Staying ahead of the technology curve means strengthening your competitive advantage. That is why we give you data-driven innovation insights into the energy industry. This time, you get to discover 5 hand-picked energy sharing solutions.
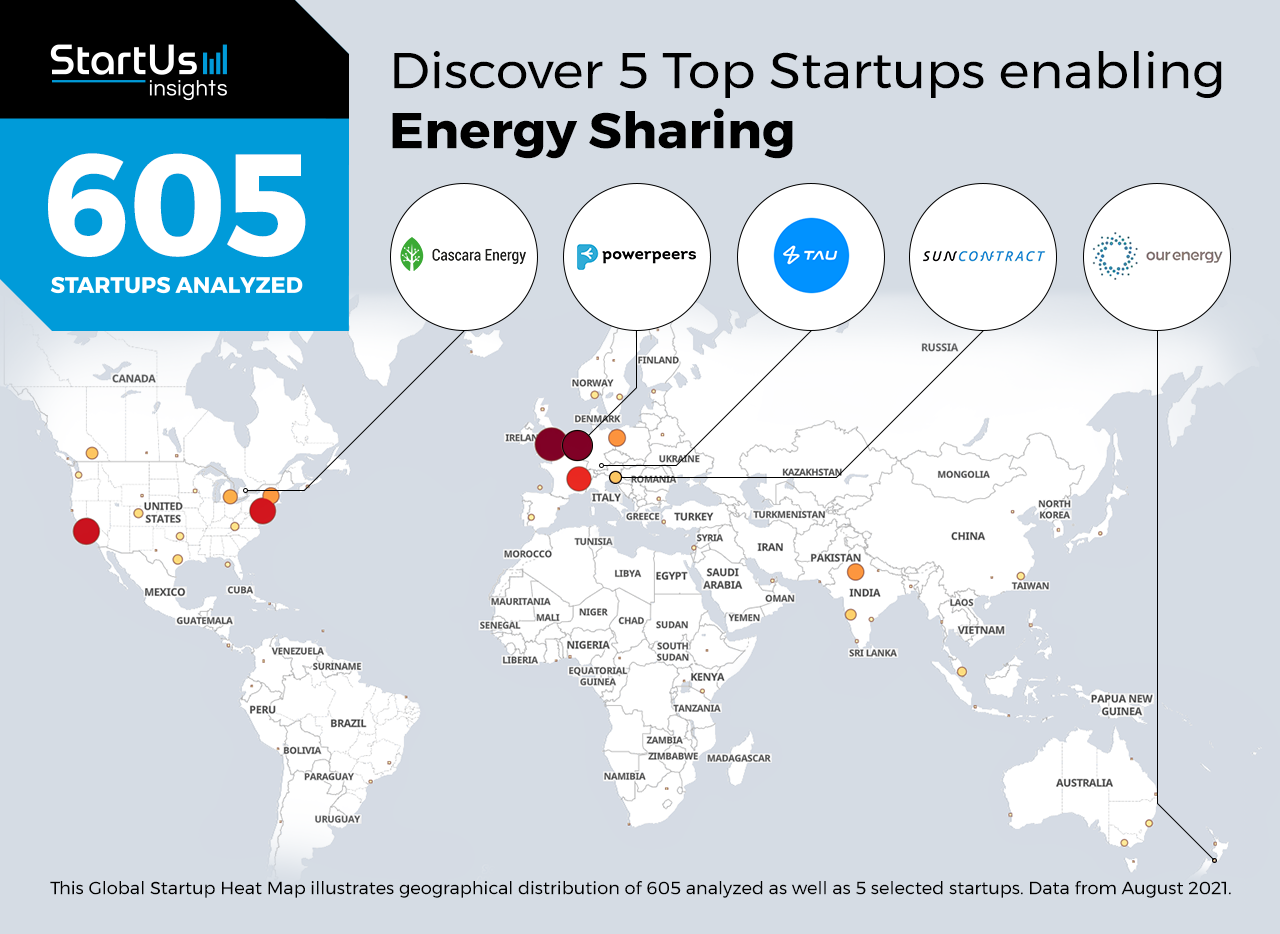
Global Startup Heat Map highlights 5 Top Energy Sharing Startups out of 605
The insights of this data-driven analysis are derived from the Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 2.093.000+ startups & scaleups globally. The platform gives you an exhaustive overview of emerging technologies & relevant startups within a specific field in just a few clicks.
The Global Startup Heat Map below reveals the distribution of the 605 exemplary startups & scaleups we analyzed for this research. Further, it highlights 5 energy startups that we hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, and more. You get to explore the solutions of these 5 startups & scaleups in this report. For insights on the other 600 energy sharing solutions, get in touch.
