Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
In 2025, water management is evolving to address sustainability, resilience, and efficiency. Water management trends like artificial intelligence (AI) and operational intelligence support real-time decision-making for utilities. The water quality monitoring technologies improve safety and reliability in the water supply.
Advances in sustainable water treatment, desalination, and water reuse have tackled resource scarcity and environmental challenges. Simultaneously, integrated water management and decentralized infrastructure enhance system flexibility and resilience. As digitalization grows, cybersecurity and blockchain solutions enable safeguarding and optimizing critical water infrastructure. These developments guide the future of water management in a world facing climate challenges.
What are the Top 10 Water Management Trends in 2025?
- Artificial Intelligence and Operational Intelligence
- Water Quality Monitoring
- Sustainable Water Treatment
- Water Reuse and Recycling
- Integrated Water Management
- Flood Prevention
- Desalination
- Cybersecurity in Critical Infrastructures
- Blockchain for Water Management
- Decentralized Water Infrastructure
Methodology: How We Created the Water Management Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 7M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our own startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the water management industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the water management innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Trends in Water Management & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Water Management Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 2400+ global startups & scaleups. The Water Management Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the water management industry trends & startups that impact your company.

Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Water Technology Trends
The Tree Map highlights key trends influencing water management in 2025, focusing on innovation, infrastructure resilience, and digital transformation. AI and operational intelligence optimize distribution, detect anomalies, and improve demand forecasting. Blockchain for water management ensures transparent tracking of usage and compliance, while cybersecurity protects critical infrastructure from digital threats.
Further, desalination technologies increase energy efficiency and improve access to potable water in arid regions. Flood prevention systems use advanced sensors and modeling tools to address climate-related risks. Moreover, decentralized water infrastructure supports localized treatment and reuse, especially in underserved or remote areas.

Global Startup Heat Map covers 2400+ Water Management Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 2400+ exemplary startups and scaleups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in Western Europe and India, followed by the United States. From these, 20 promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.
Want to Explore Water Management Innovations & Trends?
Top 10 Emerging Water Management Trends [2025 and Beyond]
1. Artificial Intelligence and Operational Intelligence
The AI in water and sanitation market is set to grow, reaching USD 24.45 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 26.8% between 2024 and 2031.
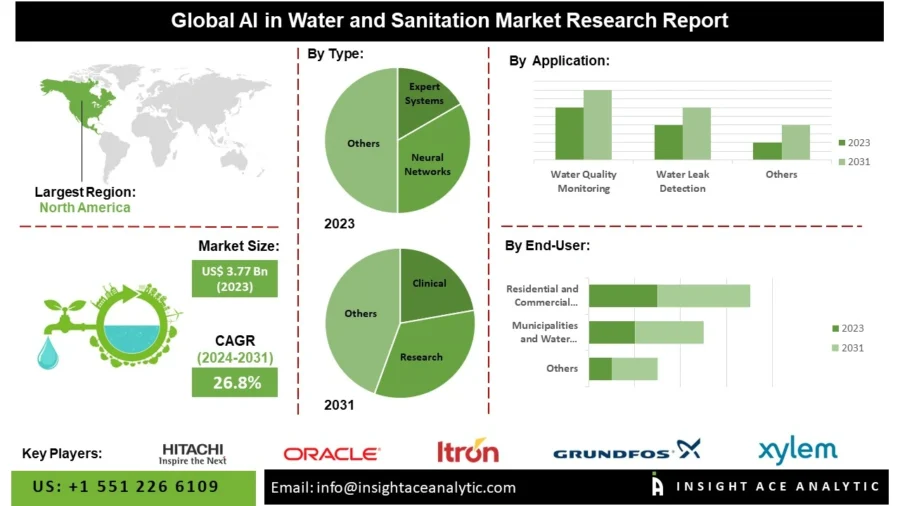
Credit: InsightAce Analytic
In the United States, investments in digital water solutions are projected to increase at 6.5% annually, hitting USD 10.8 billion by 2030. These funds are mainly directed toward metering (41%), network management (20%), and asset management (18%). It underscores a shift toward real-time data and AI-enhanced systems to optimize water operations.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market due to urbanization, industrial growth, and water insecurity, with over 75% of the region considered water insecure. AI adoption is allowing countries to manage scarce resources more efficiently.
Horizon 2020-funded projects in Europe have shown AI’s effectiveness in wastewater treatment. Some regions achieving a 15% improvement in water quality standards.
Besides, AI integration is improving energy efficiency. Predictive algorithms have reduced energy use in pumping stations and treatment facilities by 25%, with further gains anticipated as real-time climate data influences operational models.
Digital twin technologies are also enhancing treatment plants by simulating complex operational scenarios. These systems improve treatment line performance during stress conditions, such as floods or industrial discharge surges.
Also, AI-based predictive analytics strengthens infrastructure resilience. Advanced algorithms detect leaks, fraudulent usage, and equipment failures early to lower repair costs and extend network lifespans.
Further, algorithms adjust water distribution networks to manage consumption peaks and weather-driven fluctuations to reduce waste.
In wastewater treatment, AI ensures compliance with stricter environmental regulations. It automates dosing and control systems, which support sustainable water reuse.
