The blue economy encompasses sustainable and inclusive economic activities in the world’s oceans and coastal areas. With a focus on the conservation, utilization, and management of marine resources, emerging companies and startups work on innovative applications. Major trends in the industry include climate-positive aquaculture, renewable energy integration, and marine biotechnology. This industry research focuses on the top 10 blue economy trends based on our analysis of 1955 emerging companies. They include autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), remote sensing technology for ocean monitoring, offshore wind farms, and desalination technologies. Read more to discover global markets in the blue economy and how they ensure climate-conscious operations.
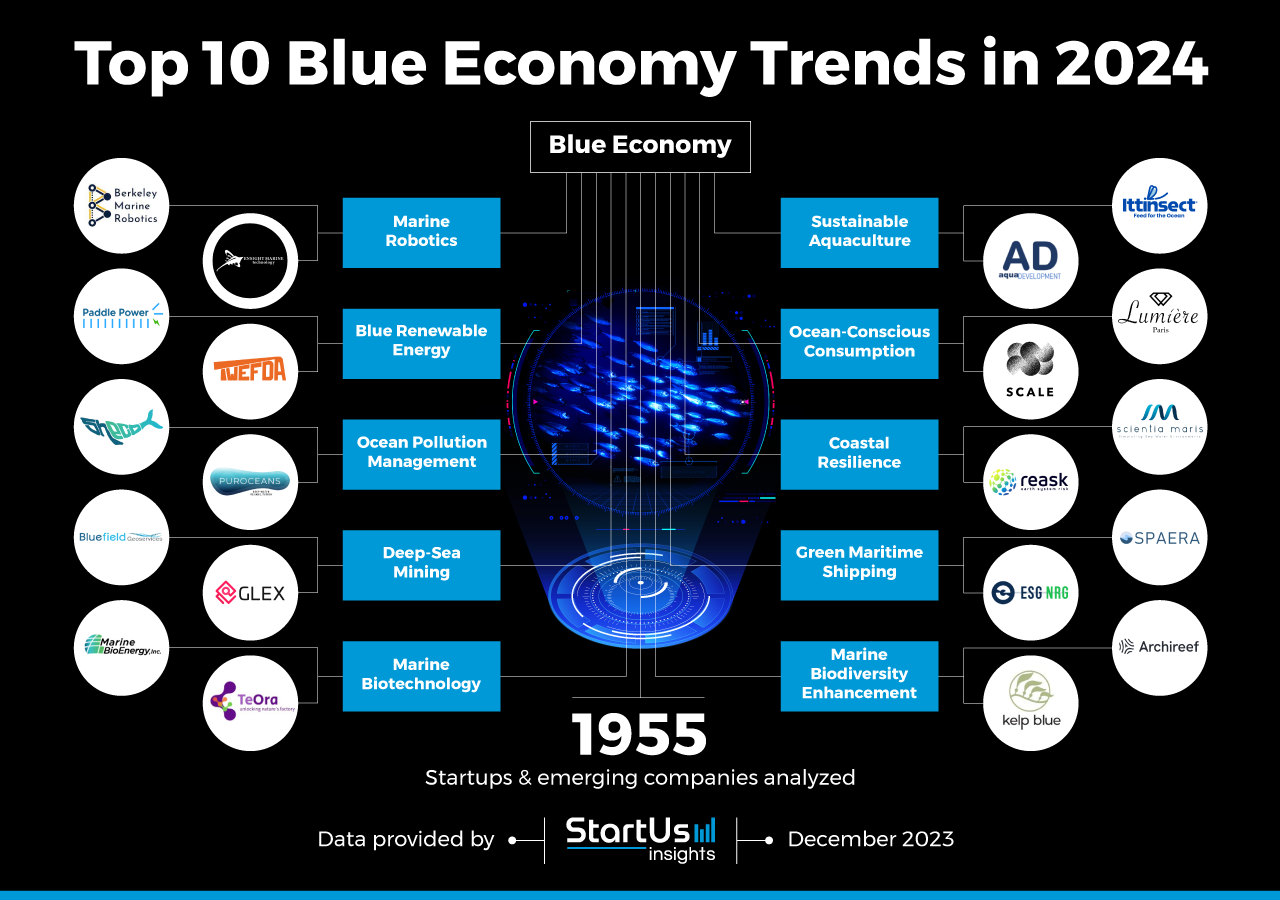
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Blue Economy Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Blue Economy Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 1955 global startups & scaleups. This data-driven research provides innovation intelligence that helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging technologies in the marine industry. In the Blue Economy Innovation Map, you get a comprehensive overview of the innovation trends & startups that impact your company.
