The circular economy presents a sustainable alternative to the traditional linear economy — based on the ‘take, make, and dispose’ model — by designing waste out of the system. This innovative approach encompasses a broad spectrum of practices to extend product life cycles, maximize resource efficiency, and promote reuse, repair, and recycling. In the following sections, you will explore various real-world examples of the circular economy, demonstrating its implementation across different industries and sectors. These applications of circular practices span compostable materials, sustainable packages, zero-carbon food waste management, and more.
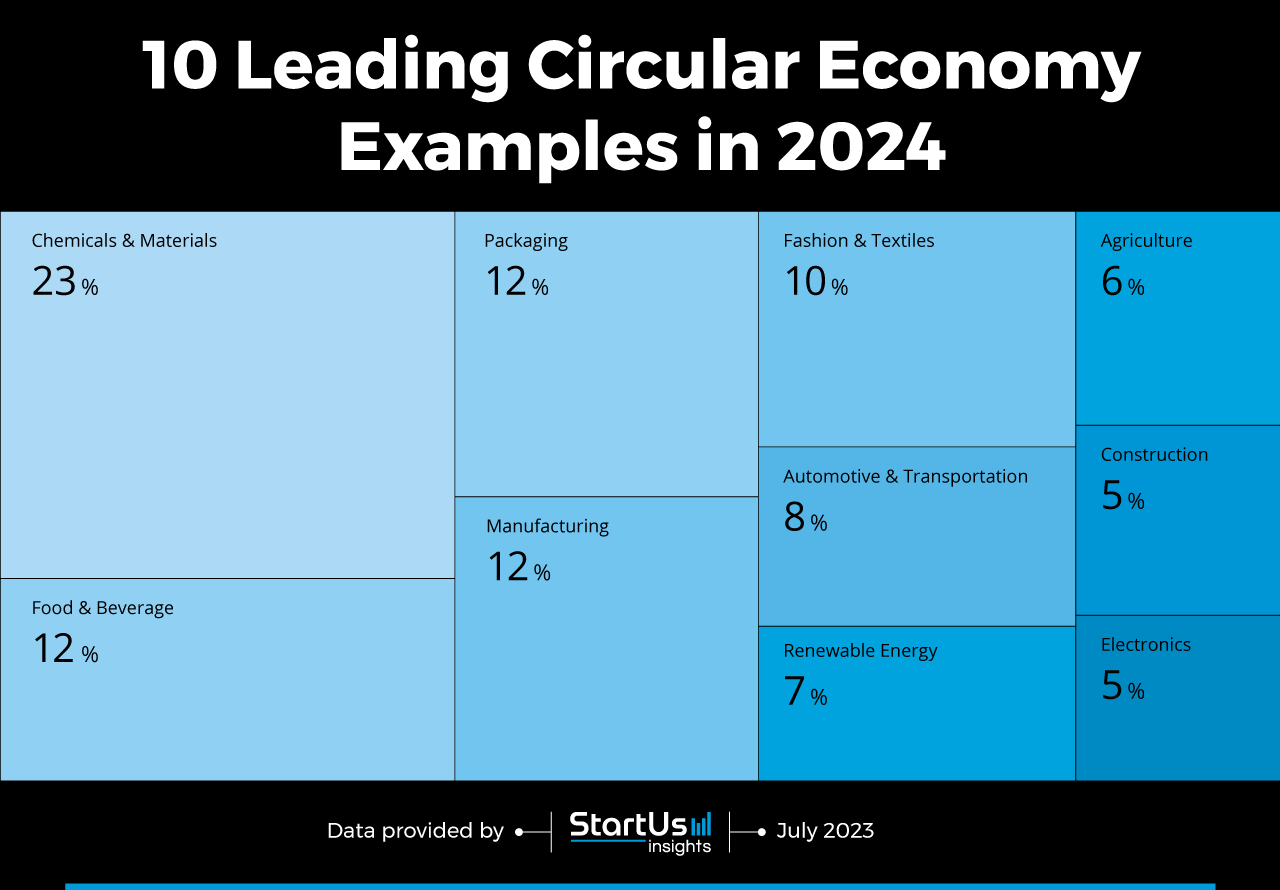
Tree Map reveals the Impact Circular Economy Practices on 10 Industries
Based on the Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the applications of the circular economy across 10 industries in 2024. The circular economy is driving a profound transformation across multiple industries. In the chemicals and materials sector, it encourages the shift towards bio-based, recyclable, and non-toxic materials. The food and beverage industry promotes sustainable farming, reduces food waste, and encourages packaging innovation.
