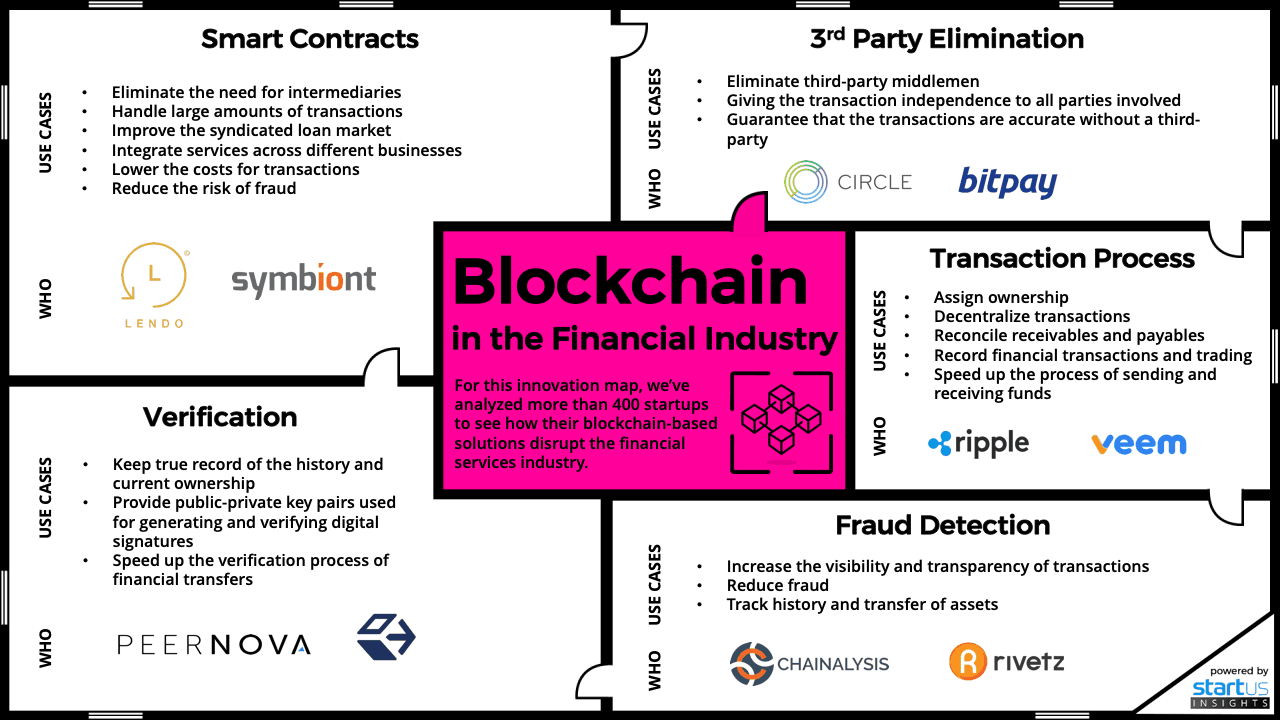
Key Takeaways
Blockchain technology is radically transforming the financial services industry in a number of ways. These are the main points in a nutshell:
- Transaction process – by cutting out the middlemen, transactions are safer, faster, and more easily traceable.
- Fraud detection – due to blockchain’s connected ecosystem, deceiving payments or tampering with contracts is highly unlikely and too costly to gain profits from. The technology basically ensures immunity to fraudulent actions.
- Smart contracts – are automated, easy to be verified, interpreted, and enforced. These contracts reduce legal paperwork and enable organizations to handle large amounts of financial transactions automatically.
Heat Map: Blockchain Startups Disrupting The Financial Services Industry
Our team at StartUs Insights has created the Heat Map below to showcase the hotspots of where Blockchain startups are located around the globe:
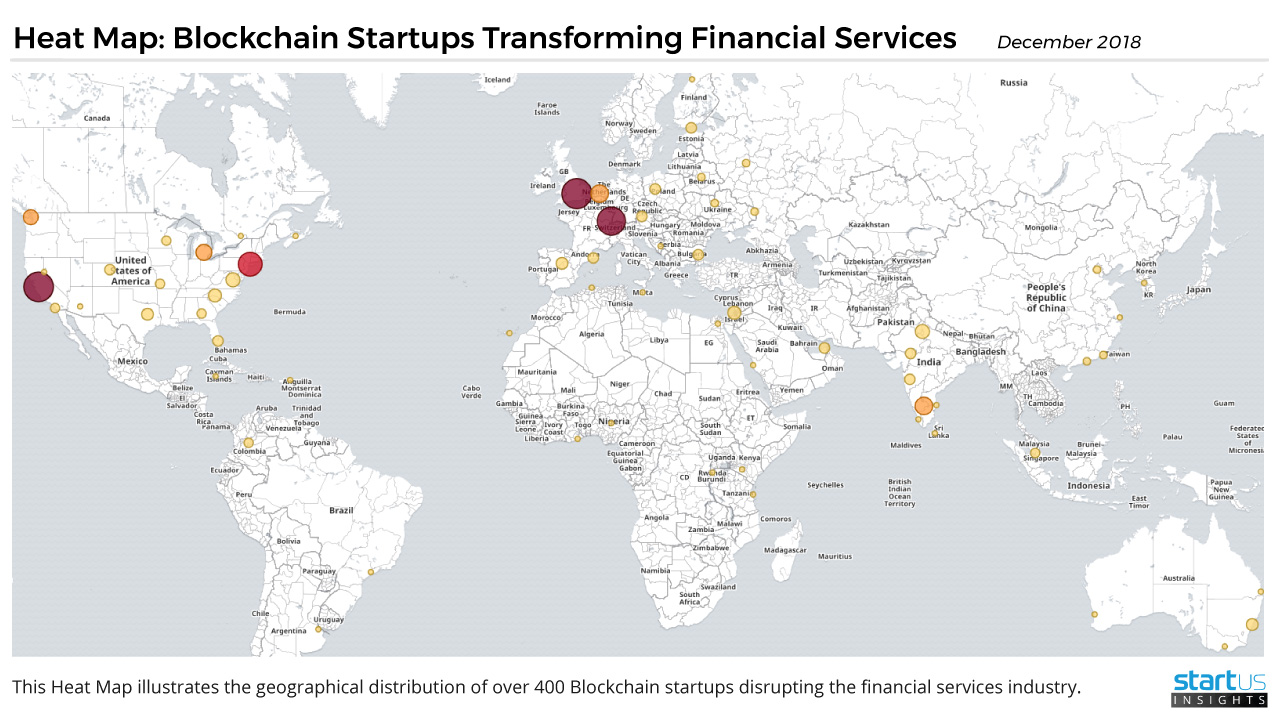
Click to enlarge
Global Distribution of Blockchain Startups in Financial Services (c) StartUs Insights
Selected Blockchain Startups Disrupting The Financial Services Industry:
- Synaps – A joint initiative by Symbiont and Ipreo, which focuses on automating and improving the global loan syndicate market using blockchain-based smart contracts.
- Bitpay – An American payment service that allows businesses to accept and transact with Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash as well as invest and exchange between cryptocurrencies and fiat currency.
- Request Network – A decentralized Ethereum-based network allowing users to perform transactions between each other, send or request payments, issue invoices, pay and receive money for online purchases and more.
- Ripple – A payment solution which represents a distributed payment settlement system built on the blockchain and a shared public ledger called XRP ledger. The system serves both private users and organizations and banks, allowing them to settle money transfers and payments faster and cheaper.
Innovation Map: How Blockchain Startups Transform Financial Services
Our innovation analysts carried out an extensive, data-driven analysis of blockchain’s impact on financial services, encompassing over 400 startups.
Below, you’ll find the Innovation Map highlighting the most promising application areas as well as a deep dive in each of the sections.
In multiple transactions between parties, blockchain removes the need for an intermediary, which in turn increases transparency and security. Unsurprisingly, financial services have seen a trend of significant adoptions of blockchain innovations.
However, since the blockchain fundamentally changes the way banks operate and even raises the question if banks will survive the era of the blockchain.
Transaction Process