Moreover, real-time water quality monitoring using AI and IoT sensors protects public health. These systems identify pollution plumes, contaminants, and harmful algal blooms quickly to enable timely responses and maintain water safety standards.
MAJI enables AI-Powered Biomass Analysis
Israeli startup MAJI creates an AI-based biomass analysis platform for wastewater treatment plants. It captures and processes microscopic images or videos of activated sludge to enable users to upload content in one step.
The startup’s platform analyzes microbial composition and combines this data with sensor and process parameters to identify potential issues. It continuously monitors trends, provides diagnostics, and recommends operational actions based on detailed analysis.
MAJI operates without additional hardware, offers instant insights from the start, and allows facilities to reduce costs. It also prevents failures and meets regulatory requirements through optimized and proactive treatment management.
Blue Waters offers Intelligent Water Management
Botswana-based startup Blue Waters builds an AI- and IoT-powered platform for monitoring and predicting water quality in real time. It uses data from sensors and algorithms to evaluate physical, chemical, and biological parameters in freshwater systems.
The platform detects mining runoff contaminants early, forecasts sediment pollution events, and monitors bacterial risks to ensure agricultural water safety. Its real-time dashboard displays key metrics, tracks trends, and provides predictive insights using historical and live data.
Blue Waters’ platform includes offline functionality, customizable interfaces, and automated alerts that notify users of potential issues before contamination occurs. It enables informed, proactive decisions to safeguard ecosystems, maintain compliance, and improve access to clean water.
2. Water Quality Monitoring
The global water quality monitoring systems market reached USD 5.67 billion in 2024 and is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2025 to 2030.
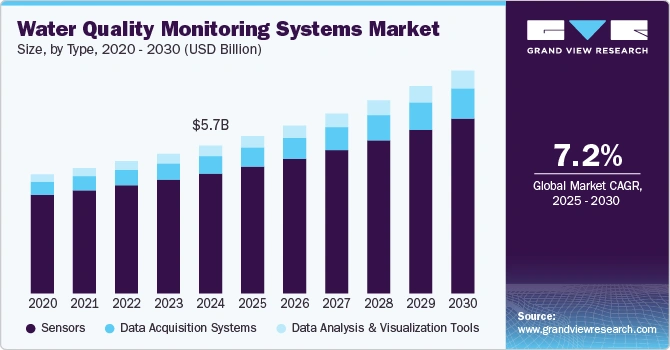
Credit: Grand View Research
Singapore’s Public Utilities Board expanded its Smart Water Assessment Network in 2024 by integrating real-time water quality sensors into reservoirs. These sensors enable authorities to quickly detect contaminants and respond effectively. This initiative reflects a global move toward digitized water surveillance infrastructure that supports public health and ecosystem resilience.
Besides, triboelectric nanosensors (TENS) offer high detection efficiency in portable formats. These sensors play a critical role in monitoring agricultural runoff and urban water distribution networks.
Machine learning algorithms achieve accuracy in forecasting water quality indices and detecting contaminants, including heavy metals, pharmaceuticals, and pesticides, before they reach hazardous levels.
Also, IoT-enabled sensor networks facilitate continuous, centralized monitoring of parameters such as pH, turbidity, temperature, and dissolved oxygen. These networks provide real-time alerts to utility operators for supporting dynamic system responses and ensuring compliance and safety in municipal water systems.
Moreover, remote sensing, combined with fluorescence spectroscopy, is increasingly used in coastal and river basin monitoring. It detects nutrient loading, sediment transport, and harmful algal blooms to offer early warnings to fisheries, tourism operators, and public health officials.
In addition, platforms like the US EPA’s Water Quality Portal enhance data collection and accessibility. The portal supports over 430 million records, informing regulatory actions and policies to enable governments to implement pollution control measures.
Lastly, industrial effluent monitoring systems are being installed at discharge points to detect anomalies in chemical compositions and flow rates. These systems enable the prevention of unauthorized discharges and reduce environmental contamination risks, particularly in industries like mining, chemicals, and textiles.
Olpas builds Concentration Measurement Instrument
Belgian startup Olpas creates ultrasonic sensors for water monitoring, targeting suspended sediment concentration (SSC) and total suspended solids (TSS) in natural and engineered environments. It applies proprietary 3–8 MHz acoustic backscattering technology to measure various particle sizes and provide accurate data with minimal drift.
The startup’s sensors resist (bio)fouling and operate without mechanical wipers to extend maintenance intervals by four to sixteen times, depending on conditions. They support inline and chain mounting, function effectively in direct sunlight, and remain unaffected by water color changes.
Each sensor integrates into IoT and PLC systems via Modbus RTU and consumes little energy. It either runs on battery or solar power. Olpas enables real-time, long-term sediment and solids monitoring in rivers, canals, sewers, overflows, and wastewater treatment plants.
DIAMSENS makes Diamond-based Sensors
French startup DIAMSENS develops diamond-based electrochemical sensors for monitoring water quality in industrial and environmental settings. It uses boron-doped diamond nanocrystals, assembled through automated microelectronics techniques, to create amperometric sensors.
