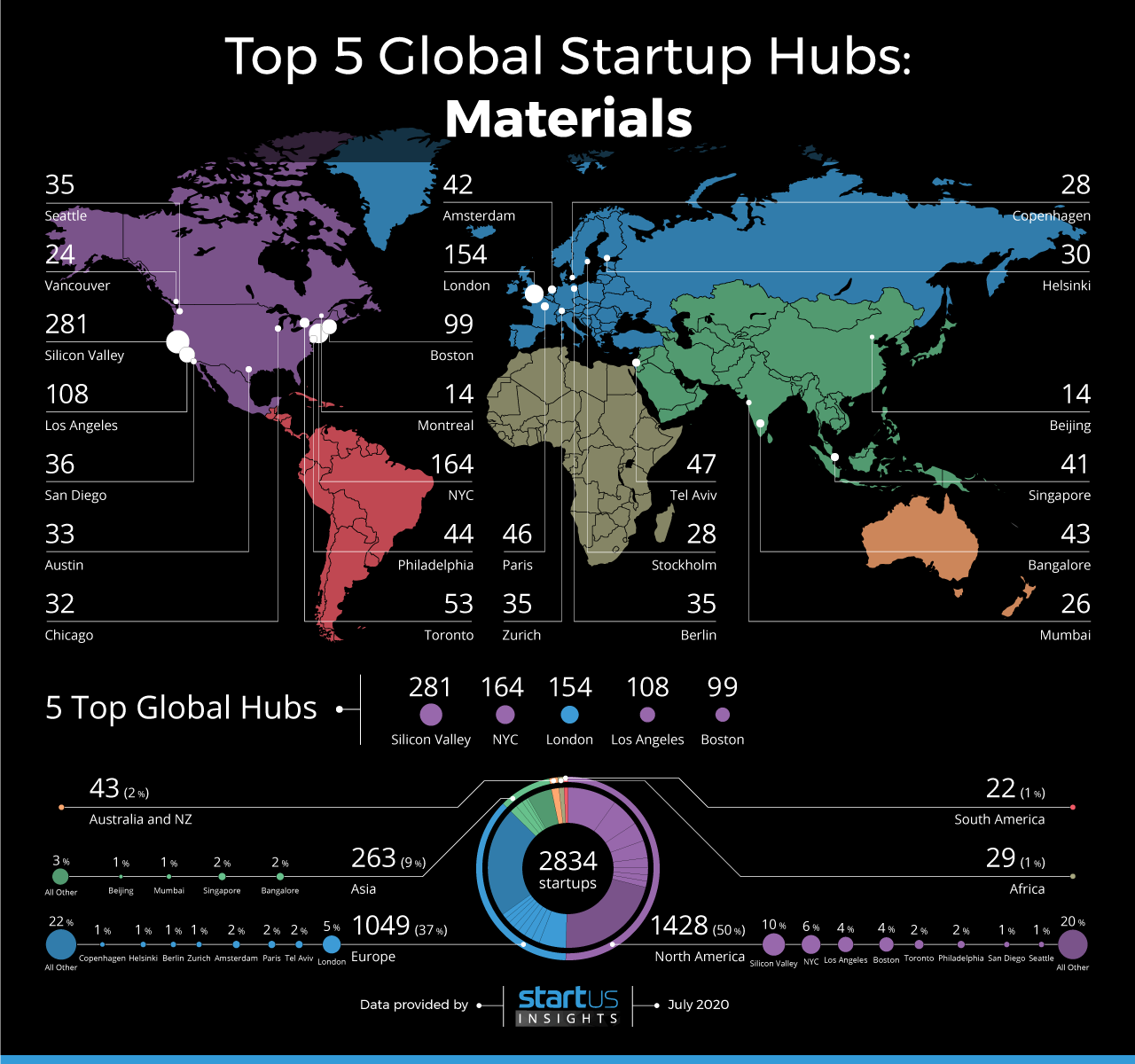
Using our StartUs Insights Platform, we analyzed the geographic distribution of global activity in the materials industry. We identified 39 regional hubs* that observe high activity in developing technology-driven solutions across the industry like sustainable dyes and adhesives, lightweight composites, and hydrophobic coatings to name a few.
Within the hubs, we analyzed a sample of 2.834 startups* employing technology-driven solutions to innovate in the industry. Silicon Valley, New York City, London, Los Angeles, and Boston are home to 806 startups and account for 28% of global activity in materials. Let us have a look at some of the innovative solutions from these 5 top hubs.
