We live in a fast-paced age full of game-changing innovations. Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) that create content, computers that use quantum physics, and robots with human-like skills are just the tip of the iceberg. And as we move further into this new reality, it’s crucial for business leaders to understand which emerging technologies and tech trends are the most impactful and will shape our future.
Here is what this extensive report on 10 emerging technologies across 40+ industries will cover:
- Top Tech Trends: We’ll dive into up-and-coming technologies that make business more efficient and productive than ever before.
- Industry Breakdown: How Emerging Technologies are Impacting Industries
- Heavy Industries: Think large machinery and equipment.
- Process Industries: Sectors like chemicals and food.
- Light Industries: Areas like electronics and apparel fall here.
- Service Industries: This includes sectors like finance and healthcare.
- The ‘Outliers’: Some industries like agriculture and packaging don’t fit neatly into any box but are vital players on the global stage.
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Explore the hurdles and societal questions arising from new technologies.
- Future Outlook: Discover the anticipated developments and trends in technology.
This article was last updated in January 2025.
Key Takeaways
- Top emerging technology trends are AI, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), big data, advanced analytics, blockchain, cleantech, the Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics. Other emerging technology trends include additive manufacturing or 3D printing, connectivity technologies like 5G and LoRaWAN, nanotechnology, wearables, and biometrics.
- Impact & Use Cases of Emerging Tech:
- Emerging tech in Heavy Industries: 3D printing, cloud computing, and AI have a substantial impact in strengthening the supply chain and improving manufacturing workflows. Asset maintenance, quality control, and remote asset monitoring are the prominent use cases in this segment.
- Emerging tech in Process Industries: They emphasize AI, ML, IoT, and nanotechnology to increase operational efficiency, sustainability, and precision. AI & ML are pivotal in areas like drug discovery and quality control while nanotech delivers high-performance materials for this sector.
- Emerging tech in Light Industries: Technologies like AI, IoT, and 3D Printing are transforming consumer experiences and manufacturing processes. Trend forecasting, connected clothing and smart homes, rapid prototyping, and immersive experiences are major use cases in this sector.
- Emerging tech in Service Industries: This sector leverages technology to personalize customer experiences and enhance customer satisfaction. Primary applications include hyper-personalization, real-time monitoring, transparent transactions, and more.
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Compatibility issues with legacy systems and costly upgrades are the major challenges. Safeguarding data privacy and ensuring bias-free technologies is also important.
- Future Outlook: Bridging accessibility gaps of cutting-edge technologies will take center stage. Further, climate-positive practices and human-machine collaboration will evolve.
How We Researched and Where this Data is from
- Analyzed our 3100+ industry reports on innovations to gather relevant insights and create a master technology-industry matrix.
- Cross-checked this information with external sources for accuracy.
- Leveraged the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, an AI- and Big Data-powered innovation intelligence platform covering 4.7M+ emerging companies and over 20K+ technology trends worldwide, to:
- Confirm our findings using the trend analysis tool and
- Find emerging tech companies for “Spotlighting an Innovator” sections.
So, let’s look into the future of technology and see how it impacts every industry, big or small.
Top 10 Emerging Technology Trends in 2025 & Beyond
- Artificial Intelligence
- AR & VR
- Big Data & Analytics
- Blockchain
- CleanTech
- Internet of Things
- Advanced Robotics
- Additive Manufacturing
- Cloud Computing
- Nanotechnology
1. Artificial Intelligence: The Game-Changer for Future Industries
AI has quickly become a cornerstone for the future. How? By bringing smart, automated decision-making into the business world. It allows machines, especially computers, to mimic human-like thinking. This includes learning from data, making logical decisions, and even improving over time.
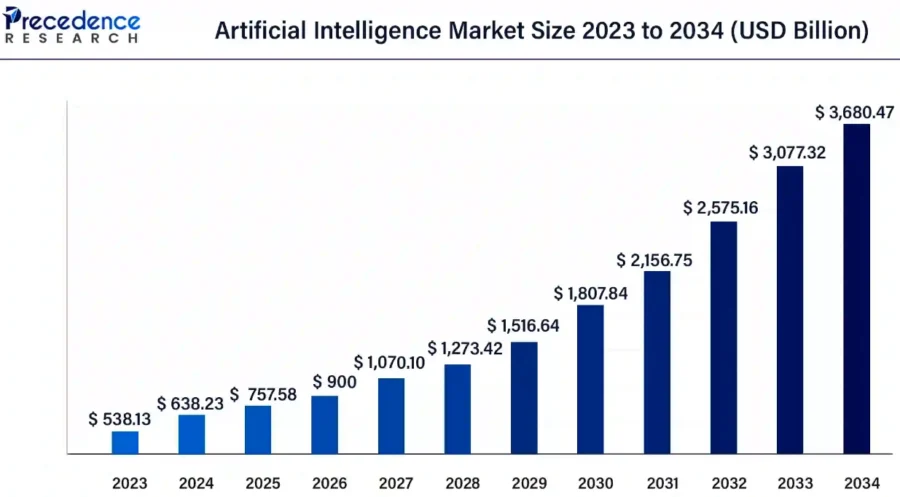
Source: Precedence Research
About 83% of companies have made AI a top priority, with sectors like healthcare and finance leading adoption due to efficiency gains and cost savings
PwC predicts AI will contribute USD 15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, while McKinsey’s latest research estimates that generative AI will add USD 2.6 trillion to USD 4.4 trillion annually across the 63 use cases.
Generative AI funding reached USD 56 billion in 2024 and investments in AI are forecasted to approach USD 200 billion in 2025, with the US contributing nearly USD 100 billion.
Noteworthy AI Advancements
- OpenAI’s ChatGPT: Beyond its general conversational abilities, ChatGPT finds B2B applications in customer support automation, content creation, and training simulations, enhancing efficiency and personalization.
- IBM Watson: Leveraging cognitive computing, Watson has been crucial in sectors like healthcare for drug discovery and tailored treatment plans. In finance, it aids in risk assessment and fraud detection.
- UiPath: A leading figure in robotic process automation (RPA), UiPath uses AI to automate monotonous business operations, optimizing sectors like finance, HR, and supply chain.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: GlobeNewswire predicts a global AI market size of USD 757.58 billion.
- 2025-2034: It also expects:
- A yearly growth of 19.1%.
- AI market value to reach USD 3.68 trillion by 2034.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Parea AI – LLM Development
Parea AI is a US-based startup that offers a developer toolkit allowing engineers to build and optimize LLMs for production use. It enables testing prompts across different cases and defining custom metrics to evaluate performance.
Minimal Python and Typescript SDKs provide access to deployed prompts with automatic logging and metadata for debugging, enhancing prompt engineering workflows.
Core Technologies Connected to AI
- Machine Learning (ML): ML allows systems to learn from data to improve their performance at tasks without being explicitly programmed.
- Neural Networks: By mimicking the human brain, neural networks facilitate deep learning, allowing computers to process and interpret vast datasets.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, powering chatbots and voice assistants.
- Computer Vision: This technology allows machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual data, finding applications in image recognition and autonomous vehicles.
Discover all trends in AI here.
2. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality: Use Cases Beyond Entertainment
AR and VR are not just transforming entertainment; they are revolutionizing business operations. By integrating immersive experiences, businesses enhance training, streamline design processes, and improve customer interactions using AR and VR.
AR and VR Market Forecast
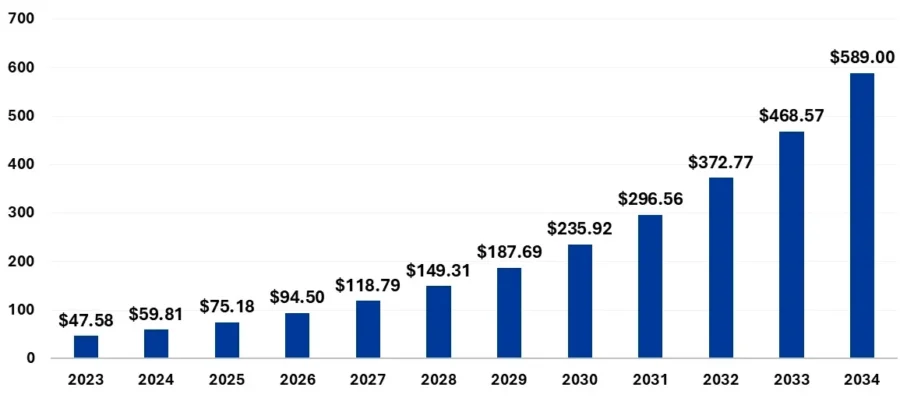
Source: Precedence Research
While AR introduces digital enhancements to the real-world view, VR immerses users in a completely simulated environment. Together, they are becoming indispensable tools in the B2B landscape.