These sensors measure parameters such as free chlorine, bromine, pH, and conductivity. They apply voltage between electrodes to trigger oxidation-reduction reactions, with the resulting current correlating to the target species’ concentration.
They are designed for high sensitivity, provide wide scan windows, low base currents, and consistent accuracy with minimal signal drift, even during long-term use. A patented self-cleaning mechanism activates only when required, maintaining measurement integrity while conserving energy. DIAMSENS enables continuous water quality monitoring in remote and industrial systems.
3. Sustainable Water Treatment
The green water treatment chemicals market is expected to grow from USD 1.70 billion in 2025 to USD 2.25 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 7.2%.
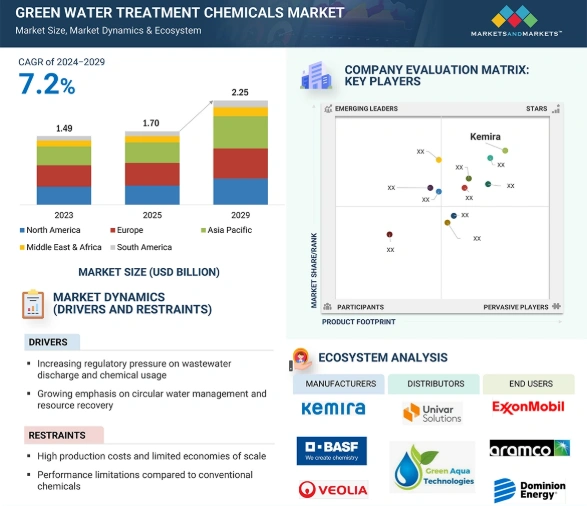
Credit: Markets and Markets
The EU’s Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF) has allocated EUR 13 billion for water-related projects by 2027. These funds aim to enhance treatment capacity, improve resilience to drought and contamination, and expand eco-friendly technologies.
Corporations are also adopting sustainability measures. PepsiCo, for instance, has implemented closed-loop water treatment systems in its manufacturing processes to reduce freshwater use and wastewater generation.
Moreover, thin-film composite and biomimetic membranes are improving desalination performance and energy efficiency. Reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration systems now play a key role in removing salt, heavy metals, and organic compounds in municipal and industrial settings.
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) are increasingly used to break down persistent pollutants such as pharmaceuticals and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. These methods generate highly reactive radicals, which enable water utilities to meet stricter discharge regulations while minimizing chemical use.
Further, biological treatments, like constructed wetlands and bioreactors, offer low-energy, nature-based alternatives. These systems use microbial activity to break down organic contaminants and are effective in decentralized or rural treatment facilities.
Besides, the circular economy is driving water reuse and conservation innovations. Zero-liquid discharge (ZLD) systems are becoming common in industries like textiles, chemicals, and power generation. These systems recover water completely and eliminate pollutants, reducing freshwater use and waste volume.
Municipalities and industrial facilities report up to 30% reductions in sludge generation, along with lower chemical use and improved energy efficiency. These results are encouraging a shift from traditional, chemical-intensive systems to greener alternatives.
WaterWise Technologies builds Ṣustainable Aquatic Drone
US-based startup WaterWise Technologies develops the Manta v1.0, an autonomous aquatic drone for algae prevention and toxin control in natural and artificial water bodies. It uses UV-C LED technology to neutralize algae and harmful microorganisms without chemicals to maintain the ecological balance of ponds, lakes, and reservoirs.
The drone operates continuously, combining round-the-clock water quality monitoring with automated treatment schedules adjusted to environmental conditions. Its design promotes sustainable water care by minimizing reliance on manual intervention and chemical additives. WaterWise Technologies supports communities, agriculture, and recreational sectors in maintaining healthier aquatic systems.
Algaesys advances Bioreactor Wastewater Treatment
Australian startup Algaesys makes a wastewater treatment system that uses algae and phototrophic organisms to purify water and recover biomass in a compact, energy-efficient setup. It starts with tailored pre-treatment based on the influent source, which may include filtration, pH adjustment, or nutrient addition.
The startup’s system exposes algae colonies on rotating logs to controlled light and dark cycles, and creates a stressed state that accelerates reproduction and pollutant removal. This process generates reactive oxygen species, which oxidize persistent organic compounds, eliminate pathogens, and extract nitrogen, phosphorus, and heavy metals.
The detached biomass collects naturally for reuse as flocculants, fertilizers, or animal feed. The system operates within 4 to 8 hours, avoids energy-intensive aeration, and improves resilience to toxic shocks. Algaesys provides a sustainable solution that achieves EU Class C water quality while enabling resource recovery.
4. Water Reuse and Recycling
The water recycling and reuse Market is expected to grow from USD 38.77 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 10.24% between 2024 and 2032.
