Due to their fossil origin and persistence in nature, plastics aren’t unsustainable. Natural, sustainable, and renewable alternatives are crucial to substitute for their widespread use. This is why startups are creating materials that are renewable and biodegradable which also offer the functionalities of plastics. This trend article contains the top 10 biopolymer trends in 2025 that are shaping the industry.
Additionally, biomass garners a lot of attention due to its low cost and compatibility with various substances to make composites. Due to the environmental impact caused by petroleum-based polymers, the cost-effectiveness and less resource-intensive manufacturing of bio-based polymers make them a sustainable alternative to traditional materials.
This article was last updated in August 2024.
What are the Top Biopolymer Trends in 2025?
- Protein Biopolymer
- Cellulose Biopolymer
- Starch Biopolymer
- Polylactic Acid (PLA)
- Chitosan
- Plant Biopolymer
- Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
- Bio-PET
- Alginate Biopolymer
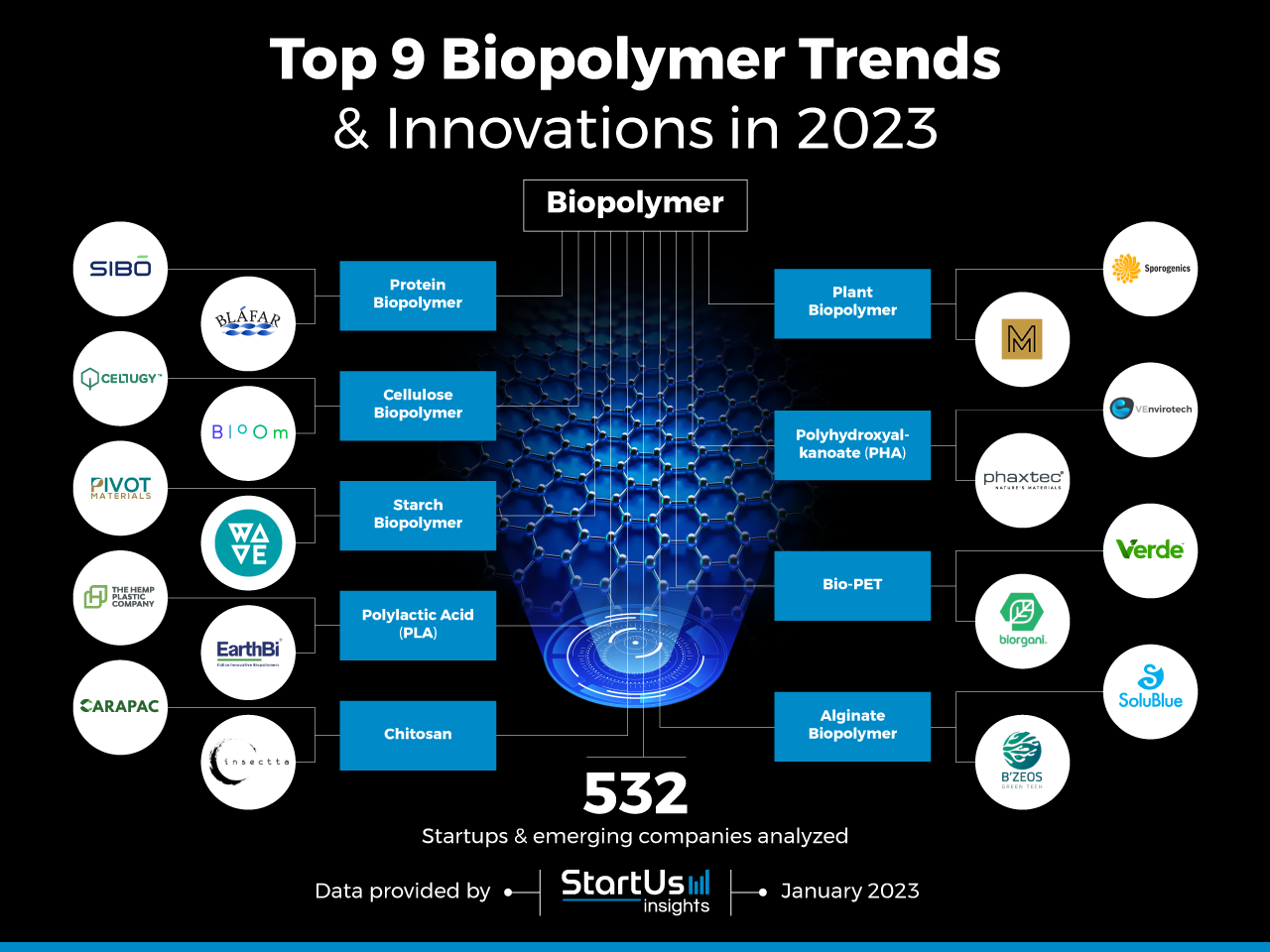
Innovation Map outlines the Top 9 Biopolymer Trends & 18 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the top global decarbonization trends and startups, we analyzed a sample of 532 global startups & scaleups. This data-driven