Based on our analysis of a sample of 2.834 emerging solutions, North America alone accounts for half of the global activity in the materials sector. Several large materials hubs in the US combine data-driven tech with materials science advancements.
European hubs in London, Tel Aviv, Paris, Amsterdam, etc account for nearly 37 % of global activity. Emerging Asian hubs in Bangalore and Singapore lead the region’s activity in the sector.
1. Silicon Valley: 281 Startups
Silicon Valley’s leading position in technologies such as big data and artificial intelligence (AI) contributes to the growth of the hub’s materials sector. Material startups combine these technologies with materials science to discover new chemicals, optimize design processes, and test applications. Startups in the region develop novel materials for a range of solutions such as flexible screens and sustainable fashion items.
The textile industry uses hundreds of gallons of water and toxic chemicals to produce a single pair of jeans. Tinctorium is a Silicon Valley startup that offers sustainable indigo dyeing solutions. It uses biotechnology to convert sugar into an indigo blue dye, eliminating the need for toxic chemicals like petroleum, cyanide, and formaldehyde. The solution also does not require water-polluting chemicals in the dyeing process.
2. New York City: 164 Startups
New York City houses some of the world’s leading companies in the materials field, such as Dupont and 3M. Besides, materials processing startups serve a wide range of sectors such as ceramics, chemicals, metals, plastics, etc. The city fosters industry-academia collaborations via its Centres for Advanced Technology (CATs) that work on advanced materials, nanomaterials, and multifunctional printing, to name a few technologies.
Sunthetics is a New York City-based startup that offers a sustainable method to produce nylon. Its reactor design and machine learning tool provide raw materials and energy use in the electrochemical production of adiponitrile, the key precursor for hexamethylenediamine (HMDA) and Nylon 6,6. The startup’s solution reduces greenhouse gases (GHGs) emissions from the manufacturing process.
3. London: 154 Startups
The United Kingdom is advancing digital approaches to materials. The manufacturing and materials program under Innovate UK aims to increase resource efficiency and flexibility in materials processes. As food manufacturing and textiles make a comeback in London, startups in the materials sector offer smart solutions in packaging and textiles.
London-based startup Materialize.X combines chemistry and machine learning to develop sustainable adhesives. It uses abundant feedstock to produce toxin and formaldehyde-free adhesives in a process that is integrable into existing manufacturing practices. The startup also offers a process optimization software that enables it to integrate adhesives in customers’ production processes faster.
4. Los Angeles: 108 Startups
Los Angeles is a hub for the manufacturing industry, largely because of its proximity to large ports that allow for the swift movement of raw materials and finished products. The booming aerospace and automotive industries in the region also necessitate continuous innovations in materials, most notably lightweight alloys. LA’s top universities also research extensively on advanced materials, in line with the city’s green economy goals.
PolyCera is a Los Angeles-based startup that manufactures innovative membrane technology. PolyCera is a polymeric material platform that uses organic polymers with unique electronic behavior from metal-like conduction to plastic-like insulation. The startup’s membranes offer extreme hydrophilicity, permeability, and robustness, as well as find applications in both drinking water and industrial wastewater treatment. They have improved fouling resistance and are easy to clean, thus, saving water and energy costs.
5. Boston: 99 Startups
Manufacturing in Boston embraces technology and the materials sector that is largely focused on biomaterials, polymers, and specialty chemicals. The engineering universities in the region, such as Harvard and MIT, contribute with both innovations and tech talent in materials science. Focused venture firms and incubators such as Material Impact also stimulate the growth of material startups.
Boston-based startup Graviky Labs harvests carbon emissions and turns them into ink. It uses a carbon capture technology to collect carbon emissions, which it then analyzes and sorts by physical and material properties. The startup uses a proprietary method to convert these into usable carbon and, subsequently, into different grades of inks, dispersions, and coatings. AIR-INK is carbon-negative and directly usable as packaging ink, silkscreen ink, and in writing instruments.
What’s next?
Startups continue to incorporate technologies such as AI and big data in the discovery, production, and manufacturing processes of materials. Novel formulations, including nanomaterials and biomaterials, impart new functionalities to existing materials. These will improve resource utilization across a wide range of industries.
*We define a hub as the regional geographic center of activity for this topic. It covers the center point with a radius of 100km. We define startups as those founded after 2015.