Microsoft leads the innovation race with over 10 000 AR/VR patents, while companies like Meta and Sony continue to invest heavily in optics and device capabilities. By 2030, the AR/VR sector is expected to create over 23 million jobs and contribute USD 1.73 trillion to the economy.
Noteworthy AR & VR Advancements
- Microsoft HoloLens: Used in industries for training, remote assistance, and design visualization, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
- Varjo VR: Offers high-resolution VR headsets designed for professional use in sectors like aviation for pilot training and automotive design.
- PTC Vuforia: An AR platform for industrial applications, aiding in machine maintenance, factory design, and remote collaboration.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: Precedence Research predicts a global AR and VR market size of USD 75.18 billion.
- 2025-2029: Statista expects:
- A yearly growth of 8.97%.
- AR & VR market value to reach USD 62 billion by 2029.
Spotlighting an Innovator: IMMERSIVE HEARING TECHNOLOGIES – Spatial Audio
US-based startup IMMERSIVE HEARING TECHNOLOGIES develops a virtual reality system for hearing aids. It utilizes a proprietary spatial audio rendering algorithm to demonstrate hearing aids to patients in realistic noisy environments. This allows audiologists to place patients in VR simulations of restaurants, churches, or playgrounds, enabling wearers to better understand hearing aid benefits.
Core Technologies Connected to AR and VR
- Computer Vision: Essential for interpreting and interacting with the real world in AR applications, computer vision enables devices to overlay digital information onto the physical world.
- 3D Mapping: This facilitates the creation of three-dimensional models of physical spaces, which is crucial for both AR and VR to create immersive environments.
- Sensors and Cameras: These hardware components are vital for tracking user movements and enabling them to interact with virtual environments.
- Haptic Technology: Novel haptic systems allow users to engage with virtual environments through touch, enhancing the immersive experience.
- Spatial Audio: It provides a three-dimensional audio experience to enhance immersion and deliver a spatially accurate auditory experience.
Explore all trends related to augmented reality and virtual reality.
3. Big Data & Analytics: Transforming Business Insights & Strategy
For businesses today, data is the new currency. Big data and analytics are enabling businesses to translate vast amounts of data into actionable insights and competitive strategies. Through the power of advanced analytics tools, businesses predict market trends, optimize operations, and deliver personalized customer experiences.
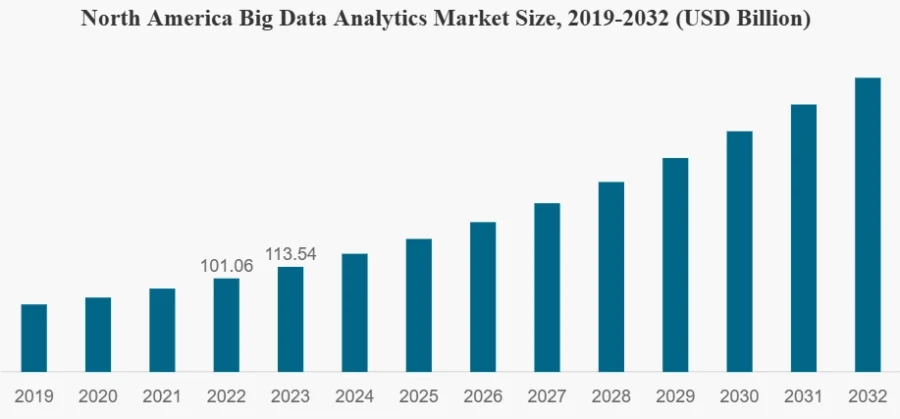
Source: Fortune Business Insights
In 2024, 97.2% of organizations actively invested in big data and AI, with data modernization (migration to cloud-based environments) being a top priority. Significant investments in big data platforms include Databricks raising USD 1.6 billion.
Noteworthy Big Data & Analytics Advancements
- Robust Intelligence: Specializes in ensuring the integrity of machine learning (ML) models from conception to deployment by analyzing data in real-time. Through this, it identifies biases, security vulnerabilities, and other potential issues.
- Spotify: Renowned for its Wrapped feature which provides personalized yearly summaries of listening habits to its users. This feature has evolved to include new elements like Audio Day and categorizing users into one of 16 “listening personalities”.
- Splunk: Known for its solutions that allow searching, monitoring, and analyzing machine-generated big data, in real-time or near real-time.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: Research Nester predicts investment in big data and business analytics will reach USD 323.9 billion.
- 2025-2032: Fortune Business Insights anticipates
- A CAGR of around 13%.
- BDA’s market value is to reach USD 924.39 billion by 2032.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Media Hero – Data-driven Marketing
Brazilian company Media Hero delivers data-driven marketing using big data, AI, and machine learning. Its solution collates data from 17K sources to perform sales and brand results analysis. The insights from this analysis allow brands to plan marketing investment budgets based on per platform, per format, and per region criteria.
Core Technologies Connected to Big Data & Analytics
- Distributed Computing: Crucial for handling vast amounts of data, technologies like Hadoop’s MapReduce allow for data processing across multiple machines.
- Data Lakes: Offering a single repository to store structured and unstructured data, data lakes enable businesses to scale their data analytics needs efficiently.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data to forecast future trends, predictive analytics aids businesses in market analysis, inventory management, and customer behavior prediction.
- Real-time Analytics: Technologies that process data as it’s generated or collected, allowing businesses to make instant decisions based on live data.
4. Blockchain: Revolutionizing Trust and Transparency
Blockchain, often associated with cryptocurrencies, has far-reaching applications beyond digital currency. As a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a network, blockchain offers unparalleled transparency and security. For businesses, this translates to enhanced trust, traceability, and reduced fraud.
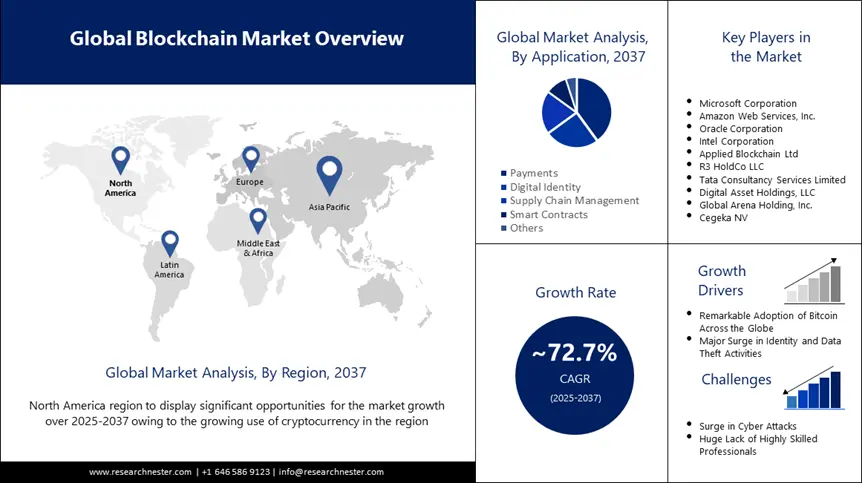
Source: Research Nester
Blockchain’s integration into the financial sector alone is expected to account for over 37% of global blockchain revenue. By 2029, the market is expected to grow exponentially to USD 248.9 billion – driven by increasing adoption in the finance, supply chain, and healthcare industries.
Spending on blockchain technologies is also forecasted to reach USD 18 billion in 2025, fueled by enterprise adoption and Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms.
In 2024, significant investments included JPMorgan Chase processing over USD 1 billion in real-time settlements using its JPMCoin platform and Salesforce integrating blockchain solutions into its ecosystem.