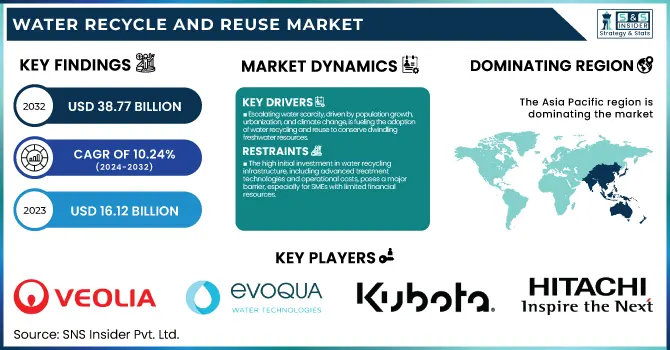
Credit: SNS Insider
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 2024 approved a USD 268 million Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act (WIFIA) loan for the Hampton Roads Sanitation District under the Sustainable Water Initiative for Tomorrow (SWIFT) program. This program aims to recharge the Potomac Aquifer with highly treated wastewater that meets drinking water standards, which marks a shift toward large-scale potable water reuse in the United States.
Adding to this federal initiative, the US Department of Energy (DOE) allocated USD 75 million to the National Alliance for Water Innovation (NAWI) to advance reuse technologies. These advancements include direct potable reuse (DPR) and premise-scale solutions to accelerate decentralized treatment models that enable facilities to reclaim and reuse water onsite.
Technological progress is enhancing system performance. For example, Membrion’s electro-ceramic desalination membranes recover up to 98% of water, making recycling feasible even in high-contaminant industrial settings.
Nanobubble technology, which injects ultra-fine gas bubbles into water, improves contaminant breakdown, restores polluted water bodies, and reduces energy consumption in wastewater treatment.
Further, wastewater treatment plants are transforming into biorefineries, extracting biogas, biopolymers, and nutrient-rich fertilizers from sludge and effluent. This approach improves water reuse rates while lowering greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel dependency.
Treated wastewater is increasingly used for non-potable purposes, such as toilet flushing, street cleaning, park irrigation, and public fountains. In water-stressed regions, these practices are being incorporated into building codes and infrastructure planning.
Moreover, smart rainwater harvesting systems with sensors and automated controls manage rainfall capture based on weather, storage levels, and usage forecasts to minimize loss and maximize efficiency.
In industrial operations, on-site recycling systems are being adopted for cooling towers, boilers, and process water loops. These systems reduce dependence on freshwater sources, cut wastewater discharge volumes, and improve operational resilience, particularly in areas with high water tariffs or strict withdrawal limits.
Nexus by Sweden builds Closed-loop Wastewater Treatment
Swedish startup Nexus by Sweden creates the Compact Nature-based Solution (Compact NbS), a decentralized wastewater treatment system for onsite water regeneration and reuse. It uses a plant-microbial system with two compact circular modules that establish aerobic and anaerobic conditions to speed up treatment through enhanced thermo-hydraulic functions.
The startup’s system replicates natural aquatic ecosystems and works sustainably across various climates with minimal maintenance. Its scalable design supports diverse applications, including homes, farms, car washes, public toilets, and community clusters. This promotes decentralized water security and closed-loop recirculation.
Nexus by Sweden provides an eco-friendly solution that reduces pollutant discharge, replenishes local aquifers, and supports biodiversity. It contributes to water-food security and sustainable community development.
Soluwater facilitates Mobile Water Treatment
Spanish startup Soluwater develops the PW Mobile Reuse Plant, a modular water treatment system that complies with EU Regulation 2022/679 for safe water reuse. It uses multiple oxidation and filtration processes to remove micro-contaminants, including endocrine-disrupting compounds such as 17-ß-estradiol and nonylphenol.
The startup’s plant applies AOP by combining ozone and hydrogen peroxide or ultraviolet light with hydrogen peroxide to produce hydroxyl radicals. These radicals break down persistent pollutants. In addition, ozone oxidation, coagulation, and filtration remove organic matter and oxidized metals. An optional granular activated carbon unit adsorbs any remaining contaminants.
The system includes remote monitoring and automation, which reduces the need for constant supervision and improves efficiency. Soluwater offers a scalable, mobile solution that supports municipalities, industries, and agriculture in delivering safe, high-quality water for reuse while meeting public health standards.
5. Integrated Water Management
Integrated water resources management (IWRM) faces significant global funding challenges, with 85% of countries reporting insufficient financial resources.
This gap restricts institutional development and limits the construction and maintenance of critical infrastructure required for equitable and sustainable water management.
Tools such as AI, machine learning, and digital twins are optimizing water systems. AI forecasts demand, reduces non-revenue water (NRW), and improves water distribution.
Whereas, digital twin models simulate real-time water network dynamics that enable utilities to predict and address leaks, pressure issues, and chemical dosing more effectively.
In wastewater treatment, AI-enabled systems have reduced energy use, with further improvements expected as live climate data integrates into operations.
Further, the use of IoT sensors has transformed real-time monitoring in both municipal and agricultural systems. These sensors track parameters like pH, turbidity, and pressure, which allows quicker responses to contamination and improves hydraulic efficiency.
Smart irrigation technologies are also gaining traction, particularly in water-scarce regions. Centralized platforms now automate irrigation schedules using soil moisture and weather forecast data, conserving water.
Agriculture, which accounts for over 70% of global freshwater withdrawals, benefits significantly, and urban landscapes are also seeing efficiency improvements.
Besides, multilateral funding continues to support IWRM in developing economies. In Karnataka, India, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) approved a USD 150 million multi-tranche financing facility for urban water infrastructure. Of this, USD 75 million will go to Tranche 2 in 2025, focusing on resilience-building in coastal towns like Mangalore and Udupi.