In manufacturing, fashion, and textiles, circular economy inspires design for longevity, repairability, and recyclability. This fosters a move away from the traditional ‘take-make-waste’ model. Automotive and transportation are also evolving through shared mobility, electrification, and extended product life cycles. The renewable energy sector benefits from improved battery lifecycles and efficient resource use with circular economy solutions.
Regenerative farming practices and waste-to-resource approaches are gaining ground in agriculture. The construction sector focuses on sustainable materials, energy-efficient designs, and buildings that are repurposed or disassembled. Finally, the circular economy drives the adoption of product-as-a-service models, design for repair, and comprehensive e-waste recycling in electronics.
Global Startup Heat Map covers 3753 Circular Economy Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 3753 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform that covers 3 790 000+ startups & scaleups globally, the Heat Map reveals that Western Europe has a high concentration of circular economy companies, followed by the US.
Below, you get to meet 10 out of these 3753 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These emerging circular economy companies are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Circular Economy Applications across 10 Industries
1. Chemicals & Materials
Green chemistry keeps the circular economy approach central to chemicals and materials production, reducing their carbon footprint. This also leads to more recyclable and reusable raw materials for manufacturing. Further, chemical and material manufacturers are leveraging bio-based raw materials to replace fossil-based materials. Such materials, like bioplastics, are easily recycled or composted.
Industrial symbiosis is another example of circular economy in the chemicals industry where one waste stream becomes the input for another industry or process, generating value. For example, waste heat from chemical processes runs power generation systems to produce electricity. Lastly, chemical leasing allows manufacturers to retain ownership of their products and generate revenue for the performance of chemicals, optimizing consumption.
ReSolved Technologies advances Closed-Loop Plastic Recycling
ReSolved Technologies is a Dutch startup that offers a closed-loop plastic recycling solution. The startup’s solvent-based recycling technology upcycled engineering plastics from complex waste streams. Engineering plastics are difficult to recycle due to their complex compositions and the presence of legacy additives. Resolved Technologies’ solution offers a way to separate different types of plastics and remove a broad range of additives, including colorants and legacy additives.
The company’s technology is particularly relevant for the circular economy as the material of an end-of-life product is recycled and used to produce the same type of product. This reduces waste and also decreases the demand for virgin materials, promoting sustainability. Moreover, the startup’s solvent-based recycling technology complements existing mechanical recycling infrastructure, offering additional opportunities to treat complex waste streams.
2. Food & Beverage
The food and beverage industry leverages circular economy solutions to reduce food waste, mitigate package waste, and generate energy. For instance, some food businesses use end-of-life and surplus products as ingredients for other food products, like beer. This food waste also finds use in generating bioenergy through anaerobic digestion, providing a renewable energy source. Matching supply and demand by using technologies like predictive inventory planning also plays a crucial role in reducing food waste.
Alongside other initiatives, food and beverage chains, including restaurants, are significantly integrating plant-based products to replace traditional animal-based foods. This shift, driven by the growing understanding of animal agriculture’s environmental impact and health-conscious alternatives, reduces water and land usage. Simultaneously, the industry is adopting plant-sourced materials to replace plastic packaging. This decreases the industry’s carbon footprint, enhancing environmental sustainability in production and last-mile deliveries.
CIRCULAR FOOD makes Upcycled Flour
CIRCULAR FOOD is an Italian startup that manufactures upcycled flour. The startup’s patented technology converts by-products of distillation and fermentation processes into flours. It reduces waste and also finds use as an ingredient in a variety of food items. Circular Food’s approach promotes the principle of “waste as a resource”. By finding a use for materials that would otherwise be discarded, the startup is reducing waste, promoting sustainability, and creating value.
3. Packaging
As global governments enforce bans on single-use plastic, the packaging industry is turning towards plant-sourced raw materials to create sustainable packaging solutions. This leads to the rise of bio-based materials an alternative to traditional plastics. They have beneficial properties of traditional plastics, such as durability and flexibility, while offering significant environmental benefits, including reusability and biodegradability.
Apart from biodegradable packaging, eco-design and recyclable packages are prime examples of circular economy approaches in the packaging sector. They improve material recovery at the end of the life of products and eliminate packages reaching landfills and oceans. Thus, integrating the circular economy in packaging reduces carbon footprint across industries.
Treetop Biopak manufactures Compostable Packages
Treetop Biopak is a UK-based company that makes compostable packages. It utilizes renewable resources, such as corn starch, to produce biopolymers that are compostable and replace fossil-based plastics.
The company offers compostable bags, stretch film, tubular net, shrink film, and adhesive tape. These products are suitable for applications from fresh produce and bakery products to garments, electronics, and more. The packaging solutions are durable, puncture-resistant, water-resistant, and printable, making them a viable alternative to conventional plastic packaging.