Noteworthy Blockchain Advancements
- Ethereum: Beyond being a cryptocurrency, Ethereum’s platform enables the creation of smart contracts that automate and ensure the transparency of B2B transactions.
- Hyperledger: An umbrella project of open-source blockchains and related tools initiated by the Linux Foundation. It is adopted by various industries for supply chain transparency.
- IBM Blockchain: Catering to businesses, IBM offers solutions ranging from food safety and supply chain transparency to identity verification and fraud prevention.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: Research Nester projects a market size of USD 42.26 billion.
- 2025-2030: It also estimates:
- A compound annual growth of 72.7%.
- Blockchain market value to reach USD 3.13 trillion.
Spotlighting an Innovator: AstraKode – Enterprise Blockchain Development
Italian startup AstraKode offers a low-code enterprise blockchain development platform. It allows businesses to develop and validate private blockchain networks and smart contracts. The platform also pre-built projects to accelerate blockchain development.
Core Technologies Connected to Blockchain
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): The foundational technology of blockchain, DLT ensures that the data is replicated across all participants to bolster transparency and security.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into lines of code, enabling automatic, trustless transactions.
- Cryptography: Ensures data security and participant anonymity, making transactions tamper-proof.
- Consensus Algorithms: Mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) that validate and verify transactions on the blockchain.
Read about all blockchain trends here.
5. Clean Tech: Spearheading a Sustainable Business Future
In an era where we all experience the effects of climate change, clean technology solutions emerge as the beacon of hope for a sustainable future. Beyond environmental preservation, it is revolutionizing the B2B landscape by offering efficient, green alternatives that promise both profitability and eco-responsibility.
Green Technology and Sustainability Market
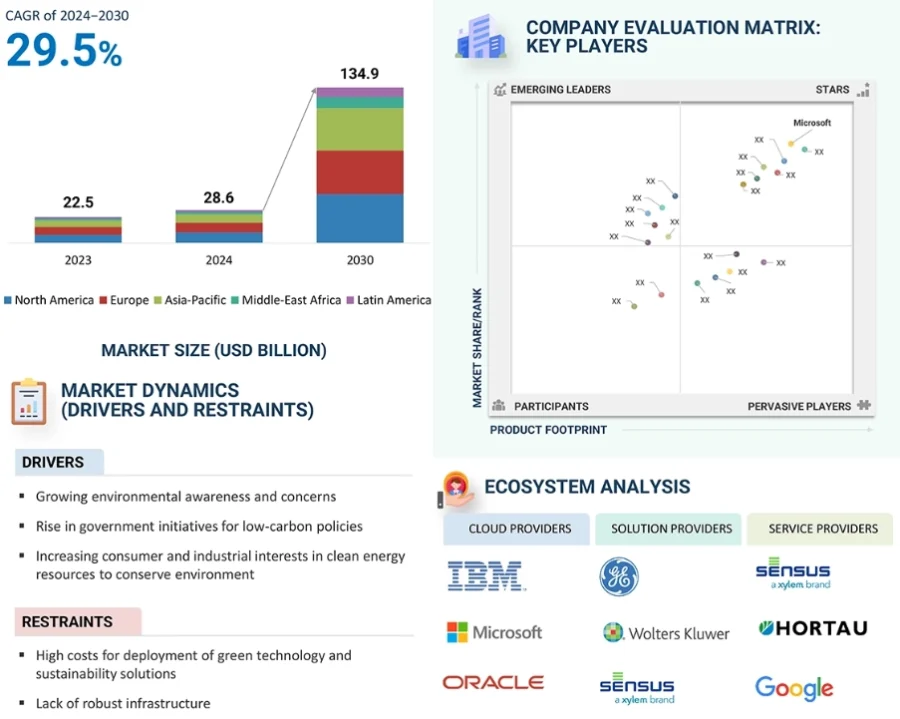
Source: MarketsandMarkets
In 2024, global clean energy investments exceeded USD 2 trillion. Investments in solar PV manufacturing also doubled to USD 80 billion, while battery manufacturing investments grew by 60% to USD 110 billion.
EV sales also grew by 25% in 2024, with over 16 million vehicles sold. This was primarily driven by strong adoption in China and supportive policies worldwide.
Noteworthy CleanTech Advancements
- Twelve: Converts carbon dioxide emissions into sustainable jet fuel using its suitcase-sized electrochemical reactor – O12.
- Commonwealth Fusion Systems: Its proprietary fusion reactor uses 10 000 kilometers of high-temperature superconductor tape to generate carbon-free power.
- H2 Green Steel: The company builds a fossil-free electricity-powered giga-scale electrolyzer to generate green hydrogen as a raw material to produce steel.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: GlobeNewswire estimates a market size of USD 36.6 billion.
- 2025-2030: MarketsandMarkets projects:
- A compound annual growth of 29.5%.
- The green technology and sustainability market will reach USD 134.9 billion by 2030.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Blue Skies Minerals – Direct Air Capture (DAC)
Canadian startup Blue Skies Minerals develops a Carbonated Tailings process for carbon sequestration. The process uses direct air capture to convert CO2 into a solution that is mixed with mining waste rock, forming carbonate minerals that permanently store carbon.
This eliminates metal leaching from mine tailings while providing an environmental benefit. Blue Skies Minerals then sells the resulting carbon credits to companies short of their emission goals.
Core Technologies Connected to CleanTech
- Advanced Material Science: Innovations in material science are crucial for the development of bioplastics, energy-efficient insulations, and new battery chemistries.
- Geospatial Technology: For everything from monitoring deforestation to tracking ice melt and urban heat islands, advanced satellite imagery and geospatial analytics are key.
- Synthetic Biology: This field, combining biology and engineering, is crucial for developments such as lab-grown meat or engineered algae that absorb more CO2.
- IoT and Edge Computing: The integration of Internet of Things devices and edge computing allows for real-time monitoring and management of environmental factors.
Discover all CleanTech and Climate Tech trends.
6. Internet of Things: Connecting the World Seamlessly
The Internet of Things emerges as the fabric binding the physical and digital worlds in today’s hyper-connected age. Seamlessly stitching together devices, people, and processes, IoT is made possible by advancements in connectivity. These technologies are so integral to IoT that they often become synonymous with it.
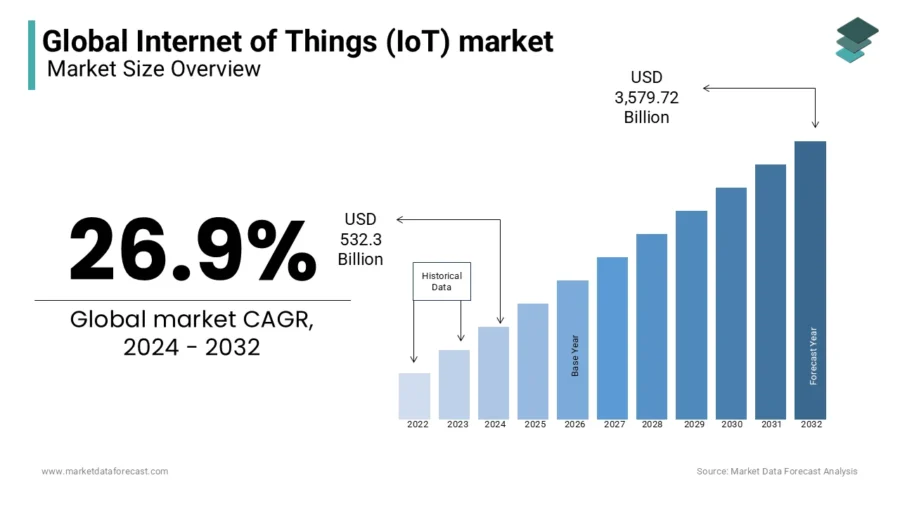
Source: Market Data Forecast
By embedding sensors and software into everyday objects, IoT transforms them into smart entities to gather, share, and act upon data, often autonomously. This interconnected mesh bridges the gap between data collection and actionable insights, crafting a seamless, interconnected business world.