Blockchain technology fixes the painful and long procedure of sending money traditionally by getting rid off costly and lengthy processes of involving various intermediaries, thereby facilitating the transaction and ensuring that money safely gets from one place to the other.
The startup Request Network, for example, developed a solution for not only directly sending and receiving money but also for paying and issuing invoices, for businesses to accept money for online payments, as well as for cities and governments to be more transparent and allowing citizens to monitor their transactions.
Fraud Detection
Around 5% of revenues are lost by any given company to fraud on an annual basis. Online fraudulent activities are varied and plentiful, including various transaction manipulations, executing multiple payments one after the other to fool the seller into thinking they have been paid, and so on.
The nature of blockchain assumes a shared publicly-available ledger of transactions, each of which has a timestamp and is linked to the preceding entry, making it that much more difficult to deceive the payment system.
As the blockchain is essentially a distributed ledger without a central database, one would have to effectively break into all of the computers of the chain simultaneously to rattle with the chain. On top of that, the transactions themselves are irreversible, making it an even less attractive target for a hacker.
Smart Contracts
There are a number of reasons why smart contracts are so promising. First of all, they are entirely devoid of ambiguous interpretation. This feature helps save substantial resources on legal matters.
Secondly, by being embedded into a blockchain, a smart contract does not rely on a centralized stakeholder for hosting and controlling, which eliminates chances of data manipulation and/or conflicts of interests.
As such, any attempts to modify the contract or its contacts will be automatically corrected by other blockchain nodes, making it too expensive and nearly impossible to tamper with the agreement.
Credit Suisse, for instance, collaborated with Synaps in developing a solution for easing the process of arranging, signing and executing syndicated loan agreements.
Verification
Perhaps one of the most natural use cases of blockchain is verification of transactions and processes, thanks to its transparent and decentralized nature.
This cornerstone of the blockchain allows to keep a true record of the history and current ownership of certain amounts of money, to provide public-private keypairs used to generate and verify digital signatures, and to ultimately speed up the verification process of financial transfers.
Conclusion
As blockchain’s potential is growing by the day, it is quickly challenging the status quo of financial institutions and intermediaries of the financial services industry.
It has become a necessity to stay informed of the most recent developments in the field to stay ahead of the competition.