research provides innovation intelligence that helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging technologies and trends in the materials industry. In the Biopolymer Innovation Map, you get a comprehensive overview of the innovation trends & startups that impact your company.
These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 4.7M+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant technologies and industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
Want to explore all Biopolymer innovations & trends?
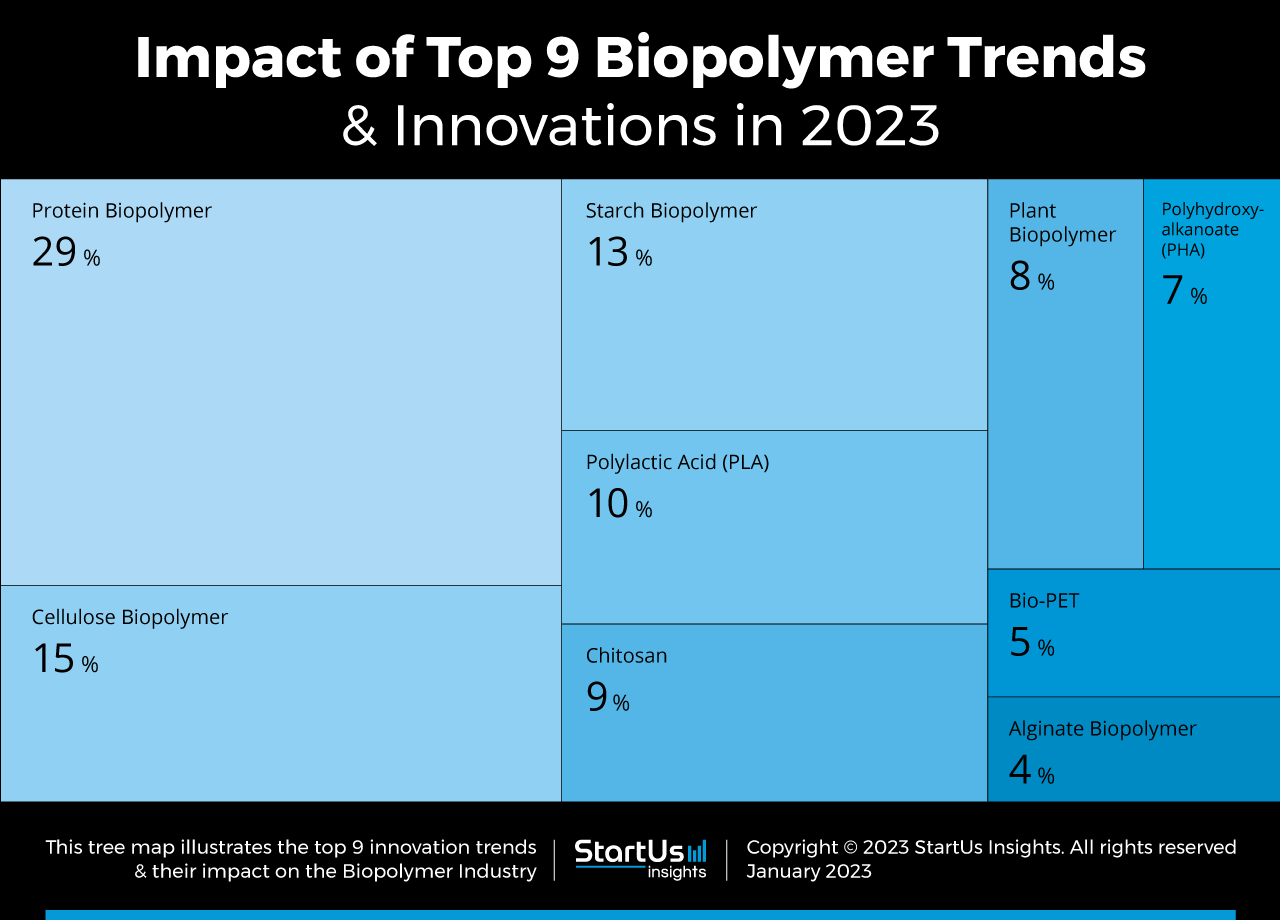
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 9 Biopolymer Trends
Based on the Biopolymer Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 9 Biopolymer Trends in 2025. Protein biopolymers offer excellent gas barrier and mechanical properties, making them the most prominent trend in the biopolymer sector. Cellulose, the most abundant renewable resource in the world, takes the next spot. Starch Biopolymer enables innovations in the packaging industry, while polylactic acid (PLA) enhances energy reduction during production processes.