SNS Insider predicts that IoT devices will generate 175 zettabytes of data by 2025. Additionally, the number of connected devices is expected to exceed 75 billion by 2025, compared to 18.8 billion at the end of 2024. This growth is driven by advances in 5G, edge computing, and AI integration.
Significant acquisitions in the IoT space included Synopsys’ USD 35 billion acquisition of Ansys and Siemens’ USD 10.6 billion acquisition of Altair Engineering, reflecting growing interest in IoT platforms and solutions.
Noteworthy IoT Advancements
- Cisco: Leads the way to create smart cities with interconnected traffic systems, energy grids, and public services.
- Verizon 5G: Provides ultra wideband 5G networks low-latency mobile edge computing and real-time status monitoring and business intelligence.
- Siemens: Develops end-to-end industrial IoT solutions for data acquisition, catering to the automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, food, power utility industries, and more.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: Polaris Market Research projects a global market size of USD 1.018 trillion.
- 2025-2032: Market Data Forecast estimates:
- A yearly growth of 26.9%.
- IoT market size to reach USD 3.58 trillion.
Spotlighting an Innovator: PX5 – IoT Operating System
US-based startup PX5 makes PX5 RTOS – an industrial-grade, real-time operating system that features priority-based preemptive multithreading and synchronization. It allows an unlimited number of threads, mutexes, condition variables, and counting semaphores. All inter-thread communication and synchronization primitives have deterministic, microsecond-level response times.
In addition to standard POSIX thread and synchronization APIs, PX5 extends functionality to allow user-controlled memory allocation and naming for threads, mutexes, and condition variables. This enhanced real-time operating system thus enables highly efficient and customizable implementation of multithreaded systems for IoT devices, industrial mobile, and mobile control units.
Core Technologies Connected to IoT
- Connectivity Technologies: Technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, LPWAN, and cellular networks (including 5G) provide the necessary connectivity for data transmission between IoT devices and networks.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing allows data processing closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and bandwidth use. This is particularly useful in IoT settings where real-time processing is crucial.
- Security Technologies: Security technologies, including encryption and authentication, are essential for protecting data privacy and ensuring the integrity and security of IoT systems.
- Application Enablement Platforms (AEPs): AEPs provide a set of middleware capabilities that empower in building and deploying IoT applications, abstracting the underlying complexities.
Explore the recent IoT trends here.
7. Robotics: Advancing Human Capability
As the lines between human capability and machine efficiency blur, advanced robotics emerges at the intersection. More than mere machines, these robots are imbued with intelligence, adaptability, and precision that reshape industries and redefine operational excellence.
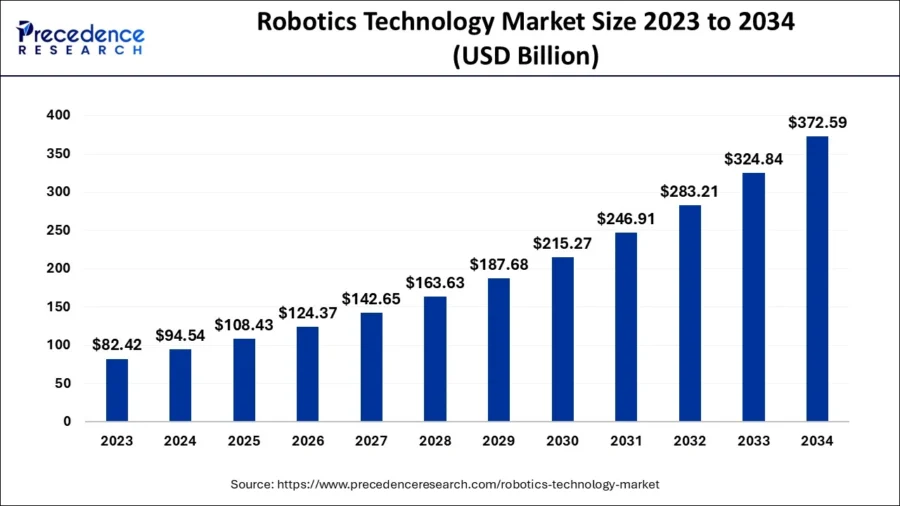
Source: Precedence Research
The global market value of industrial robot installations reached an all-time high of USD 16.5 billion in 2024.
Governments and private sectors are also heavily investing in robotics research and development. For example, India committed over USD 13 billion to industrial robotics research and development as part of its “Make in India” initiative.
Noteworthy Robotics Advancements
- Boston Dynamics: Creates robots with human- and animal-like dexterity. Their solutions automate inspections, site management, warehousing, and more.
- Kuka Robotics: Develops industrial robots for manufacturing operations such as welding, milling, palletizing, assembly processes, and more.
- Formic: Offers Robots-as-a-Service by providing factory and warehouse robots to companies on a rental basis, automating welding, case packing, injection molding, and more.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: Statista expects the revenue in the robotics market to reach USD 50.8 billion.
- 2025-2034: Precedence Research predicts:
- Yearly growth of up to 14.7%.
- Market size to reach up to USD 372.59 billion in 2034.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Progressive Robotics – Robot Automation
Progressive Robotics is a Greek company that provides AI-powered software solutions to automate complex packing and palletizing tasks. Its dense packing software allows robots to efficiently organize items without fixtures and supports a range of objects on production lines.
The software’s teaching-by-demonstration feature allows robots to learn tasks from a single example. This increases productivity while reducing labor and capital investment needs for small and medium businesses (SMBs).
Progressive Robotics also completed a EUR 1.55 million SEED funding round led by Marathon Venture Capital and with the participation of existing investors Genesis Ventures.
Core Technologies Connected to Advanced Robotics
- Machine Vision: Enables robots to ‘see’ and interpret their surroundings, essential for tasks ranging from quality inspection to navigation.
- Sensor Fusion: By integrating data from multiple sensors, robots better understand and interact with their environments.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks: These AI subfields empower robots with capabilities like object recognition, decision-making, and even learning from mistakes.
- Mechatronics: A multidisciplinary field combining mechanical design and electronic control into a unified discipline, essential for the intricate movements and tasks robots perform.
- Cloud Robotics: By leveraging the cloud, robots access vast computational resources, share knowledge with other robots, and benefit from remote processing power.
Explore all top robotics trends here.
8. 3D Printing: Tailoring Tomorrow’s Products, One Layer at a Time
No longer confined to prototyping, 3D printing or additive manufacturing is revolutionizing industries, offering unparalleled customization, and rapidly driving innovation. With its ability to transform digital designs into tangible products, this technology promises accelerated production while reducing waste and catalyzing on-demand manufacturing.
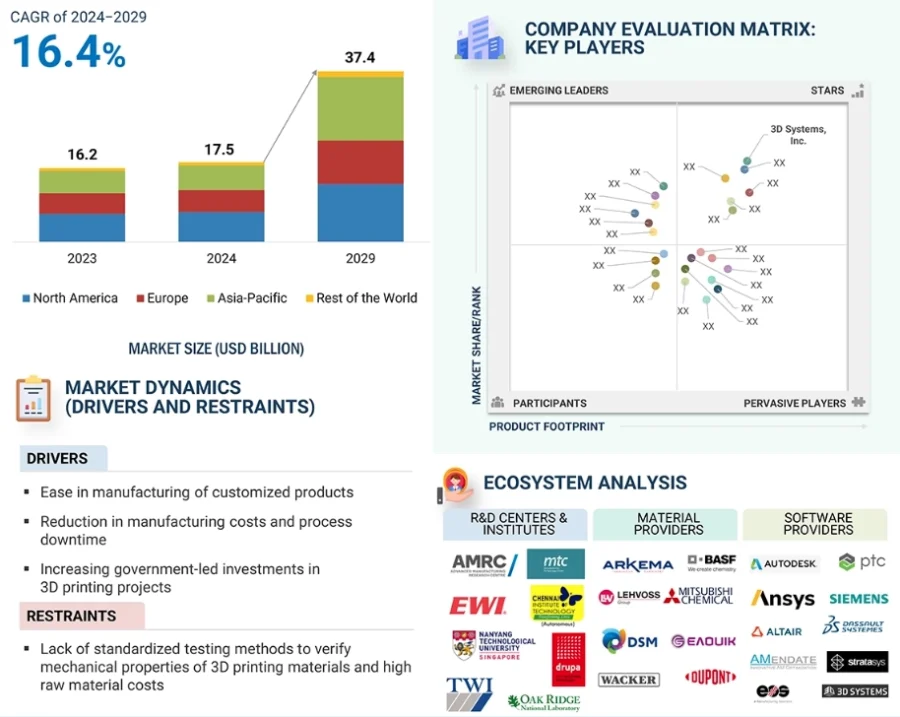
Source: MarketsandMarkets
Entry-level 3D printers under USD 2500 saw explosive growth in 2024, with shipments increasing by 41% year-over-year (YoY). However, industrial systems experienced declines due to high interest rates.