These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 3 790 000+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant technologies and industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
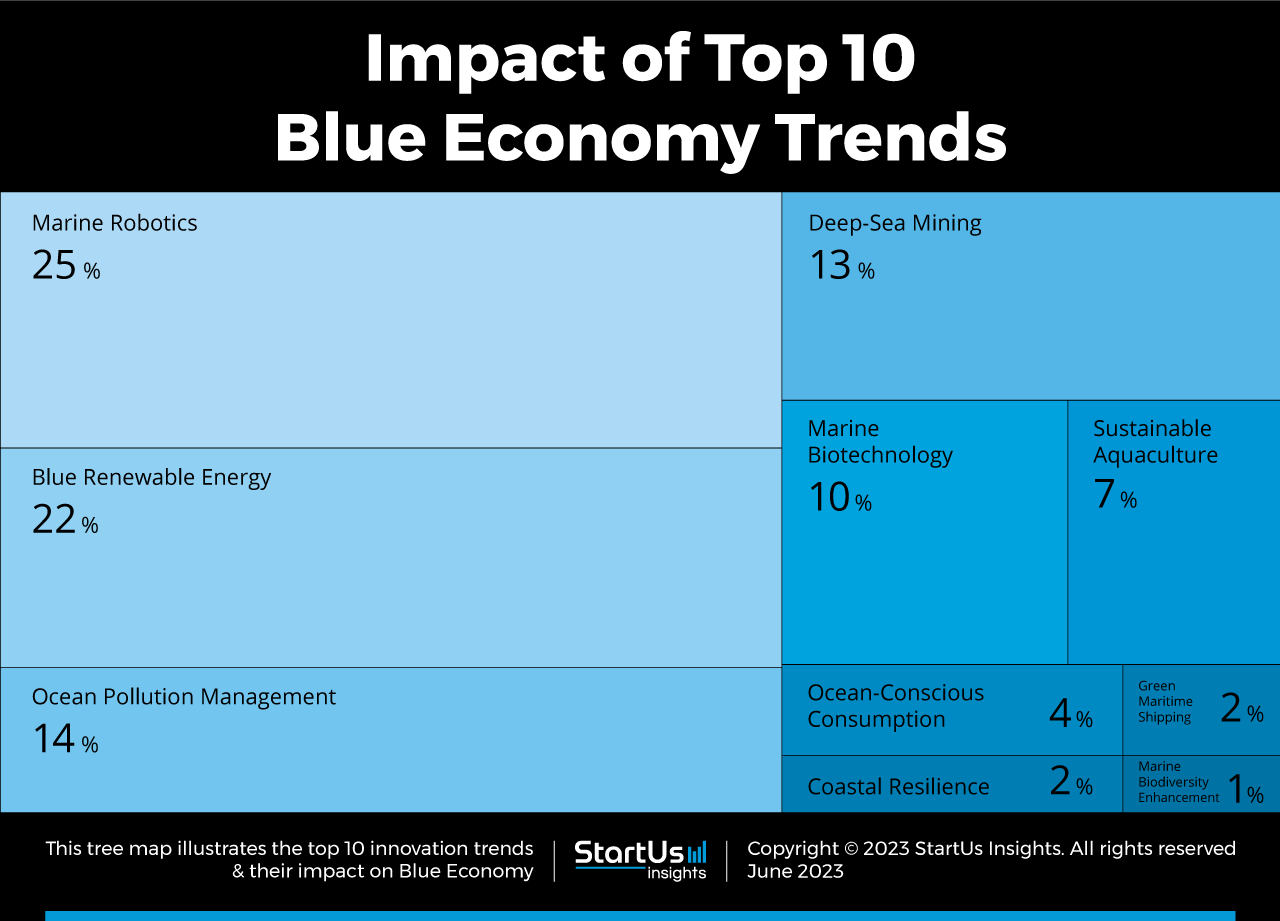
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Trends in Blue Economy
Based on the Blue Economy Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 10 Blue Economy Trends in 2024. In marine robotics, AUVs perform precise ocean monitoring tasks. Government agencies create coastal protection systems to mitigate erosion and storm surges. Blue renewable energy promotes sustainable electricity generation while green maritime shipping that uses renewable energy makes logistics sustainable. Biodegradable packaging from cornstarch or seaweed also reduces ocean plastic pollution and cleaning machines combat contaminants and oil spills.