Further, chitosan has many biomedical applications like wound healing and drug delivery. Recent advancements in biopolymers include polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) which withstands high temperatures and is compostable as well as bio-polyethylene terephthalate (PET) from renewable raw materials. Lastly, alginate demonstrates antibacterial activity and nontoxicity, while microbial biopolymers have the potential to improve waste bioremediation efficiency.
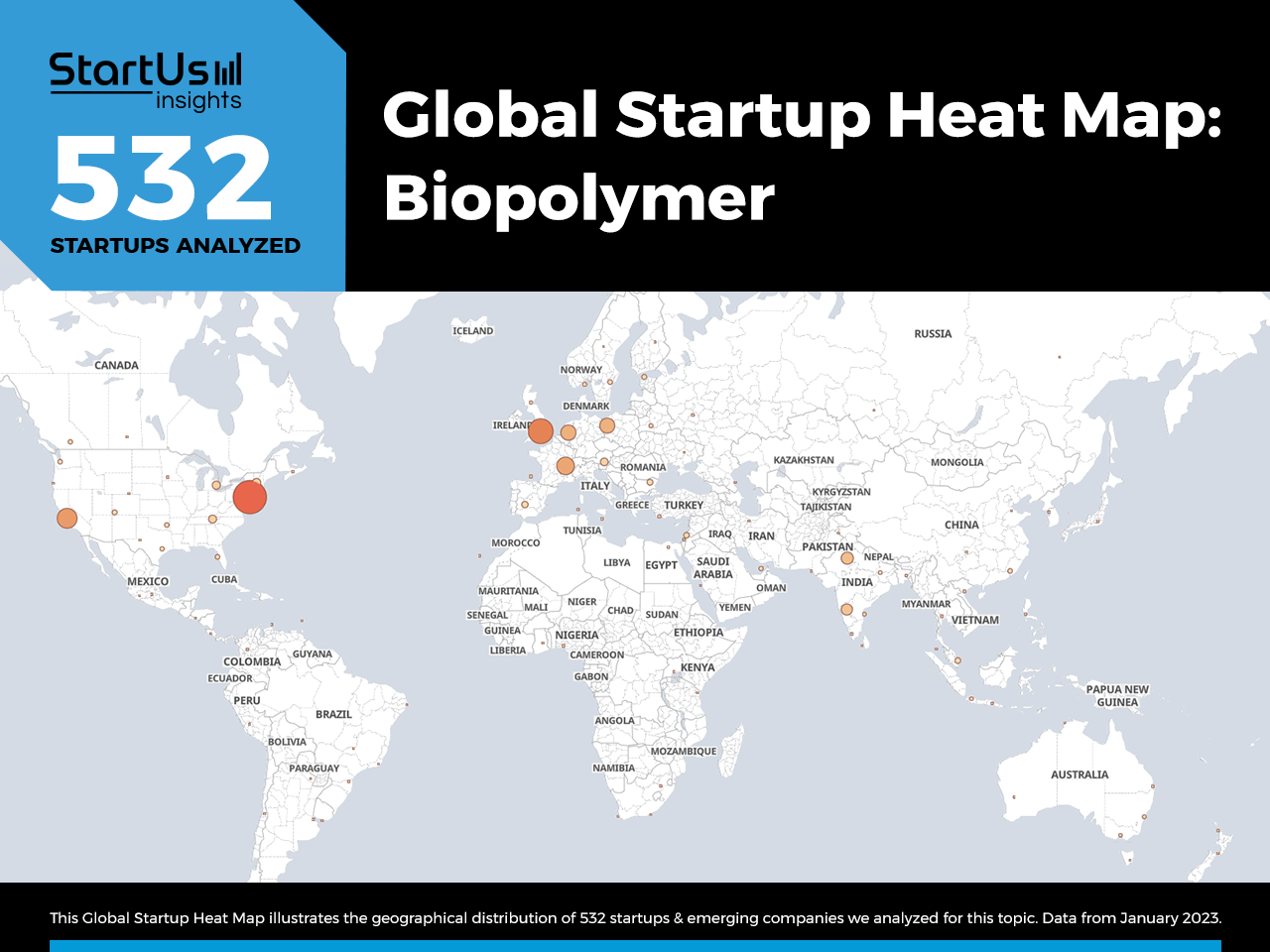
Global Startup Heat Map covers 532 Biopolymer Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 532 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals that the US and UK see the most activity, followed by other European countries and India.
Below, you get to meet 18 out of these 532 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These 18 startups are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, and more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Top 9 Biopolymer Trends in 2025
1. Protein Biopolymer
Protein-based biopolymers are one of the most promising classes of biomaterials due to their biocompatibility and biodegradability. Compared to polysaccharide-based materials, they are useful for most material applications with superior gas barrier and mechanical properties.
Due to its possibility of interaction with a wide range of bioactive molecules, protein biopolymers find applications in the medical industry for tissue engineering and tablet coating. They also find use in the packaging industry due to their high nutritional qualities, the potential for food protection, and organoleptic properties.
MarraBio offers Extracellular Matrix Protein Alternative
UK-based startup MarraBio engineers a proprietary protein biopolymer that leverages genetically modified Caf1 proteins, produced within bacteria, to construct elongated, flexible, and inert biopolymers. These biopolymers serve as a foundation for integrating bioactive peptides that interact with cell receptors, inducing specific biological responses.
The protein enables the creation of multifunctional materials by combining various biopolymers. Additionally, these materials demonstrate stability at ambient temperatures, eliminate the need for animal-derived components, and facilitate large-scale manufacturing. This technology holds potential for applications across diverse fields, including medicine, materials science, and biotechnology.
Blafar produces Fast-Gelling Gelatin
Irish startup Blafar offers fast-gelling thiolated gelatin for tissue engineering applications. It is applicable for hydrogel production in the investigation of wound healing. Fast-gelling gelatin is a modification of natural proteins, making it suitable for cell culture and tissue engineering as well as cosmetic and medical applications.