Further, Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid growth due to advancements in automotive manufacturing and healthcare applications. China dominates the entry-level segment with over 94% of shipments under USD 2500 in Q2 2024.
Noteworthy 3D Printing Advancements
- VulcanForms: Uses industrial-scale laser powder bed fusion to manufacture complex, high-value engineered components in serial production.
- Steakholder Foods: 3D prints ready-to-cook cultured meat products by extruding paste materials through a narrow nozzle.
- Sakuu: Leverages multi-material 3D printing to mass produce batteries for agile and modular production while minimizing waste.
Financial Forecast
- 2024: MarketsandMarkets expects a market value of USD 17.5 billion.
- 2025-2032: Fortune Business Insights predicts:
- A CAGR of 23.6%.
- Market value to reach USD 150.2 billion.
Spotlighting an Innovator: a-metal – Affordable Metal 3D Printing
Swiss company a-metal offers a compact and safe entry-level solution for metal 3D printing. Its machine is priced for even small businesses and training institutions to access metal additive manufacturing technology.
The printer also features a small footprint to fit in existing workshops while the simple software interface allows operation without expensive experts. This allows for an affordable and user-friendly metal 3D printing solution without compromising process robustness or part quality.
Core Technologies Connected to 3D Printing
- Stereolithography (SLA): This technique uses UV light to solidify liquid resin layer by layer, suitable for producing highly detailed objects.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Melts and extrudes thermoplastic filament, commonly used for prototyping and simple parts.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Uses lasers to fuse powdered material to create robust and complex structures without the need for support.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA but uses digital light projectors to ensure faster print times.
Read about the top technology trends in 3D printing here.
9. Cloud Computing: Redefining Horizons through the Internet
From startups to Fortune 500 companies, cloud computing has become the backbone of the business ecosystem. Offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, this technology allows companies to access and store vast amounts of data without the need for physical IT infrastructure. This, in turn, transforms how businesses operate and compete in the digital age.
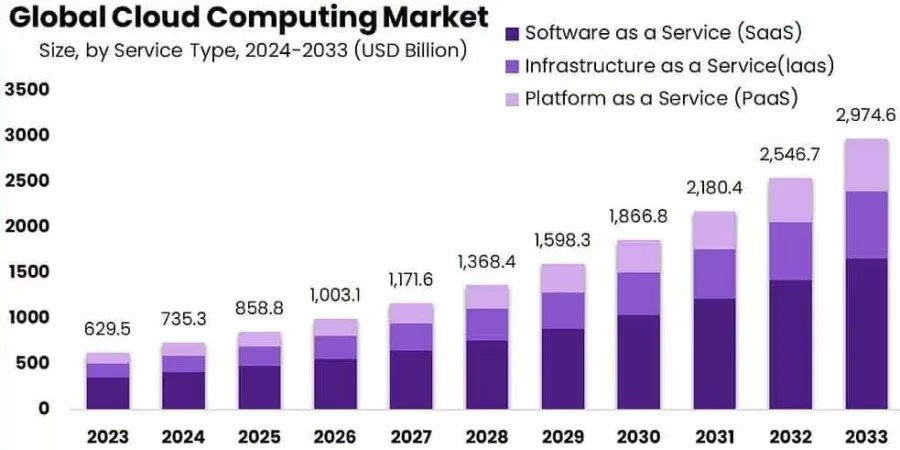
Source: Market.Us
Gartner estimates the end-user spending on public cloud services to reach nearly USD 723.4 billion in 2025. Moreover, approximately 90% of organizations now use some form of cloud computing, with two-thirds operating in public clouds and nearly half adopting private clouds.
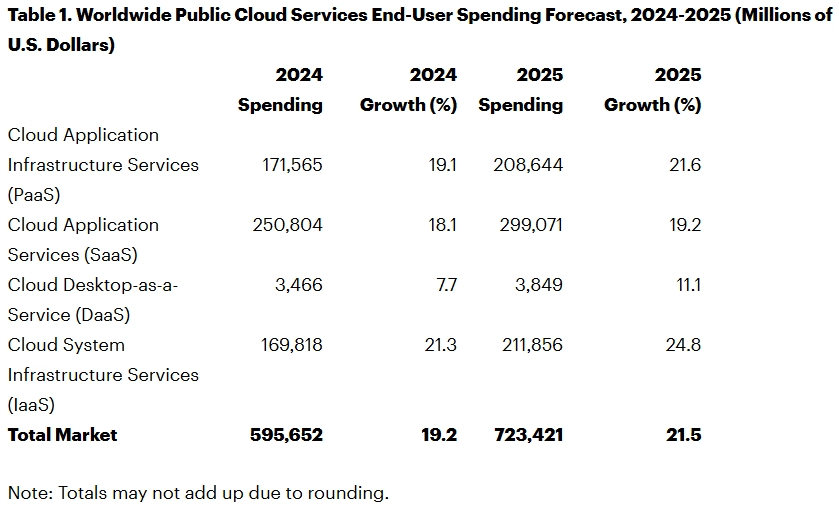
Source: Gartner
Noteworthy Cloud Computing Advancements
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Provides compute power, database storage, content delivery, and other functionality to build applications with flexibility, scalability, and reliability.
- Microsoft Azure: Delivers cloud-based analytics in real-time using data warehousing, big data, and machine learning in the cloud.
- IBM Cloud: Builds a hybrid and open cloud platform to deploy pre-configured, customized security controls, distribute workloads, and improve compliance.
Financial Forecast
- 2025: Market.Us anticipates a market value of USD 858.8 billion.
- 2025-2033: It also forecasts:
- An annual growth of 16.8%.
- Cloud computing market value to reach USD 2.97 trillion.
Spotlighting an Innovator: XeroCodee – Cloud Infrastructure Management
Indian startup XeroCodee enables developers to easily deploy applications across multi-cloud infrastructures from a single dashboard. Its platform automates infrastructure provisioning and application deployments to save developer time.
The platform integrates with common tools like GitHub for continuous integration and delivery. It also allows non-technical founders to rapidly deploy products to market, improving the resilience and scalability of cloud infrastructure.
Core Technologies Connected to Cloud Computing
- Virtualization: At the heart of cloud computing, it allows multiple users to share single physical resources, maximizing efficiency and scalability.
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Tools like Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage enable vast data storage with easy retrieval and durability.
- Cloud Management Platforms: Tools such as RightScale and Scalr offer centralized control over multi-cloud environments, simplifying resource allocation, monitoring, and cost management.
- Cloud Security Solutions: As cloud adoption grows, so does the need for robust security. Such platforms safeguard data and applications in the cloud.
10. Nanotechnology: Harnessing the Power of the Minuscule
Diving deep into the atomic and molecular scale, nanotechnology transforms industries by leveraging the unique properties and behaviors of materials at the nanoscale. This pioneering field revolutionizes everything from medicine to electronics, offering innovations that could reshape the way we live and work.