In Sri Lanka, the Green Climate Fund (GCF) committed USD 54.27 million to restore ancient irrigation networks across three river basins, with USD 6.59 million disbursed in 2024 to begin infrastructure rehabilitation aimed at improving climate resilience.
AdeptAg offers Precision Irrigation Systems
US-based startup AdeptAg provides irrigation solutions to optimize water management in controlled environment agriculture. Its systems include boom irrigation, drip irrigation, and nutrient management technologies for precise water and nutrient delivery to plants.
Its boom irrigation systems, such as the Dual Rail Watering Boom, achieve uniform water distribution to improve crop consistency. Drip irrigation systems focus on the root zone to reduce water and nutrient waste while lowering labor requirements.
Further, nutrient management tools, like the Cyclone Pump Set, deliver fertilizers accurately through computer-controlled injection for reducing errors and maintaining consistent plant nutrition.
AdeptAg enables growers to improve yields, enhance crop quality, and use water efficiently, which supports productive agricultural operations.
AIAQUA makes Integrated Water Supply Systems
Italian startup AIAQUA develops a platform to manage small- and medium-scale water distribution systems. It offers AIDESK, a GIS-based PC viewer that consolidates system details, including memos, remote control data, network elements, reports, and recommendations.
The startup’s AIDAS dashboard enables real-time system monitoring through sensor data and an alarm system. It provides a clear aqueduct scheme and integrates measurement and control inputs.
Its mobile app, AIAPP, extends these features to the field by allowing users to view distribution networks, capture images and memos, and receive alerts remotely. AIAQUA also supports utilities with consulting services, such as criticality assessments, sensor strategies, water loss evaluations, and energy use optimization.

6. Flood Prevention
The global flood barrier market is projected to reach USD 2.63 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 9.1%.

Credit: The Business Research Company
Rising climate risks and extreme rainfall events are driving investments in flood resilience. Countries are increasingly incorporating green infrastructure and digital forecasting into their flood defense strategies.
For example, Wales has allocated GBP 77 million (USD 97 million) for the 2025–26 fiscal year to protect over 4640 properties. The funding supports 23 natural flood management projects, using nature-based approaches like wetland restoration and reforestation.
Similarly, New Zealand committed USD 200 million in 2024 for 42 flood resilience projects, including stopbank upgrades and riverbed clearing, funded in collaboration with regional councils.
Moreover, Google’s flood forecasting API delivers more accurate inundation maps and early alerts compared to traditional models like GloFAS.
Tools like aquaFLOOD by Vassar Labs analyze real-time hydrological data using machine learning to offer infrastructure managers dynamic flood forecasts and risk alerts.
Besides, smart flood barriers with IoT sensors are increasingly used in urban centers for automating deployment based on rising water levels. These systems shorten response times and reduce property damage from flash floods.
Meanwhile, Denmark’s Green Climate Screen, which uses willow panels and gravity-fed systems, provides an energy-efficient alternative to pump-based drainage.
In addition, sponge city principles, such as permeable pavements and green roofs, reduce surface runoff and recharge aquifers.
Also, research indicates that planting 1.3 million trees in cities could capture up to 7 billion cubic meters of rainwater annually to ease the load on stormwater systems.
Dutch Water Prevention builds Flood Defense Systems
Dutch startup Dutch Water Prevention develops temporary flood defense systems to protect against water ingress in various environments. Its BoxBarrier system uses interconnected, water-filled containers to form temporary dams or elevate dike crests. It prevents flooding by relying on water’s weight to counteract rising levels.
The startup’s TubeBarrier features a flexible tube filled with water to create a self-stabilizing barrier held in place by water pressure on a front flap. Further, RapidH2O combines a rigid frame with lightweight, water-filled tanks to provide resistance to debris and enable use in flooded areas or during flash floods.
The Dam Easy flood barrier includes a pneumatic pump action seal for quick installation without specialized tools. It offers immediate protection for doorways and large entrances. Dutch Water Prevention supports flood preparedness and strengthens resilience for communities and infrastructure.
ManholeMetrics develops Wastewater Networks
US-based startup ManholeMetrics designs an IoT solution for wastewater monitoring, combining the ManholeMonitor sensor and Porthole analytics platform. The ManholeMonitor installs in a few minutes without confined space entry, using standard tools and a mobile app that guides setup while collecting site data.
It operates as a self-contained unit with a built-in battery and antenna to offer mounting options such as a universal stainless steel bracket, strapping, or magnetic attachment under hinged manhole covers.
Once deployed, the sensor tracks wastewater levels and sends real-time and predictive alerts through the Porthole platform, which functions independently without external systems. The platform provides level and rate-of-change alerts and offers predictive insights into flooding, blockages, infiltration and inflow (I&I), and silt accumulation using historical data and rainfall trends.
ManholeMetrics allows operators to manage sanitary, stormwater, and combined systems efficiently to ensure responsiveness and environmental compliance.
7. Desalination
The global water desalination plant equipment market was valued at USD 41.95 billion in 2024 and is expected to exceed USD 109.42 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.06% during the forecast period.