Due to the fast-gelling properties, the process is cross-linked with a very short gelation time and multi-vinyl cross-linkers that make it insoluble. This allows for the effective immobilization and release of active agents and biomolecules.
2. Cellulose Biopolymer
Cellulose is a renewable, biocompatible, and non-toxic biopolymer. It is present in plants, algae, and some bacteria, and is also obtained from agricultural waste. Cellulose is the most abundant renewable resource on the planet. They have a high degree of crystallinity and molecular weight while remaining hydrophilic but insoluble in water or other common solvents. Nanocellulose, obtained through nanotechnology, is also emerging as a cost-effective material for tissue engineering and the development of drug delivery systems, among others.
Cellugy offers Nanocellulose-based Materials
Danish startup Cellugy develops EcoFLEXY, a nanocellulose-based material made from bioconversion of sugars. The startup’s white biotechnology process utilizes a specific strain of bacteria to produce nanocellulose. It is a robust and versatile material with applications across the packaging, food, hygiene, and cosmetics industries. For example, EcoFLEXY is suitable for packaging partners looking to produce a recyclable and biodegradable barrier coating solution.
Bloom Biorenewables designs Highly Crystalline Cellulose
Swiss startup Bloom Biorenewables provides pure and highly crystalline cellulose. It is highly pure and has crystalline fibers, doesn’t need harsh bleaching, and the cellulose structure is not chemically modified. This natural polymer is a sustainable alternative to the polymers currently used in the pulp and paper industry. Additionally, the startup’s alternative for petroleum derivatives serves as a raw material for a wide range of products, including bioplastics, textiles, cosmetics, and perfume.
3. Starch Biopolymer
Starch is one of the most abundant, naturally biodegradable polymers and is a base material for a wide range of green materials. It has absorbency, biodegradability, biocompatibility, and non-toxicity properties. Starch is extracted from edible plant sources such as potato, corn, rice, wheat, or barley and has the potential for mass commercial production.
Advances in starch-based materials for packaging enable antimicrobial films to prevent microbial growth in food products. Further, startups aim to meet the growing demand for starch in applications from cosmetics, medicine, and agriculture to packaging and textiles.
Pivot Materials offers Natural-Fiber-based Composite Plastics
US-based startup Pivot Materials specializes in manufacturing natural fiber-based lightweight, sustainable, and durable composite plastics for injection and extrusion molding. The startup uses bamboo and rice waste fiber, among others, to increase the sustainability of the final product while improving specific material properties. This sustainable alternative to traditional plastic is suitable for the household, packaging, and transportation industries.
Solublion produces Starch-based Bioplastics
Solublion is a Spanish startup that offers bioplastics derived from starch, presenting a sustainable alternative to conventional plastics. Their product range includes a biodegradable, compostable, and water-soluble thermoplastic starch-based biopolymer, targeting the packaging industry. This biopolymer, manufactured using patented technology, can undergo reprocessing through standard industrial equipment to create final products.
4. Polylactic Acid
PLA is a promising biodegradable biopolymer produced from plant-based materials. It offers sufficient gloss and transparency, which is comparable to polystyrene (PS) films. Moreover, PLA has a high level of heat resistance and mechanical strength and also enables the creation of biodegradable plastics with superior antibacterial and antifungal properties. In addition, PLA consumes less energy than conventional plastic production. The versatile bio-based polymer finds applications in the 3D printing, textiles, agriculture, medicine, and food industries.
Bioworkers offers Polylactic Acid (PLA) Bioplastics
Japanese startup Bioworks provides PLA bioplastics. It produces PlaX, a plant-derived PLA polymer. PlaX combines PLA with a proprietary plant-based resin for enhanced functionality. It is used in injection molding, blow molding, fiber compounds, and 3D printing monofilaments. Bioworks’ plastic-based fiber has antibacterial and water-absorbing properties, making it ideal for applications such as face masks and medical sutures.