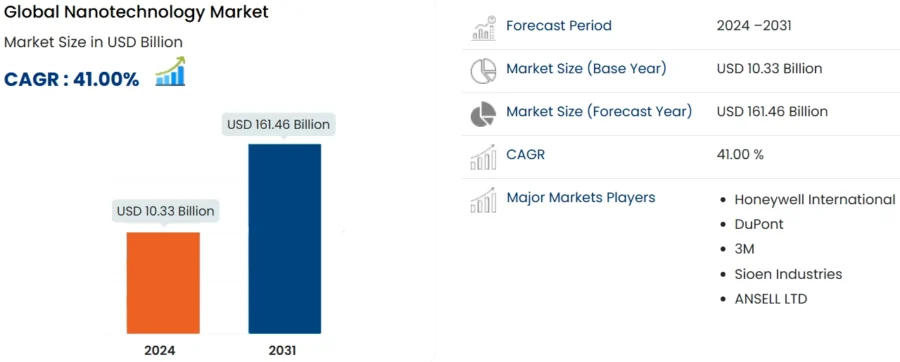
Source: DataBridge
For instance, the US National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) has received over USD 43 billion in cumulative funding since its inception, with a record budget of USD 2.16 billion earmarked for 2024 to support foundational research and commercialization.
Noteworthy Nanotechnology Advancements
- Nanoramic Laboratories: Utilizes nanotechnology in electrodes to increase energy density and faster charging times while removing toxic chemicals in battery production.
- Advanced NanoTherapies: Makes a nanoparticle drug delivery platform that releases two synergistic drugs in-tissue long term.
- Sigma Technologies: Develops nanoscale functional layers for use in materials for thermal management, barrier films, performance pigments, and energy storage devices.
Financial Forecast
- 2024: IMARC Group forecasts a market size of USD 11.4 billion.
- 2025-2031: DataBridge estimates:
- A yearly growth of 41%.
- Market value to reach USD 161.46 billion.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Neptune Nanotechnologies – Bio-Nano Material
Canadian startup Neptune Nanotechnologies manufactures a nano-structured material made from organic ocean waste. Its proprietary technology utilizes chitin nanocrystals found in crab shells to double the strength of materials. Potential applications include biodegradables, adhesives, aerospace composites, 3D printing materials, and biomedical implants.
Core Technologies Connected to Nanotechnology
- Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM): A tool that allows scientists to visualize and manipulate individual atoms, providing an unprecedented understanding of nanoscale materials.
- Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD): A method used to deposit materials one atomic layer at a time, ensuring precise control over nanoscale structures.
- Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE): Enables the growth of highly crystalline films at the atomic level, vital for advanced electronics and optoelectronics.
- Nano-Imprint Lithography: A technique for producing nanoscale patterns, which is essential for the next generation of semiconductor devices.
Explore all nanotechnology trends here.
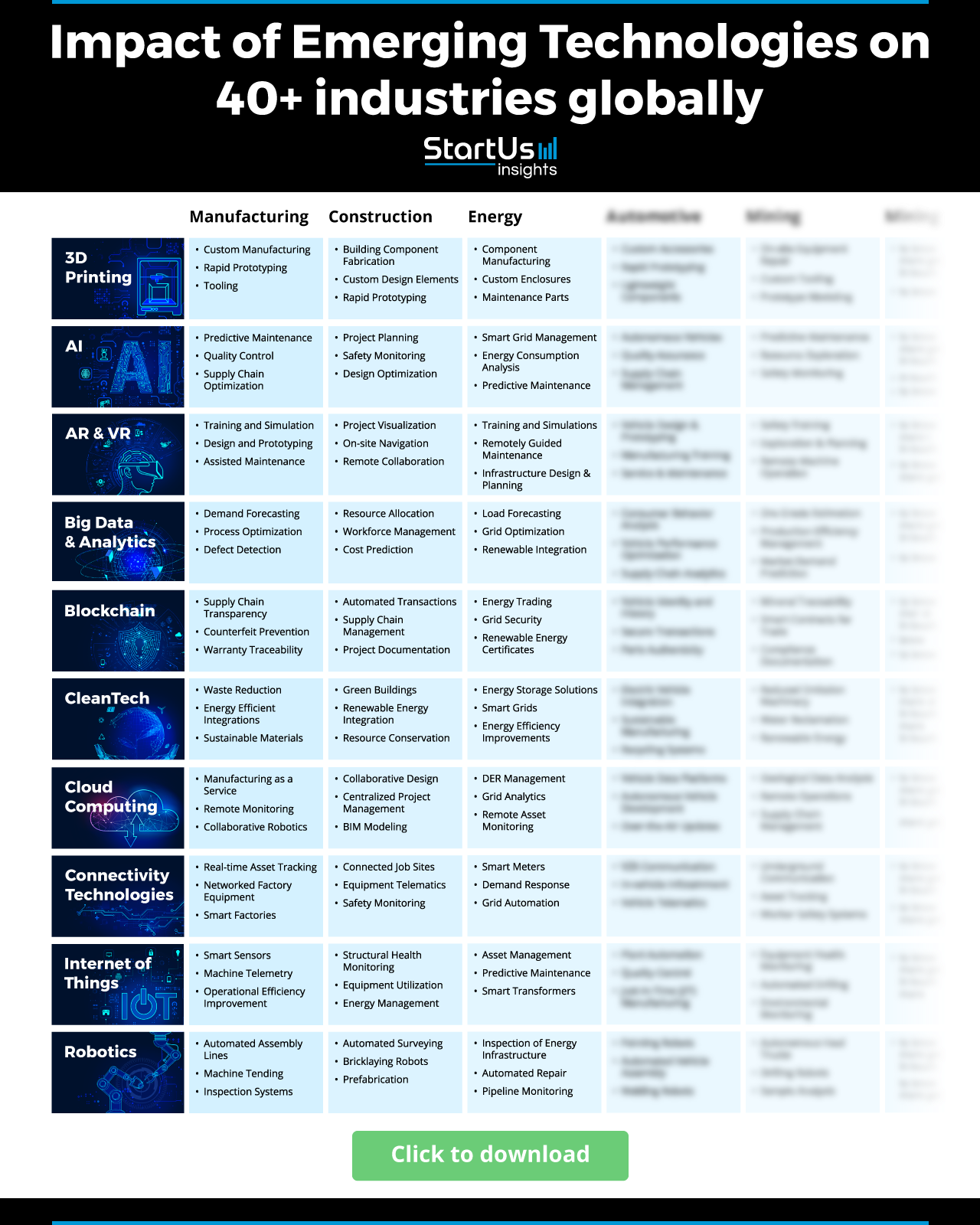
Impact of Emerging Technologies on 43 Industries Globally

Table of Contents
Emerging technologies, once part of science fiction, are now at the heart of everyday applications, streamlining operations and unlocking new potentials. In this section, we take a deeper look into the tangible ways these technologies. We’ll explore how they are revolutionizing sectors – be it heavy industries with their large-scale operations or service industries that define modern consumer experiences.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Heavy Industries
In a world where innovation continually redefines the norm, heavy industries are not exempt from the transformative wave of disruptive technologies. From the sprawling fields of manufacturing to the precise nature of aerospace, technological advances are shaping the way we produce, construct, and operate.
Let’s explore how modern tools and methodologies are sculpting a new era for these vital sectors.
Manufacturing
- 3D Printing: enables rapid prototyping and on-demand production to reduce waste and inventory.
- IoT: allows real-time equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance for improved asset management, enabling smart factories.
- AI & ML: provides automated quality assurance and process optimization to increase production efficiency.
Construction
- Augmented Reality: enhances on-site visualization to accelerate project planning.
- Drones: improve site inspection and topographical mapping for project tracking.
- Robotics: automates labor-intensive tasks to enhance precision and worker safety.
Oil and Gas
- IoT: enables pipeline and refinery monitoring in real-time to enhance visibility.
- Blockchain: empowers secure and transparent transaction trails for increased efficiency.
- Nanotechnology: improves extraction processes and enables advanced materials for better petroleum processing.
Utilities
- Smart Grids: ensure efficient and responsive electricity distribution through interconnected systems.
- AI: improves predictive maintenance and demand forecasting accuracy to optimize energy production.
- Cloud Computing: enables centralized data management to improve data access and analytics capabilities.
Automotive
- AI & ML: drive the advancements in autonomous driving and elevate safety features to enhance road safety.
- Additive Manufacturing: streamlines rapid prototyping and accelerates spare parts production, aiding product development.
- IoT: facilitates vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication to optimize traffic flow.
Mining
- Advanced Robotics: replaces humans for exploration in deep-sea and hazardous environments.