Startups also develop seabed monitoring platforms to aid deep-sea miners with mine mapping. Further, scientists and researchers utilize marine biomass for pharmaceuticals, biomaterials, and aquaculture. Startups also promote marine biodiversity through artificial reefs and habitat restoration. Lastly, farmers use recirculating aquaculture systems and precision feeding to ensure responsible seafood production. These advances drive the blue economy, preserving biodiversity and promoting conservation.
Top 10 Blue Economy Trends in 2024
- Marine Robotics
- Blue Renewable Energy
- Ocean Pollution Management
- Deep-Sea Mining
- Marine Biotechnology
- Sustainable Aquaculture
- Ocean-Conscious Consumption
- Coastal Resilience
- Green Maritime Shipping
- Marine Biodiversity Enhancement
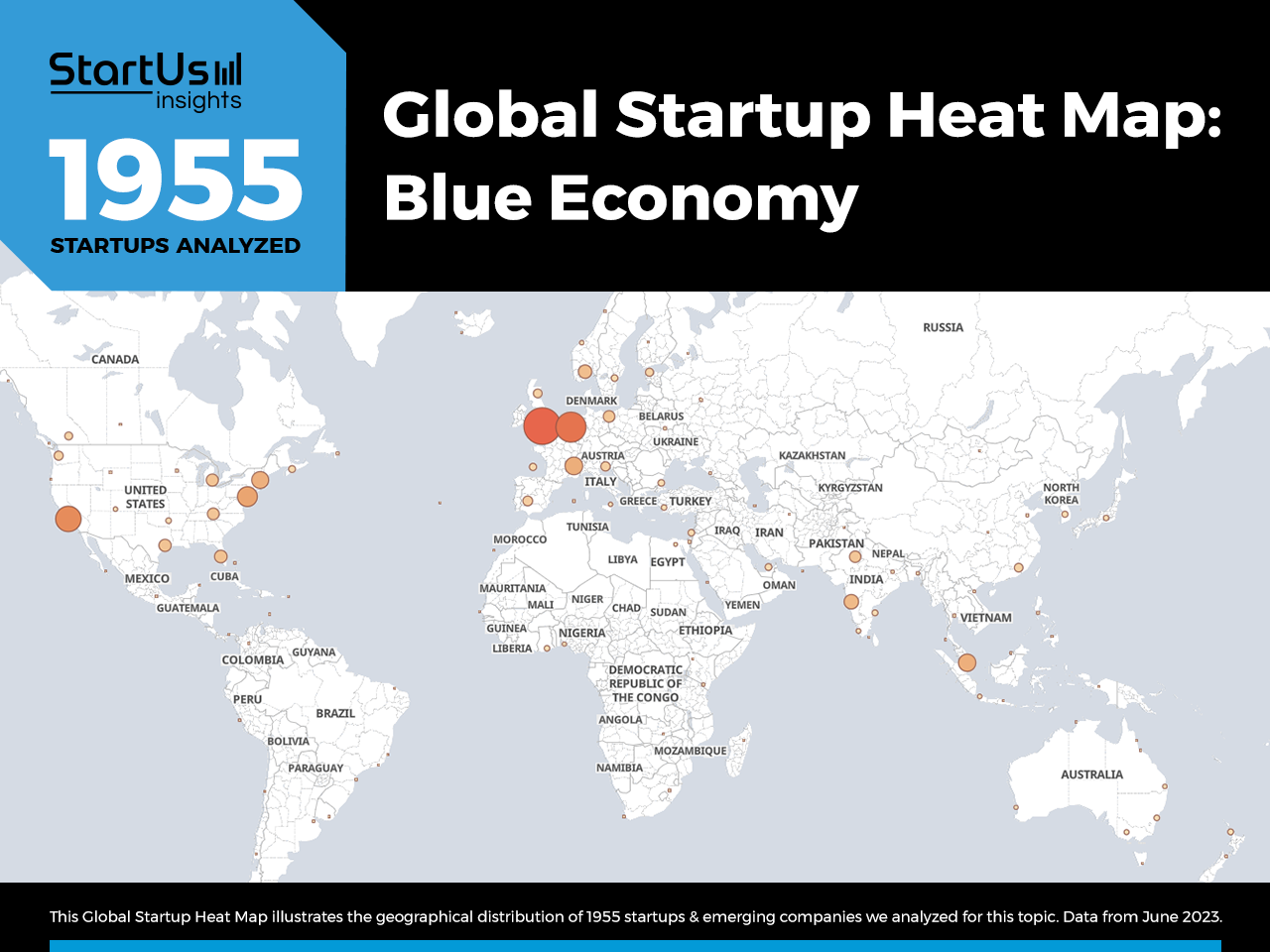
Global Startup Heat Map covers 1955 Blue Economy Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 1955 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals that the UK is the blue economy innovation hub, followed by the US and other European countries. Below, you get to meet 20 out of these 1955 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These blue economy startups are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Top 10 Blue Economy Innovation Trends in 2024
1. Marine Robotics
Without robots, monitoring and surveillance missions in the seas are time and labor-intensive. Nowadays, marine robots augment manual workflows to replace humans in dangerous environments and accelerate mission timelines. They explore the deep ocean to understand the ocean surface and search for resources like oil and gas. Maritime companies and fisheries also utilize robots for surveying and mapping the ocean floor to protect marine ecosystems and plan sustainable offshore development. Apart from monitoring coral reefs, robots track fish populations to aid fisheries management and ecosystem conservation. Further, robots collect debris, such as plastic or oil, to safeguard marine life and improve ocean quality.
Berkeley Marine Robotics offers an Autonomous Swarm Robot
Berkeley Marine Robotics is a US-based startup that develops an autonomous underwater swarm robotic system to help ships reduce carbon emissions. It focuses on autonomous swarm control and underwater wireless communication to enable fast, low-cost, and automated ship inspections. The system measures and tracks hull-fouling levels to optimize cleaning schedules and increase coating performance. Simultaneously, it flags invasive species to the ports, thereby reducing delays in manual spot checks. These swarm robots enable shipping operators to decrease fuel costs and comply with International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) carbon emission reduction goals.