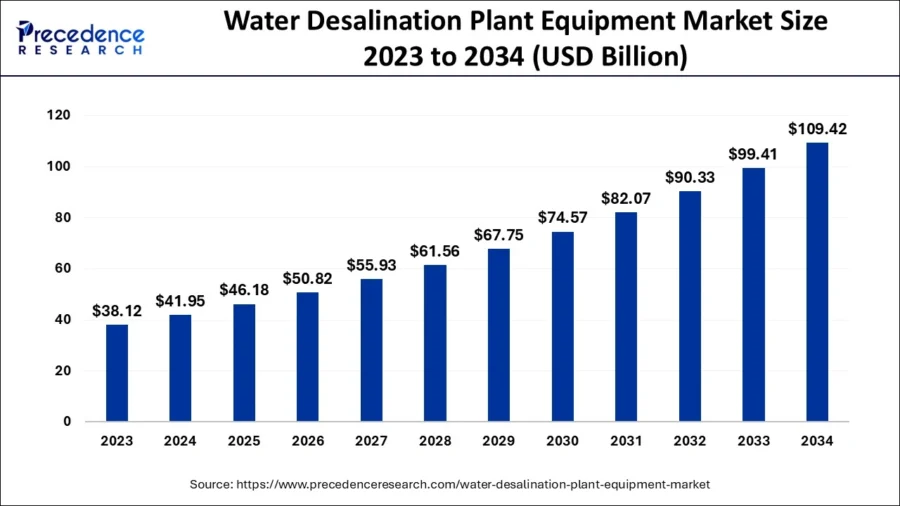
Credit: Precedence Research
In 2024, the Middle East and Africa accounted for 52.95% of the market share, reflecting the region’s reliance on desalination for water security.
Infrastructure investments support this trend; for instance, the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) allocated USD 10.9 billion to water and electricity projects, including substantial funds for expanding desalination capacity.
Reverse osmosis (RO) remained the dominant technology in 2024, representing 77% of the market due to its cost-effectiveness and energy efficiency. Advances in graphene-based membranes and nanofiltration systems are improving water recovery rates and reducing energy consumption.
Moreover, solar-powered systems are being deployed in off-grid and remote areas to treat saline groundwater and seawater, while wind-powered RO units are gaining popularity in coastal regions.
Circular economy models are creating new opportunities. Brine, a by-product of desalination, is now mined for minerals such as lithium and magnesium, adding economic value and reducing waste. It aligns desalination efforts with resource recovery and sustainability goals.
Further, IoT systems provide real-time monitoring of salinity levels and energy consumption, while AI-powered predictive maintenance minimizes downtime and extends equipment lifespans.
Desalinated water remains vital for municipal water supplies, providing clean drinking water in water-scarce regions like the Middle East and North Africa.
Industrial sectors, including power generation, semiconductors, and pharmaceuticals, are also increasingly dependent on ultra-pure desalinated water, which underscores the market’s importance across diverse applications.
Flocean builds Subsea Desalination Systems
Norwegian startup Flocean provides subsea desalination systems that use natural hydrostatic pressure at depths of 400 to 600 meters to drive reverse osmosis. This approach lowers energy consumption compared to traditional methods.
The system accesses deep ocean layers with low biomass to reduce biofouling and minimize pre-treatment needs, cutting operational costs and improving efficiency.
Each modular pod produces up to 5000 cubic meters of freshwater daily, with the capacity to scale up to 10 pods to meet varying needs. Subsea placement decreases coastal land use and avoids chemical discharge.
Flocean provides municipalities, industries, and agricultural operations with a sustainable and cost-effective solution to address water scarcity.
INOSEP facilitates Membrane-based Desalination
South Korean startup INOSEP develops membrane-based technologies for water purification and medical applications using polymer nano-structure control and hollow fiber membrane manufacturing. Its membranes provide precise filtration for household water systems, wastewater treatment, seawater desalination, semiconductor processes, and clinical environments.
The startup produces organic polymer membranes, including polyamide, PVDF, and polysulfone, as well as inorganic ceramic and metal membranes. Each type offers specific advantages in chemical resistance, heat tolerance, and filtration capability.
INOSEP’s innovations include high-purity water systems for hospitals and laboratories, along with portable medical-grade water purification devices for dialysis and other healthcare applications.
8. Cybersecurity in Critical Infrastructures
The global industrial cybersecurity market is expected to grow from USD 17.3 billion in 2024 to USD 45 billion by 2035, with a CAGR of 9.08% during the forecast period.
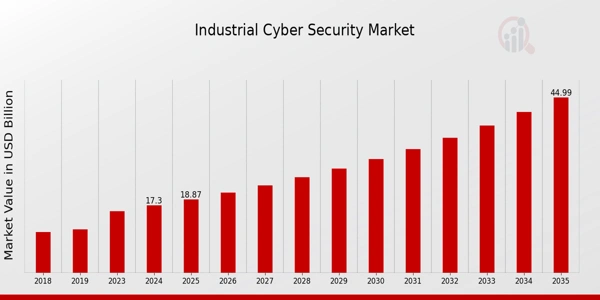
Credit: Market Research Future
The major breaches in 2024 exposed vulnerabilities in water utilities. Southern Water in the UK faced a data breach in February, compromising sensitive employee and customer records.