- Big Data: delves into geological and operational data to identify promising exploration sites and optimize processes.
- Drones: conduct aerial surveys and map sites from a bird’s-eye view to improve operational visibility.
Energy
- AI: fine-tunes energy distribution and maximizes storage efficiency by advancing energy analytics.
- Blockchain: offers a transparent platform for peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading, aiding decentralized energy production.
- Nanotechnology: boosts battery storage capacities for prolonged energy retention.
Steel
- 3D Printing: fabricates intricate steel components to accelerate product development while minimizing material waste
- IoT: oversees and refines furnace operations in real-time through remote monitoring to avoid operational disruptions.
- Cloud Computing: enhances supply chain and inventory management efficiency by centralizing data.
Aerospace
- Advanced Robotics: ensures precision in assembly and rigorous quality control required for aerospace equipment.
- AR & VR: modernize pilot training and offer immersive aircraft maintenance simulations to improve safety.
- Nanotechnology: crafts lightweight materials to create flight bodies and increase fuel efficiency.
Railroad
- IoT: provides real-time insights into rail conditions and traffic to improve infrastructure health and traveler safety.
- AI & ML: forecast maintenance needs for locomotives to prevent breakdowns and improve data analytics.
- Augmented Reality: enables assisted maintenance for efficient on-field repairs and streamlines maintenance tasks.
Shipbuilding
- Advanced Robotics: revolutionizes tasks like welding and heavy lifting to improve production efficiency.
- 3D Printing: tailors the manufacturing of intricate components on-demand and ensures timely spare parts supply.
- IoT: monitors ship health and calibrates optimal maritime routes in real-time, enhancing ship safety.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Process Industries
Process industries are known for their role in the production of necessities like chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food products. These sectors, integral to the backbone of global supply chains, are characterized by complex and large-scale production processes.
As such, they are prime candidates for the integration of emerging technologies. From AI optimizing production lines to IoT devices ensuring real-time monitoring and quality control, the impact of these technologies is far-reaching. Explore how these advancements are streamlining operations and catalyzing a new era in the process industries.
Food & Beverage
- IoT: ensures freshness of food products through real-time monitoring of storage conditions.
- Blockchain: increases ingredient traceability from farm to table with tamper-proof data storage.
- AI & ML: analyzes customer tastes and preferences to guide product development.
Chemical
- Nanotechnology: innovates with new materials and catalysts for enhancing production and delivering high-performance applications.
- Big Data & Analytics: uses advanced models to analyze material and production data to optimize reaction outcomes and ensure optimal conditions.
- IoT: safely monitors and controls chemical processes to ensure high-quality production processes.
Pharmaceuticals
- AI & ML: accelerate drug discovery and craft personalized medicine formulations.
- Blockchain: secures transparent supply chains for medication distribution and counterfeit risk mitigation.
- Advanced Robotics: ensures precision in drug synthesis and packaging, delivering high quality in production.
Materials
- Nanotechnology: enhances material properties at the atomic level to expand use cases.
- 3D Printing: facilitates rapid prototyping and testing of novel materials for faster time-to-market.
- IoT: observes material behaviors under diverse conditions to accelerate material design.
Textiles
- AI: forecasts emerging fashion trends and discerns consumer inclinations to ensure a competitive edge.
- Nanotechnology: engineers wear-resistant fabrics and smart wearables that prioritize wearer comfort.
- IoT: promotes sustainable resource utilization during production through real-time process and equipment monitoring.
Semiconductor
- Advanced Robotics: achieves ultra-precision during chip manufacturing to deliver cutting-edge electronics.
- AI & ML: detect faults and maintain stringent quality control throughout the manufacturing process.
- Nanotechnology: pioneers the creation of smaller, more efficient chips for high-performance applications.
Cosmetics
- AI: customizes product recommendations after thorough skin analysis.
- Nanotechnology: refines product formulations for enhanced skin absorption.
- Blockchain: verifies the ethical sourcing of ingredients and increases supply chain transparency.
Water & Wastewater Management
- IoT: monitors water quality and infrastructure in real-time for optimizing processes and resource utilization.
- AI & ML: foresees and manages water usage patterns to identify water-saving opportunities.
- Nanotechnology: enables advanced techniques for water filtration and purification, tackling global water shortage.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Light Industries
The world of light industries, often associated with everyday products and consumer goods, is undergoing a silent yet profound revolution. These sectors, while differing vastly in products, share a common thread: they cater directly to end consumers.
Thus, the stakes are high for innovation, customization, and efficiency. Dive into the myriad ways emerging technologies in businesses are reimagining the fabric of these industries.
Apparel
- AI: provides customized fashion suggestions and facilitates virtual try-ons.
- 3D Printing: accelerates prototyping of innovative fashion accessories, enabling faster development cycles.
- IoT: integrates sensors into smart clothing to simplify health monitoring and they also track manufacturing processes.
Publishing and Printing
- Augmented Reality: enhances print media with interactive experiences for increased audience engagement.
- Blockchain: ensures secure content distribution and robust digital rights management for businesses.
- AI & ML: automate content curation while tailoring content to personal preferences and improving processes.
Consumer Electronics
- IoT: interlinks devices to create a unified smart home environment, thereby enhancing customer experiences.
- AR & VR: are shaping the future of immersive gaming, content consumption, and even online shopping.
- AI: curates personalized user interactions and supports voice-command operations to improve customer engagement.
Medical Devices
- Advanced Robotics: offers precision tools for remote and intricate surgeries, increasing patient safety.
- IoT: facilitates remote patient surveillance by providing real-time health data and thus enabling timely interventions.
- AI & ML: delivers predictive health evaluations based on medical device metrics for prompt medical interventions.
Furniture Manufacturing
- Augmented Reality: provides virtual furniture placements within actual spaces to reduce cart abandonment.
- 3D Printing: crafts customized furniture parts and accessories as well as enables on-demand furniture manufacturing.
- IoT: improves visibility into furniture manufacturing and integrates with furniture to elevate buyer experience.
Leather Goods
- Blockchain: validates the ethical sourcing of leather and enhances supply chain transparency to improve brand trust.
- AI: forecasts design trends and anticipates demand to increase sales.
- Nanotechnology: augments leather with superior durability and resistance to stains, thereby enabling novel product lines.
Jewelry
- 3D Printing: enables tailored jewelry designs and swift prototyping, allowing jewelry brands to make custom designs on demand and quickly.
- AR: offers virtual try-ons and enriches shopping interactions, increasing customer satisfaction.
- Blockchain: certifies the authenticity of gemstones and traces the lineage to improve customer loyalty.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Service Industries
Service industries, recognized as the pillars of modern economies, are where many individuals directly encounter the benefits of emerging technologies. This arena is marked by its focus on consumer interaction, experience enhancement, and efficient service delivery.
In this rapidly evolving environment, emerging technology acts as both a disruptor and an enabler. Let’s explore how these innovations in technology are crafting a renewed vision for each sector within the service industries.
Retail and eCommerce
- AI: offers personalized shopping journeys and product suggestions to increase conversion for brands.
- Augmented Reality: facilitates virtual try-ons and delivers immersive product displays for enhanced customer interactions.
- Blockchain: guarantees transparent supply chains and validates product authenticity by leveraging tamper-free data storage.
Finance
- Blockchain: provides secure transactions, enforces smart contracts, and enables decentralized finance (DeFi).
- AI & ML: detect fraud, aid in risk mitigation, provide investment perspectives, and advance anti-money laundering (AML).
- Cloud Computing: centralizes financial data to increase efficiency and streamline operations.
Logistics
- IoT: provides real-time shipment monitoring and adept inventory oversight for improved decision-making.
- AI: enables predictive analytics for optimal routing and demand anticipation, thereby streamlining resource utilization.
- Blockchain: ensures secure and transparent documentation and contractual agreements to increase compliance adherence and customer trust.
Tourism and Hospitality
- Augmented Reality: showcases interactive tours with detailed overlays to enhance the traveler experience.
- AI: curates personalized travel agendas and delivers virtual concierge assistance, thereby increasing traveler engagement.