Ensight Marine Technology makes Marine Inspection Robots
Australian startup Ensight Marine Technology provides underwater inspection robots for the maritime industry. Its remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) are suitable for shallow water inspection. The startup combines computer vision and laser pointers to provide fast and effective diameter estimations at different depths. The ROVs also use top-view cameras and image-stitching technology to capture high-quality data for maritime asset condition monitoring. Ensight Marine Technology’s ROVs make the process of asset condition assessment more efficient and save significant time for maritime consultants and asset managers.
2. Blue Renewable Energy
Offshore renewable energy companies develop technologies for wave power, tidal power, and ocean thermal energy conversion. They enable clean and reliable energy for coastal communities as well as power marine operations. For example, wave energy systems capture the kinetic energy of ocean waves and convert it into electricity. Utilities also establish tidal power turbines in locations such as estuaries to enhance tidal range. They also leverage ocean thermal energy by using the temperature difference between warm surface water and cold deep water to generate power. Moreover, ocean waves and tides are more reliable and predictable than other renewable sources like wind. Therefore, energy producers integrate marine energy with wind or solar power systems to maximize energy production.
Paddle Power Energy develops Tidal Power Turbines
Paddle Power Energy is a UK-based startup that deploys tidal energy turbines. The company’s technology utilizes a linear water wheel design that is more efficient and cost-effective than traditional tidal turbines. This allows the turbines to be water surface-based, reducing their cost and enabling operation in shallow depths of water. The design also avoids the creation of a vortex wake to maximize ongoing servicing, maintenance efficiencies, and total power output. Due to the low cost of production and readily available parts, Paddle Power Energy’s turbines are built easily in any commercial shipyard. With a low cost of decommissioning, it provides a reliable, sustainable, and cost-effective source of energy for businesses and general use.