4. Manufacturing
Product-as-a-service business model allows manufacturers to retain product ownership and customers pay for usage rather than outright ownership. This encourages durability and maintenance, extending the product life cycle. Another application of the circular economy is remanufacturing. This way, used products are disassembled and their components are recycled into new products, reducing waste and demand for virgin resources.
3D printing enables on-demand production, reduces overproduction, lowers waste, and permits efficient and easily customizable designs. Additionally, prioritizing energy efficiency and utilizing renewable energy sources in operations are pivotal in reducing the environmental impact of manufacturing operations. Material selection with a preference for easily recyclable materials for product development and designs that allow for easy disassembly further enhances product recyclability.
Batch.Works leverages Smart & Circular Manufacturing
Batch.Works is a Dutch startup that advances smart and circular manufacturing. The startup leverages circular materials, on-demand production, re-manufacturing, short supply chains, digital warehousing, and digital manufacturing. It uses recycled materials from traceable sources and on-demand digital production ensures just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing, reducing waste and overproduction.
The startup also offers a service to take back and find new uses for their products, promoting a circular lifecycle. Its local production model creates short supply chains, reducing transportation costs and increasing transparency and agility. Digital warehousing also eliminates storage fees and emissions from shipping stock. These technologies reduce waste and improve supply chain efficiency while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
5. Fashion & Textiles
The utilization of recycled or renewable materials, including organic fibers and synthetic materials reclaimed from waste, reduces the need for virgin materials. Design for longevity ensures products can be worn for longer periods of time, thereby reducing the frequency of new purchases and extending the life of garments. Similarly, repair and maintenance services as well as resale and rental platforms keep clothes in use for longer, reducing production demand.
Innovations in technology are enabling the recycling of textiles into new garments, an approach known as “closed-loop” recycling. This goes beyond traditional recycling and seeks to retain the full value of the original material through chemical recycling. Brands are also exploring innovative business models like take-back programs to promote reuse and recycling while fostering customer loyalty.
Circular Fashion LA enables Zero-Waste Fashion
Circular Fashion LA is a US-based direct-to-consumer (DTC) company that implements zero-waste fashion. The startup’s subscription services allow customers to repair, refit, redye, and redesign their clothes. This offers clothes a new lease of life and also reduces the need for new clothes, making their wardrobe more unique and healthier for the planet.
In addition, the company offers a recycling service, where customers send in clean clothing and home textiles they no longer want. This reduces the amount of textile waste that ends up in landfill. Circular Fashion LA further leverages zero-waste packaging and natural dyes to improve sustainability.

6. Automotive & Transportation
Consumers are giving away ownership of vehicles and relying on on-demand mobility to reduce their carbon footprint. This shift reduces the overall number of vehicles needed, leading to fewer resources consumed in manufacturing and lower volumes of end-of-life waste. Electric vehicles (EVs) represent another critical component in reducing emissions and with potential for battery reuse and recycling. Digital platforms and technologies optimize logistics and transport operations to avoid unnecessary trips and reduce fuel consumption.
Automakers are increasingly integrating recycled materials into new vehicles and developing recyclable components to minimize waste at the end of a vehicle’s life. Remanufacturing is also gaining traction in the industry, where parts from end-of-life vehicles are restored or refurbished for use in new vehicles. This approach reduces waste and also saves energy and resources compared to manufacturing new parts.
Circunomics develops a Circular Battery Platform
Circunomics is a German startup that provides a circular battery platform. It allows automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to integrate used batteries in new vehicles, delivering significant cost savings. The startup’s solution also features battery lifecycle management, first-life analytics, and second-life simulations. This, in turn, facilitates the transfer of used batteries into second life and recycling at scale.
7. Renewable Energy
The renewable energy industry is advancing and leveraging the circular economy. For example, renewable energy systems like solar panels and wind turbines power clean operations across industries while these systems use material innovations to reduce carbon footprint. Manufacturers increase the life cycle of batteries, particularly in energy storage and EVs, by refurbishing used batteries or repurposing them for less demanding applications. This extends battery life and reduces the need for new materials.
Moreover, the renewable energy industry is embracing service-based business models to invest in durable, efficient technology and take responsibility for end-of-life management. At the system level, this enhances grid flexibility and energy efficiency, reducing waste in energy distribution. The deployment of smart grids, for instance, allows for better matching of energy supply and demand to reduce energy loss. All these applications showcase the renewable energy industry’s commitment to a more sustainable and circular future.
Varme Energy advances Waste-to-Energy (WTE)
Varme Energy is a Canadian startup that makes waste-to-energy plants. The startup builds a portfolio of WTE facilities with integrated carbon capture and storage (CCS). A lot of waste heat is simply released into the environment, which contributes to climate change. Varme Energy’s technology allows industries to use this waste heat and generate electricity, which displaces fossil fuels and reduces emissions. This eliminates waste from reaching landfills and enables a sustainable solution for non-recyclable waste.