KiwiFil makes Recycled PLA Filament
KiwiFil is a New Zealand-based startup that produces recycled PLA filament using discarded 3D prints and substandard filament. This recycled filament undergoes shredding and remelting processes to ensure quality. It offers performance comparable to regular PLA pro filament, resulting in strong parts with a glossy finish.
Despite being made from 100% recycled plastics, meticulous quality control ensures consistent product quality. This control includes sorting, cleaning, grinding, and double filtering of melted plastics. The filament diameter undergoes two checks: during extrusion and re-spooling. Extensive test printing and mechanical testing further validate the filament’s quality and performance.
5. Chitosan
After cellulose, chitosan is the most abundantly available recyclable, non-hazardous, biopolymer. Chitosan, a close derivative of chitin, is obtained from crustacean shells, insect exoskeletons, fish scales, or fungal cell walls. It is currently the only known natural biopolymer to have a positive electrostatic charge, which provides its bacteriostatic and flocculating properties.
Chitosan serves as a replacement for heavy metals and toxic antimicrobials, inorganic flocculants and coagulants, as well as pesticides and insecticides. It finds applications in medicine, packaging, agriculture, manufacturing, and water management.
CARAPAC produces Crustacean Shell Waste-based Chitosan
Australian startup CARAPAC develops soft plastic alternative packaging material derived from crustacean skeletons. The solution is allergy-free, extends product shelf-life, and is marine biodegradable. The material is suitable for snack packaging, herb sleeves, meal kit packaging, and outdoor lifestyle applications. Moreover, CARAPAC’s materials fully break down within 90 days, enabling a circular economy.
Insectta manufactures Black Soldier Fly Chitosan
Singaporean startup Insectta produces black soldier fly-derived biomaterials. The startup develops a new source of sustainable chitosan with better molecular properties by utilizing black soldier fly to transform organic matter into valuable resources. The material finds use in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, anti-microbial food packaging, and agrotech industries.
6. Plant Biopolymer
Plant-based biopolymers offer the same properties as animal-based biopolymers such as techno-functionality. These plant-based alternatives are gaining interest among manufacturers due to their sustainable, ethical, and nutritional value. Moreover, such materials are non-toxic, multifunctional, relatively cheap, and biodegradable. Therefore, it prevents the accumulation of landfill waste and promotes closed-loop approaches for the plastic industry.
Sporogenics produces Plant-derived Biopolymers
Singaporean startup Sporogenics produces a plant-derived biopolymer film and microgel. The startup’s patented automated membrane casting technology ensures the continuous production of biopolymer film with controlled thickness and composition. Sporogenics’ anti-inflammatory material is suitable for medical treatments such as wound-healing and preventing post-operative adhesions.
Mushroom Material offers Mushroom-based Packaging
New Zealand-based startup Mushroom Material develops a mushroom-based alternative to polystyrene styrofoam. The startup combines mycelium and fibrous agricultural waste to create its waterproof, fire-resistant, durable, and customizable material. The startup manufactures sustainable packaging that has the same protective properties as polystyrene and is home-compostable.
7. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
Biopolymer manufacturers use microbial synthesis to create polyhydroxyalkanoates. The main feedstocks used in PHA production are sugars and vegetable oils. Moreover, emerging startups are developing PHA from wastewater streams, plastic waste, renewable methane as well as carbon dioxide. PHA is fully circulating and biocompatible with humans and other life forms. Additionally, it is readily metabolized into non-toxic compounds when ingested. PHA finds applications in the 3D printing, packaging, agriculture, and medicine industries.
VEnvirotech offers Organic Waste-based PHA
Spanish startup VEnvirotech provides biodegradable bioplastics obtained from organic waste. The startup feeds bacteria with organic waste to produce its PHA bioplastic, modifying the environment where they live. The material finds applications in biomedicine and 3D printing. Besides, VEnvirotech’s biodegradable PHA does not cause toxic side effects and is suitable for mixing with petroleum-derived plastics.