TWEFDA provides a Wave Energy Converter (WEC)
Scottish startup TWEFDA develops ES-Wave, a wave energy converter that generates or stores wave energy on demand. It converts the reciprocating heave of waves into electrical energy and also functions as an energy storage device. Using the tidal range, the machine delivers more energy than what it absorbs, making it a versatile and efficient energy source to meet both baseload and peak demand. The startup also uses an insulated box to protect fauna from noise and employs an eco-friendly fluid to prevent marine ecosystem pollution in case of spillage. ES-Wave thus offers a higher capacity factor, smaller spatial footprint, continuous resource availability, and easier maintenance compared to regular wind turbines.
3. Ocean Pollution Management
The presence of plastics and other inorganic waste leads to the death of marine life and ultimately affects the quality of life globally. Emerging companies develop innovative solutions to manage ocean pollution like marine cleanup robots and waste-eating bacteria. Some also develop microplastic filters to remove plastic particles and promote climate-conscious operations to minimize wastage. Startups also develop biodegradable alternatives to plastic packaging, which is the largest contributor to marine pollution. Companies tackling ocean pollution also employ oil-absorbent sponges or hydrogels to clean up oil spills. These solutions reduce the pollutants entering the ocean, protecting marine life and coastal communities.
Sheco facilitates Robotic Oil Spill Recovery
Sheco is a South Korean startup that develops Sheco Ark, a robot to clean up oil spills in water bodies. Its key functions include product transportation, product deployment, oil recovery, and oil discharge. The robot is considerably lightweight and also supports remote control or autonomous operation. After deployment in an oil spill region, Sheco Ark moves around oil spills, intakes the oily water, filters the oil, and then releases the water back while retaining the oil for disposal. The robots are also able to work in dangerous and remote environments, making them ideal for cleaning up oil spills in hard-to-reach areas.
PurOceans makes a Deep Water Rehabilitation System
Latvian startup PurOceans utilizes its air bubble technology to remove oil, microplastic, and chemical pollution from the seabed. The startup’s deep water rehabilitation system features a flotation method that does not require excavation, chemicals, or electricity. The technology uses air bubbles to separate pollution from sand and soil at the bottom of the seabed. It also avoids the use of chemicals and excavation, preserving waterbodies and enriching it with oxygen. PurOceans’ technology helps environmental conservation brands clean up the oceans while also improving the health of marine ecosystems.
4. Deep-Sea Mining
In the field of deep-sea mining, emerging innovations include remote-operated vehicles (ROVs) and novel extraction technologies. They improve the efficiency and sustainability of seabed mining processes. For instance, mining companies use heavy-duty ROVs with manipulator arms to mine mineral-rich nodules and ore deposits. They also leverage hydraulic systems and suction dredging to collect minerals without harming the marine ecosystem. Further, real-time environmental monitoring systems assess the ecological impact of mining. Innovations in resource recovery and processing, such as hydrocyclones and magnetic separators, optimize mineral extraction by minimizing waste. Lastly, deep-sea miners rely on deep-sea power generation and communication systems to support efficient mining operations.
Bluefield Geoservices delivers Offshore Geotechnical Surveys
Bluefield Geoservices is a UK-based startup that facilitates offshore geotechnical surveys for deep-sea mining companies. The startup deploys tools like cone penetration testing, samplers, and T-Bar test equipment using underwater ROVs. The ROVs collect data on the seabed in all water depths. Operators use the cone system to deploy a lightweight unit for in situ soil testing or sampling using an ROV, trenching machine, or similar subsea equipment. By providing data on the seabed, Bluefield Geoservices mitigates the risks of accidents and injuries as well as improves the efficiency of offshore mining operations.