Powerpeers builds an Energy Sharing Platform
Residents who generate their own electricity using solar panels often produce more energy than they require. Typically, this excess energy is anonymously transferred into the energy grid. However, startups are developing software that enables private energy producers to share their surplus electricity directly with other registered uses. This decentralizes the energy supply, provides access to energy for those who need it, and also enables producers to earn money for the same.
Dutch startup Powerpeers enables sustainable electricity sharing through its software platform. Powerpeers allows its customers to receive power from other customers who generate electricity through their solar panels. The surplus power is supplied to the energy grid and shared with Powerpeers’ customers. This ensures that consumers do not have to compromise on their consumption. However, in the case of deficits or intermittence, consumers have the option to supplement their energy with other local sources.
TAU develops Shared Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Solutions
While technology is making progress in the field of electric vehicles, we still do not see much of them on the streets globally. One of the major reasons is the lack of charging infrastructure or networks. To tackle this problem, startups are turning to the sharing economy. Novel solutions allow residents set up their own EV charging stations that utilize surplus household electricity. Thus, private individuals earn extra money while making charging accessible and cheaper for EV drivers.
TAU is a German startup that enables internet of things (IoT)-based shared EV charging. Users register on the TAU platform, create their charging stations using TAU’s hardware solution, and set up prices for charging points. A mobile application enables drivers to make reservations for charging and order additional services while charging, such as coffee or WiFi. These charging stations are powered by users’ excess electricity. Moreover, the radio-frequency identification (RFID)-tagged stations generate 7.2kW and enable the simultaneous charging of two vehicles, e-bikes, or e-scooters.
SunContract creates a P2P Energy Trading Marketplace
Among other expenditures, centralized energy distribution involves expensive electricity transmission costs. Moreover, a lot of energy is wasted during transmission. To resolve these issues, energy startups are enabling decentralized energy distribution through peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading. This reduces transportation costs and makes electricity cheaper for consumers. It also ensures sustainability since it requires sourcing from locally generated renewable energy.
SunContract is a Slovenian startup that offers a P2P energy trading marketplace. It supplies locally sourced renewable energy to its residential consumers and businesses. SunContract’s technology matches every unit of energy generated by the producers to energy consumption in real-time. The startup offers two models. One model, in which the startup buys consumers’ surplus energy for a year. Otherwise, energy producers can sell their energy directly to consumers at their desirable price using the startup’s marketplace platform.
Our Energy advances Community-driven Energy
Traditional electricity distribution restricts the choice and control of consumers. However, sharing energy among the community through many small power stations provides control and transparency while enabling even more energy sharing. Moreover, shifting to a decentralized sharing economy model reduces the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from big power stations. Startups build online platforms to enable local energy exchange.
New Zealand-based startup Our Energy advances community-driven energy. Its platform matches real-time data from those producing their own electricity with others in their communities. this allows renewable energy producers to sell their surplus energy to local consumers who need it. The platform keeps a track of the energy sources and the buyers’ consumption data. It also enables producers to monitor their energy prices.
Cascara Energy enables Thermal Energy Sharing
Thermal energy created from human activity or recovery of waste heat is sufficient to fulfill the heating and cooling requirements of many buildings. For example, places like factories, supermarkets, and hospitals generate a lot of excess energy. Sharing this thermal energy with other buildings reduces the total amount of energy needed for the community. To facilitate this, startups are connecting thermal energy flows thus enabling buildings to benefit from each other.
Canadian startup Cascara Energy enables thermal energy sharing through community district energy networks (CDEN). The startup recovers waste heat from landfills and wastewater effluent streams as well as free cooling systems such as data centers, cold storage, and supermarkets. This recovered waste heat caters to the heating and cooling requirements within the community. The startup also stores this energy in a thermal energy storage (TES) system or in a seasonal thermal energy storage (STES) facility to reduce grid peak demands.
Discover more Energy Startups
Energy startups such as the examples highlighted in this report focus on energy sharing and trading platforms, as well as community-driven energy sharing and IoT-driven energy management solutions. While all of these technologies play a major role in advancing the energy industry, they only represent the tip of the iceberg. To explore more energy technologies, simply get in touch to let us look into your areas of interest. For a more general overview, you can download our free Energy Innovation Report to save your time and improve strategic decision-making.



![Top 8 Sustainable Energy Solutions You Need to Know [2025 & Beyond]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Sustainable-Energy-Solutions-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)