- IoT: crafts intelligent hotel spaces tailored for individual guest experiences.
Transportation
- IoT: connects vehicles and sophisticated traffic control systems to manage traffic in real-time and improve road safety.
- AI & ML: advise on predictive upkeep and real-time travel route enhancement, mitigating traffic congestion.
- Blockchain: secures ticketing processes and offers transparent fare structures for improving the commuter experience.
Real Estate
- Augmented Reality: presents virtual property expeditions and intuitive layout visualizations to deliver enhanced buyer experiences.
- Blockchain: affirms transparent property exchanges and precise ownership archives to increase buyer confidence and, in turn, sales.
- AI: analyzes market predictions and evaluates property worth to drive decision-making for real estate investments.
Healthcare
- AI & ML: assists in disease diagnosis, strategizes treatments, and oversees patient health to deliver high-quality healthcare.
- IoT: enables connected wearables that provide comprehensive health insights and distant patient care, enabling remote patient monitoring (RPM).
- Blockchain: protects and ensures transparency in patient archives to advance medical research and enable secure and easy access to patient data.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Interdisciplinary Industries
While many industries can be grouped under broad umbrellas like heavy, process, or service industries, some stand out for their distinct nature and influence. These unique sectors often operate at the intersections of traditional categories, wielding the power to shape everything from our daily lives to global paradigms.
As technology permeates these sectors, it ushers in a blend of innovations tailored to their specific challenges and opportunities. Here, we spotlight five such industries: Agriculture, Biotech, Packaging, Telecom, and Smart Cities, and delve into the transformative power of emerging technologies within them.
Agriculture
- IoT & Connectivity Technologies: allow farmers to optimize crop growth and livestock care, enabling them to leverage precision farming.
- AI & ML: offer insights for pest identification, yield forecasting, and mechanized harvesting – all improving crop and soil management.
- Drones: capture aerial visuals for meticulous crop scrutiny and enable specified pesticide deployment to optimize input application.
Biotechnology
- Nanotechnology: enables targeted drug conveyance mechanisms and refined diagnostics, impacting the pharma and healthcare industries.
- Gene Editing: utilizes CRISPR technology for exact DNA alterations, advancing treatments and investigative studies.
- AI: harvests data-driven discernments for innovative drug discoveries and comprehensive genome mapping.
Packaging
- 3D Printing: pioneers tailored packaging blueprints and accelerated prototyping, enabling cost-effective personalized packages and accelerated product development.
- Nanotechnology: provides intelligent, enduring packaging substrates for packaging companies to make smart packages.
- IoT: enables ingenious packaging strategies that track product freshness and supervise thermal conditions to ensure optimal storage conditions.
Telecom
- 5G and Beyond: amplify connectivity velocities and enable instantaneous data exchanges for data-intensive applications like real-time asset monitoring.
- IoT: interlinks innumerable gadgets, setting the foundation for intelligent metropolises and domiciles.
- Cloud Computing: presents scalable frameworks and utilities while reducing IT burden for the dynamic telecommunication landscape.
Smart Cities
- IoT & Connectivity Technologies: enable interconnected systems spanning traffic, utilities, and public amenities, improving the safety and quality of living.
- Blockchain: promotes transparent governing paradigms and fortified, decentralized databanks to minimize corruption and ensure inclusive governance.
- AI, Big Data, & Analytics: facilitate urban design and upkeep of communal resources as well as enhance instantaneous civic services with real-time analytics.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Navigating the Double-Edged Sword of Disruptive Innovation
While these emerging technologies are driving unprecedented advancements, they simultaneously cast shadows of challenges and ethical dilemmas. Like any powerful tool, these technologies, if wielded without care, present risks that might overshadow their immense benefits.
In this section, we dive into the hurdles that stand before us and the ethical quandaries that compel us to ponder the deeper implications of our technological pursuits.
Challenges
- Integration with Existing Systems: Merging new technologies into current systems often demands substantial adjustments and leads to compatibility issues with legacy systems.
- Skill Gap: As newer technologies emerge, there is a growing demand for skilled professionals. Many industries face the challenge of a skill gap where there aren’t enough qualified individuals to handle novel technologies.
- Security Concerns: The growing number of connected devices increases their vulnerability to cyberattacks and data breaches.
- High Initial Costs: Investing in cutting-edge technology requires a significant financial outlay before any return on investment (ROI) is realized.
- Reliability and Maturity: Not all emerging technologies have been tested at scale, leading to concerns about their reliability and long-term viability.
Ethical Considerations
- Data Privacy: As data becomes the new oil, concerns about who has access to this data, and how it is used, become paramount. Ensuring data privacy and informed consent is crucial.
- Bias and Fairness: AI and machine learning models unintentionally perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Transparency and Accountability: With systems making autonomous decisions, ensuring transparency in how they operate and holding them accountable becomes a significant concern.
- Job Displacement: Technological advancements render certain job roles obsolete, leading to economic and social implications.
- Environmental Impact: While many technologies reduce environmental harm, producing and disposing of tech products have detrimental environmental effects.
Emerging technologies, while holding promise for a brighter, more efficient future, come with their set of challenges and ethical dilemmas. Balancing innovation with responsibility will be the key to ensuring that these technologies benefit society at large without compromising on fundamental values and rights.
The Future Outlook for Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies stand as the vanguard of a new era by enabling novel tools and profound reshaping of industries, societies, and individual lives. Rooted in the convergence of biotech, infotech, cognitive science, quantum mechanics, and nanotech, these technologies are not just incremental enhancements; they are paradigm shifts.
Several themes become evident about the shape and scope of technology of the future:
Ubiquitous Integration
Future technologies won’t stand isolated. They’ll become seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, working in harmony. We’ll see more homes, cars, and entire cities becoming ‘smart’, communicating and operating autonomously to enhance our quality of life.
Hyper-Personalization
Thanks to advances in AI and data analytics, technologies will have a deeper understanding of individual preferences. From healthcare treatments tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup to personalized learning experiences in education, technology will cater to each person’s unique needs and desires.
Sustainable and Ethical Innovations
As environmental and ethical concerns take center stage, future technologies will align more with climate-positive practices. Renewable energy, green transportation, and circular economies will be the pillars of innovation.
Democratization of Technology
Access to technology will become more widespread, breaking down traditional barriers. Innovations in cloud computing and open-source platforms will further ensure that even small enterprises or individuals in remote locations harness the power of high-end technological tools – take ChatGPT and Bard for example.
Emphasis on Human-Machine Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, future technologies will focus on augmenting human capabilities. Advanced robotics, AI, and augmented reality will work hand-in-hand with humans, leading to symbiotic collaborations where both entities play to their strengths.
Resilience and Security
As our dependence on technology grows, so does the need for robust security measures. Future technologies will not only have to be efficient but also resilient against threats to ensure the safety and security of users and data.
The future, with its amalgamation of challenges and opportunities, beckons us to move forward with hope and caution. As emerging technologies pave the way forward, it’s up to us to harness their potential responsibly and ensure a brighter, more inclusive, and sustainable tomorrow.
To Stay Ahead of the Technology Curve, it’s More Important than ever to be Proactive
As you’ve seen, the technology landscape for 2025 is brimming with potential. To make the most of these opportunities, leverage our AI-powered Discovery Platform, designed to simplify your investment journey with actionable insights.
Here’s how you can get started:
- Access Comprehensive Data: Explore over 4.7 million startups and 20 000+ emerging technologies and trends across the globe.
- Filter & Compare: Narrow down startups by technology, location, funding, and more, and compare them based on innovation potential and market fit.
- Make Informed Decisions: Analyze detailed startup profiles, including their products, team, funding history, and market position.
- Engage Directly: Connect with startups or request introductions from our expert team.
Stay ahead of the curve by equipping yourself with the insights that matter. Book a demo today to see how our Discovery Platform empowers you to spot trends early, make confident investments, and lead in the fast-evolving tech world.



![AI in Automotive: A Strategic Guide for Industry Leaders [2025-2030]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/AI-in-Automotive-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)

![AI in Healthcare: A Strategic Guide for Industry Leaders [2025-2030]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/AI-in-Healthcare-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)