Glex facilitates Collaborative Mining
Norwegian startup Glex develops Glex Energy, an analysis and collaboration SaaS platform for energy and seabed mining companies. It helps teams create, organize, and analyze a digital twin of mining site exploration data for analysis. The platform also provides a global mapping interface digital elevation models and point clouds that allow users to view the mine or seabed data in both 2D and 3D domains. This visual representation aids in planning mining operations, identifying potential risks, and optimizing extraction processes. The Glex Energy platform assists in seabed mining by providing tools for portfolio management, data analysis, visualization, and collaboration. This, in turn, streamlines the management of mining assets, facilitates data-driven decision-making, optimizes mining operations, and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
5. Marine Biotechnology
The applications of marine biotechnology, such as cytarabine and antiviral azidothymidine from sponges, revolutionize cancer and viral treatments, energy production, and more. Researchers study marine microorganisms for their unique metabolic capabilities, enabling the production of enzymes, biofuels, and bioremediation agents. This enables advances across industries. Omega-3 fatty acids from algae or fish oil, for example, improve cardiovascular health and brain function. Companies are also developing ocean-sourced bioplastics to offer biodegradable and renewable alternatives to conventional plastics. Additionally, marine biotechnology deploys marine organisms and enzymes to clean up pollution and oil spills, ensuring environmentally friendly bioremediation.
Marine BioEnergy manufacturers Kelp-based Biomass
Marine BioEnergy is a US-based startup that accelerates underwater kelp farming to produce biomass for fuel, feed, and food. The startup grows kelp attached to large grids in the ocean by permanently towing it with inexpensive automated robotic submarines. This allows the kelp to grow in the extensive regions of the ocean with access to sunlight and nutrients. The startup then processes the kelp into biocrude, which it uses to create renewable energy, animal feed, and other products. Moreover, Marine BioEnergy leverages hydrothermal liquefaction and catalytic hydrothermal gasification to process wet kelp into bio-oil. These technologies provide a sustainable and scalable source of renewable energy from ocean kelp.
TeOra manufactures a Vaccine for Aquaculture
Singaporean startup TeOra manufactures a vaccine for disease and pest management in aquaculture. The startup derives high-quality ingredients from microbial cell cultures to develop these biologicals. It also develops tailor-made biotechnology solutions with collaboration and co-development for clients. Using microfluidics and AI, TeOra offers faster and cheaper genetic reprogramming to design smart micro-organisms in shorter time periods. This vaccine enables fish farmers to replace pesticides, antibiotics, and other harmful chemicalswhile ensuring healthier shrimps and fishes.

6. Sustainable Aquaculture
Current aquaculture practices pollute water systems by discharging excess nutrients and fecal matter into oceans. Sustainable aquaculture embraces innovative techniques like recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) to reuse water, conserve resources, and reduce pollution. Fishery companies also use integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) to combine fish species and utilize nutrients more efficiently whilst increasing output. Offshore aquaculture reduces conflict with other users of coastal resources and minimizes the impacts on sensitive coastal ecosystems. Further, fisheries utilize recycled fish feeds or algae-based products to reduce the pressure on wild fisheries. These innovations drive the sustainability of aquaculture while minimizing the environmental impact and maximizing the efficiency of marine resources.
Ittinsect creates a Sustainable Fish Feed
Ittinsect is an Italian startup that develops Ittinsect Feed, a sustainable feed for aquaculture. The startup produces an insect-based fish feed that is rich in protein and nutrients as well as is more absorbable for fish digestion. This results in faster and more constant growth, a stronger immune system, and a lower risk of digestive inflammation in fish. The startup’s feed also generates fewer emissions than traditional feeds. It thus enables fish farmers to provide sustainable and high-output aquaculture yields while reducing their environmental impact.
Aqua Development advances Aquamimicry
South Korean startup Aqua Development uses KAMI sys, an aquamimicry technology to produce sustainable aquaculture products. The startup mimics the natural environmental conditions and factors of aquatic life in an indoor farm. KAMI sys provides more productivity than traditional methods with higher survival rates and resilience to disease for shrimps. It is also cost-effective and easily applicable to different types of aquatic animals. This allows Aqua Development to produce high-quality and organic shrimp without using harmful chemicals or antibiotics.