In the US, an October attack on American Water disrupted operations and raised concerns about water distribution system security.
Similarly, a September cyberattack on Arkansas City’s water treatment facility forced a shift to manual controls, highlighting the severe risks of operational technology (OT) disruptions.
A 2024 US EPA assessment identified critical cybersecurity flaws in 97 drinking water systems serving 26.6 million people. To address these issues, 60% of US water utilities announced investments in technologies such as network segmentation, endpoint monitoring, and real-time threat intelligence systems.
The State and Local Cybersecurity Grant Program allocated USD 280 million to protect critical infrastructure.
Further, the adoption of AI and IoT is becoming standard in cyber-physical systems. For example, Schneider Electric’s SCADAPack controllers now incorporate IT-grade tools like multi-factor authentication, which enables utilities to integrate modern identity verification into legacy OT systems.
Zero-trust architectures are gaining momentum across industrial sectors. These architectures emphasize real-time monitoring, network segmentation, and strict access controls, limiting lateral movement during breaches. Even if attackers compromise one segment, they cannot easily access critical operations.
Government agencies, including the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the EPA, are encouraging the convergence of IT and OT protocols. For instance, integrating tools such as Syslog for event logging and Active Directory for access control improves visibility, accountability, and audit trails across industrial control systems.
CQR provides AI-powered OT Cybersecurity
Saudi Arabian startup CQR develops AI-driven cybersecurity solutions for OT systems in critical infrastructure. The proprietary CQR Platform continuously monitors OT assets using real-time data from specialized sensors. It detects vulnerabilities and addresses threats through a managed security operations center, which provides rapid alerts, incident reporting, and 24/7 support from OT security experts.
The platform applies machine learning for proactive threat detection, offering customized intelligence feeds and trend analysis tailored to industrial control systems. CQR serves sectors like water treatment facilities, where cybersecurity ensures public safety and reliable service delivery.
Trustcore Technologies advances Anomaly Detection
Canadian startup Trustcore Technologies develops Trustcore BA, an AI-powered behavioral analytics platform to secure OT environments and IIoT infrastructure from cyber threats and system failures. It analyzes network traffic, control signals, and telemetry data to detect deviations from learned operational patterns to enable real-time identification of anomalies in systems such as SCADA, PLCs, and smart meters.
When irregularities are detected, the system provides root cause analyses, actionable alerts, and incident diagnostics through an integrated dashboard, which allows rapid response and supports preventative maintenance. Its containerized design enables easy deployment without additional hardware, while Zero Trust Architecture protects against threats such as DDoS attacks and ransomware.
Trustcore BA also facilitates secure provisioning, device management, and telemetry monitoring to improve visibility and reduce downtime across critical sectors, including water and utility networks. Trustcore Technologies safeguards connected assets, such as valves, actuators, industrial gateways, and wireless sensor networks, and allows operators to maintain operational continuity, enhance output quality, and protect public infrastructure from emerging cyber-physical risks.
9. Blockchain for Water Management
The global blockchain market is expected to reach USD 465.29 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 45.2% between 2024 and 2032.
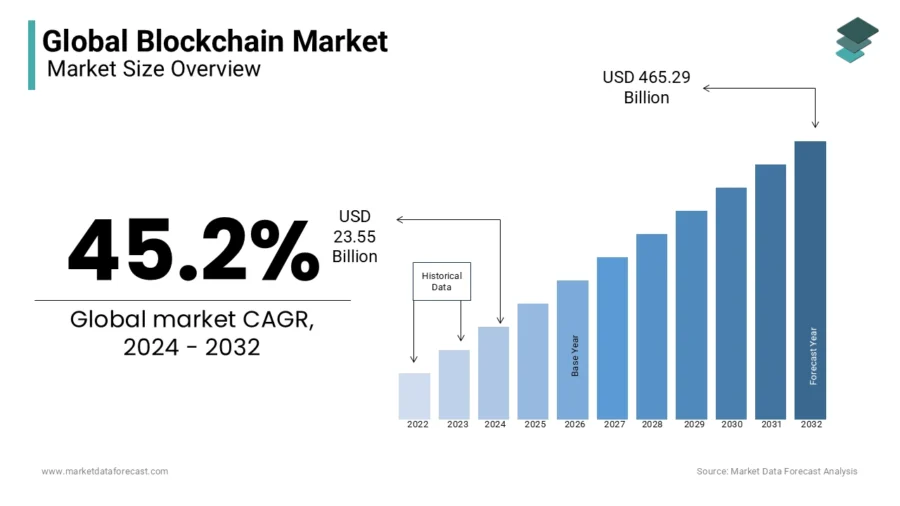
Credit: Market Data Forecast
In China’s Yellow River Basin, blockchain is used to manage water rights trading. It creates transparent, immutable records that reduce conflicts and improve resource allocation in water-scarce regions.
Blockchain-enabled IoT systems are increasingly used for real-time monitoring of water quality indicators, including pH, turbidity, and total dissolved solids (TDS).