8. Agriculture
Regenerative farming techniques improve soil health, enhance biodiversity, and sequester carbon. This improves the productivity and resilience of the land over time. Crop rotation and cover crops maintain soil health and manage pests naturally. This approach decreases reliance on external inputs and increases farm productivity and sustainability.
In livestock farming, there is an increasing movement towards integrating animals into cropping systems to form mixed farming systems. Businesses are upcycling agricultural side streams into animal feeds, thereby reducing cultivation for feed. The concept of “closing the loop” is also applied to waste management in agriculture. Rather than being discarded, organic waste, such as manure and crop residues, is composted and returned to the soil as a nutrient-rich amendment.
Further, precision irrigation and rainwater harvesting prioritize water efficiency. New business models also directly connect farmers with consumers, reducing food waste in the supply chain and bringing consumers closer to the source of food.
SWING Biomethane produces Biomethane
SWING Biomethane is a French startup that generates biomethane. The startup collects organic residues and agricultural waste from local farmers and converts it into biogas. It then purifies and upgrades into biomethane – equivalent to the natural gas used daily by households or industries. The biomethane is either injected into the gas grid or liquefied into bio-LNG for the transportation sector.
In addition to energy production, SWING Biomethane provides farmers with a sustainable fertilizer derived from the production of biomethane, known as digestate. It reduces their dependence on fossil fertilizers and greenhouse gas emissions. Swing Biomethane’s approach lowers waste and creates local jobs, supports local farmers, and contributes to the decarbonization of the gas sector.
9. Construction
Construction companies are integrating design for disassembly approach. This anticipates a building’s end-of-life from the design stage, ensuring component reuse when the building is no longer needed. The use of reclaimed materials, like concrete and bricks, in new constructions reduces the demand for new materials and construction waste.
Prefabrication and modular construction methods, powered by 3D printing, are also gaining popularity. It reduces waste and makes it easier to reuse and recycle materials. Further, the construction industry is adopting renewable energy and energy-efficient integrations to decrease energy consumption. Buildings-as-a-service shifts the focus from selling a product to selling a service, encouraging constructors to build for longevity.
revitalyze.io facilitates Building Component Reuse
French startup revitalyze.io promotes building component reuse. The startup’s platform features digital inventory analysis of buildings to classify components according to condition, de-constructability, dimensions, and position. This allows material users like architectural offices, designers, and traders to source components below market price.
The platform also supports automated matching and provides alerts about nearby materials, as well as connects businesses directly with suppliers. For project developers, municipalities, and building owners, the platform simplifies inventory analysis and increases sales. This approach reduces disposal costs, generates additional revenue, and actively contributes to a more circular economy.
10. Electronics
Modular and repair-friendly architecture is gaining popularity in the consumer electronics market, reducing the need for new products. In parallel, the electronics industry is emphasizing the use of recycled or recyclable materials in product manufacturing. Companies are using reclaimed metals and other materials from end-of-life electronics in new devices, decreasing the need for virgin materials.
In addition, the industry is focusing on comprehensive e-waste management strategies. With recycling programs, take-back schemes, and partnerships with recycling companies, manufacturers are recovering and reusing valuable materials from old electronics. There is also an increased focus on energy efficiency in electronic products to reduce power consumption.
Circular Technologies simplifies IT Device Management
Circular Technologies is an Italian startup that develops an IT device management solution. The startup’s solutions are reSource for circular IT procurement, reCover for circular IT asset disposition, and reCert for circular certification. reSource enables businesses to renew their IT infrastructure with certified refurbished products. This allows businesses to maximize their IT investments and achieve carbon neutrality.
On the other hand, reCover allows businesses to cash out on their used devices. It helps businesses develop a tailored IT asset disposition (ITAD) program and maximize the value of used assets. reCert further allows businesses to calculate the economic and environmental impact of their transactions and certify them for sustainability reporting. This helps businesses demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and the circular economy.
Discover All Circular Economy Companies
Future innovations in the circular economy will revolve around enhancing product life cycles, leveraging technology, and promoting systemic shifts. Advances in material science extend product lifespans and improve recyclability, while digital technologies like AI and blockchain will enable precise resource tracking and optimization. Additionally, biofabrication and synthetic biology offer new ways to create products without resource extraction. Together, these innovations have the potential to redefine resource consumption and waste generation. Get in touch to identify specific circular economy companies & solutions that advance your business!



![Explore the Top 10 Circular Economy Trends & Innovations [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Circular-Economy-Trends-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)