7. Ocean-Conscious Consumption
Consumers are increasingly choosing ocean-conscious products to protect the health and well-being of the oceans. In response, companies experiment with biodegradable and compostable packaging materials made from cornstarch or seaweed to reduce plastic pollution. Cosmetic brands are developing personal care products with natural, biodegradable ingredients to avoid harming marine life and water pollution. Startups are also promoting sustainable seafood practices to minimize overfishing and ensure seafood availability for the future. Textile and clothing companies are incorporating sustainable materials like recycled ocean plastic to reduce the fashion industry’s environmental impact. Additionally, the fishing industry is embracing innovative designs such as biodegradable nets and smart nets to reduce harm to marine life. These collective efforts demonstrate a shared commitment to preserving the oceans for generations to come.
Lumière provides Recycled Ocean Plastic Fabric
Lumière is a French startup that collects and recycles ocean plastic to manufacture active-wear clothing. The startup utilizes plastic waste from oceans and landfill to create its recycled fabric ECONYL. The fabric also possesses muscle-compressing properties which decrease the production of lactic acid in the wearer’s body, thus aiding recovery time after workouts. Lumière formulates ECONYL with ultraviolet light protection, making it highly resistant to color-fading chlorine and sunscreen lotions. This ocean plastic-derived fabric enables Lumiere to manufacture sustainable clothing for athletes while aiding in the cleaning up of our oceans.
SCALE develops a Fish-Scale Biomaterial
French startup SCALE creates SCALITE, a sustainable material made from fish scales – a byproduct of aquaculture. The startup collects fish scales from sustainable fisheries to extract the collagen and transform them into durable, water-resistant tiles, sheets, and blocks. SCALE extracts a natural biopolymer contained within fish scales to create the basis for SCALITE. The high-performance material offers water resistance, thermal insulation, and fire retardancy. Hospitality and retail companies use SCALITE for building interiors and decoration. SCALE’s material is a circular and ocean-friendly solution that reduces aquaculture waste while creating new opportunities for product design and development.
8. Coastal Resilience
Government agencies develop and employ coastal resilience strategies to enhance the ability of coastal areas to withstand and recover from the impacts of natural disasters and climate change. Researchers develop advanced modeling techniques and real-time monitoring systems to predict areas at high risk of flooding. Early warning systems further provide timely alerts to residents and authorities, enabling evacuation and emergency response efforts. Architects design floating homes and buildings that adapt to changing water levels and reduce vulnerability to floods. Additionally, communities implement techniques such as constructing offshore breakwaters or submerged barriers to help dissipate wave energy before it reaches the coast. This reduces the impact of storms and erosion on coastal communities.
Scientia Maris simplifies Coastal Monitoring
Scientia Maris is a Greek startup that makes software modules for coastal monitoring and planning. It combines satellite imagery and AI for the prediction of wave propagation and transformation in the nearshore. This enables the efficient planning and design of coastal protection works and port layouts. Environmental agencies use it to analyze the risks and impacts of coastal hazards, such as erosion, flooding, and storms. It also simulates the propagation of waves in different directions, enabling the study of wave disturbances in ports, harbors, and coastal areas. Further, analysis of seabed sediments enables researchers to understand areas of seabed erosion and predict possible coastal calamities. Scientia Maris’s platform provides decision support and visualization to help stakeholders plan and implement adaptation strategies, enhancing their capacity to cope with coastal challenges.
Reask facilitates Global Risk Mapping
Australian startup Reask develops AI-based global risk mapping software and modules that focus on natural hazard prediction and simulation. For example, its DeepCyc, ForeCyc, HindCyc, and Metryc help environmental organizations forecast their exposure to catastrophic events. HindCyc and Metryc provide tropical cyclone wind maps and landfall predictions, enabling residents to take precautionary measures and/or evacuate in time. DeepCyc and ForeCyc offer global probabilistic hazard maps, historical and stochastic event catalogs, and risk trend forecasting using climate signals. Reask’s modules cover all aspects of natural catastrophe risk analytics, from tail risk assessment to probabilistic trend forecasting and event reconstructions. This enables users to accurately understand and predict natural hazards, and make decisions to trigger appropriate coastal resilience measures.