PHAXTEC produces Natural PHA Biopolymers
US-based startup PHAXTEC produces natural PHA biopolymers that are biodegradable in soil, fresh and salt water, and are biocompatible and bioabsorbable. They are suitable for composting, recycling, and pyrolysis while produced from renewable sources. The startup uses biogas in its production processes, reducing the cause of global warming and therefore helping to mitigate climate change. Moreover, biogas is the main raw material for its production, making the process independent of agricultural products and excluding competition from food products.
8. Bio-PET
Bio-PET is a substitute for virgin PET made from renewable raw materials. It uses the leftovers from sugar manufacturing or is derived from plant and vegetable sources that form chains of polymers. Such materials are durable, unbreakable, and transparent. They can be processed and recycled with existing systems and are also identical to PET in appearance and function. Startups develop bio-PET that use second-generation raw materials, such as forestry or agricultural waste products, to eliminate the need for virgin PET.
VERDE BIORESINS develops Durable Bio-PET
US-based startup VERDE BIORESINS produces PolyEarthylene, a plant-based sustainable and renewable biopolymer that finds applications for durable consumer goods. The material is environmentally friendly, economically more feasible, and lighter compared to petroleum-based polymers. The startup’s bio-PET materials are competitive with other bio-based materials such as PLA, PHA, or green PE.
Biorgani produces Bio Resin
US-based startup Biorgani offers bio-resin for film-grade packaging. The startup’s bio-based resin, FAUNNUS, is used as a filler with blends with conventional polyolefins. This results in a bio-based product with a lower carbon footprint that can match a conventional plastic’s weight resistance and performance. It also manufactures a zero polyethylene resin, SOLUM Compost Resin, suitable for conventional plastic equipment. The production process of these bio-based materials requires less temperature and, in turn, saves energy and reduces manufacturing carbon emissions.
9. Alginate Biopolymer
Alginate is a natural biopolymer obtained from brown algae or a culture of microorganisms. This biopolymer finds applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, paper, art, building, chemicals, and textile industries. However, alginates have poor mechanical properties, especially when hydrated in water. Therefore, startups work to improve their chemical, physical, and biological properties and expand alginates’ applications where mechanical performance, water absorption, and antimicrobial activity are important.
SoluBlue manufactures Seaweed-based Biopolymer
UK-based startup SoluBlue offers a natural polymer made from FDA-approved seaweed-based ingredients. It is suitable for food packaging as it absorbs moisture and prevents mold growth on fresh food, extending its shelf life. The startup’s seaweed biopolymer production also captures a vast amount of carbon and locks it in the soil when composted. This alternative to single-use plastics breaks down in the ocean within weeks and can also be safely ingested by marine life.
B’ZEOS offers Algal Biomass Packaging
Norwegian startup B’ZEOS develops bio-based packaging materials using seaweed biopolymers to replace disposable plastic articles in the food service industry. The startup uses green processing technology and partners only with seaweed cultivators and harvesters that work with sustainable and ethical practices. After sourcing the seaweed, it extracts valuable compounds to create a packaging solution that is circular, home-compostable, and edible.
Discover all Biopolymer Trends, Technologies & Startups
The high amount of plastic used on the daily basis is paving the way for finding sustainable alternatives. Bio-based and biodegradable materials have shown strong growth across industries over the past years, mainly in packaging, driven by consumer market trends towards greener packaging and waste reduction. In addition, they find wide applications in the medical industry for drug delivery and tissue engineering, among others. On the way to a sustainable future, innovations in the field improve biomaterials properties and make production processes environmentally friendly.
The Biopolymer Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation and startup scouting process. Among others, nanotechnology, advanced manufacturing processes, and novel material extraction methods will transform the sector as we know it today. Identifying new opportunities and emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage. Get in touch to easily and exhaustively scout startups, technologies & trends that matter to you!