9. Green Maritime Shipping
Maritime shipping companies employ alternative fuels like liquified natural gas (LNG), biofuels, hydrogen, and ammonia to reduce emissions. They utilize electric, hybrid, and auxiliary propulsion systems with batteries, fuel cells, and hybrids to further cut emissions. The industry is also relying on aerodynamic hull designs, air lubrication, waste heat recovery, LED lighting, and smart energy management to optimize fuel efficiency. Additionally, shipping companies install scrubbers in ship exhausts to remove sulfur dioxide and pollutants for air pollution control. Some also use ballast water treatment systems to neutralize harmful organisms, minimizing ecological impact. Data analytics, AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT) further enable better route planning, optimized vessel performance, and real-time monitoring of emissions and energy consumption. These innovations drive the maritime industry towards sustainability and a lower ecological footprint.
Spaera builds a Net Zero Ship Prototype
Spaera is a UK-based maritime startup that offers Project Lovelock, a net-zero emission prototype ship for the shipping industry. It leverages green methanol fuel cells to power its engines, eliminating harmful emissions and reducing fuel costs. The ship also employs an automated sails system to provide propulsive power under normal conditions. This reduces crew workload and uses adverse weather conditions to its advantage. Project Lovelock also utilizes a battery rechargeable via inbuilt solar panels to ensure sufficient energy even when the ship is at the port. Spaera’s ship offers a way for shipping companies to reduce emissions and save money while maintaining their current level of efficiency and productivity.
ESG-NRG aids Maritime Carbon Offsetting
Norwegian startup ESG-NRG offers a marine offset platform (MOP). It features a suite of tools and services that allow maritime shipping companies to track, measure, and offset their carbon emissions. MOP utilizes algorithms that consider the vessel, cargo, and operational variables to estimate emissions. It then offers quality carbon credits from pre-screened projects that align with sustainable development goals (SDGs). The platform also allows shipping companies to share their carbon certificates and mitigation strategies on the public carbon ledger and gain recognition for their ESG efforts. ESG-NRG helps them attract new customers, enhance their reputation, appeal to green capital, and boost their net zero commitments.
10. Marine Biodiversity Enhancement
With the rise in excess fishing and mining activities, marine biodiversity is being hit hard. Some environmental companies and startups are developing technologies and strategies to preserve and enhance the quantity and quality of marine life. Artificial reef structures leverage materials like concrete, steel, or sunken ships to provide new habitats for marine organisms to thrive. Governmental agencies set up marine protected areas (MPA) as specific zones where they regulate human activities to protect marine biodiversity. Some environmental research companies also employ techniques like coral gardening to cultivate and transplant coral fragments onto damaged reefs. Further, 3D printing of artificial coral structures provides a substrate for coral colonization.
Archireef develops 3D-Printed Artificial Corals
Chinese startup Archireef uses 3D printing to create artificial coral reefs. The startup combines computer programming, 3D printing, and traditional clay-making techniques to ensure that tiles do not crack or change shape during the drying and firing process. It designs its reef tiles using terracotta to provide a safe and stable habitat for marine life. The startup also provides a range of benefits for the ocean, such as increased fish populations, improved water quality, and reduced erosion. Archireef modules are easy to install and deploy in a variety of marine environments. This makes the startup’s solution a cost-effective and scalable means for businesses looking to improve marine biodiversity.
Kelp Blue facilitates Ocean Re-Wilding
Kelp Blue is a Dutch startup that leverages rewilding to help mitigate climate change. It grows and manages large-scale kelp forests, which absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their tissues. Kelp forests also provide food and shelter for marine life, and manufacturers harvest kelp for sustainable products such as fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and textiles. Kelp forests provide ecosystem functions, habitat for biodiversity, and benefits like reducing local acidity, raising oxygen levels and improving water conditions. Kelp Blue’s ocean rewilding technique is scalable and cost-effective, making it a viable solution for marine biodiversity enhancement.
Discover all Blue Economy Trends, Technologies & Startups
Researchers and entrepreneurs are actively exploring untapped opportunities within our oceans and water bodies. They are developing cost-effective ocean desalination methods such as forward osmosis (FO) to deliver a sustainable source of fresh water for coastal communities. It supports agriculture, industries, and human consumption. Underwater robotics also holds promise in various sectors, such as deep-sea exploration, offshore infrastructure maintenance, and underwater resource extraction. The Blue Economy innovations & trends outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.


![15 Top Defense Companies and Startups to Watch in Europe [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Defense-Companies-in-Europe-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)