These systems provide secure and traceable data flows to enable quick identification and resolution of water quality issues. Automated smart contracts further improve governance by enforcing agricultural water quotas based on predefined rules. This reduces disputes and ensures regulatory compliance.
In addition, tamper-proof records of water quality across supply chains enable stakeholders to identify pollution sources and hold responsible parties accountable.
In Dubai, the DEWA uses blockchain to trace desalinated water from production to end users, increasing transparency and public trust.
For water rights management, blockchain securely tracks ownership, transfers, and consumption, ensuring equitable access and accountability.
Similar principles apply to water quality monitoring, where blockchain platforms store compliance data from treatment plants, distribution networks, and end-user locations. This improves adherence to environmental regulations and enables faster responses to health or contamination incidents.
RiverPulse facilitates Blockchain-powered Water Monitoring
French startup RiverPulse creates a real-time water quality monitoring system that enables communities to track river health. The system relies on devices built from components, such as ESP32 microcontrollers, TDS sensors, and DS18B20 temperature sensors. These measures key parameters like total dissolved solids and water temperature.
These sensors transmit data continuously to a blockchain-secured platform to ensure transparency, traceability, and accessibility. The project’s open-source framework allows users to contribute to development. It also allows for replicating the system, or adapting it for local use by accessing schematics and source code through GitHub.
RiverPulse also includes a token-based incentive mechanism to encourage participation from local data collectors, which expands monitoring reach and promotes environmental stewardsh
ip. It supports informed decision-making and better protection of freshwater ecosystems.
LAKE develops Real World Asset (RWA) Ecosystem
Swiss startup LAKE builds a blockchain-based platform featuring the LAK3 token to decentralize and democratize the global water economy. The platform uses real-world asset tokenization to connect water sources directly to consumers through the spring-to-consumer (S2C) model, which eliminates intermediaries and simplifies distribution.
In addition, the community-to-business (C2B) model allows individuals to participate in large-scale water sales. It broadens access to economic opportunities typically reserved for institutions.
The LAKE Launchpad lets LAK3 token holders invest in global water projects to offer equity and potential dividends. Through its Water Shop Web3 platform, users are able to directly purchase water volumes from natural springs for improving supply chain transparency and traceability.
10. Decentralized Water Infrastructure
The global decentralized wastewater treatment market is projected to reach USD 2 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7% from 2024 to 2032.

Credit: Business Research Insights
The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) allocated USD 5 million through its Rural Decentralized Water Systems (DWS) program to fund household water well systems and decentralized wastewater technologies. These initiatives focus on energy efficiency, water reuse, and system resilience, especially in rural areas without centralized infrastructure.
In addition, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) and Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) are channeling billions of dollars into modernizing water systems, including decentralized treatment, to address lead contamination, emerging pollutants, and climate adaptation.
Technological advancements are driving deployment, particularly in remote or off-grid areas. Containerized treatment plants offer modular, scalable options that reduce installation time and costs.
For example, Biozone Manufacturing’s nanofiltration system treats hard water at 12 kiloliters per hour using an eco-friendly process. It reduces reliance on conventional salt-based methods.
IoT-enabled sensors embedded in decentralized systems provide continuous data on water quality parameters like turbidity and pH. These sensors allow operators to meet regulatory requirements and lower maintenance costs by enabling predictive responses to system issues.
Moreover, in Peshawar, Pakistan, a UNICEF-backed Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System (DEWATS) serves 75 households. It treats wastewater for agricultural reuse to reduce reliance on overdrawn groundwater resources.
Tellus Habitat builds Decentralized Sewage Treatment Plants
Indian startup Tellus Habitat designs the R3H2O system, a sewage treatment solution that recycles wastewater for reuse. The system features an automatic, plug-and-play design with polypropylene modules and aluminum composite panel covers. It is installed either underground or at ground level.
The startup’s system reduces operational costs by eliminating the need for chemical additives and manual oversight. It recovers 97% of wastewater, producing treated water that meets strict standards, including pH values between 7.5 and 8.5, turbidity below 10 NTU, BOD under 10 mg/L, and COD less than 50 mg/L.
Further, the R3H2O system is available in modular configurations ranging from 5 KLD to 1000 KLD. It addresses water contamination risks while supporting water conservation.
SimuGro makes Decentralized Water Systems
Taiwanese startup SimuGro develops systems for controlled environment agriculture. It integrates wireless IoT-enabled modules for water quality monitoring, dosing, flow management, and ozone-based water treatment. Its platform includes the SimuCare Sensor Hub, which supports up to four interchangeable sensors. These sensors measure parameters such as pH, EC, ORP, temperature, ammonia, CO₂, and dissolved oxygen in freshwater and saltwater environments.
Each sensor connects to a BLE-meshed network, syncing with Urban Blue Admin and Urban Blue Assistant for configuration, visualization, and mobile alerts. The platform also includes SimuFlow water flow sensors, dual water level sensors, and SimuValve solenoid valves. For water treatment, Topzone and Coolflow ozone generators use dual ceramic electrode technology to produce up to 25 g/hour of ozone. Data integrates easily into the Urban Blue web and mobile interfaces.
SimuGro’s dosing pumps automate nutrient delivery and pH balancing, while AI-enabled computer vision enhances operational insight. The startup allows aquaculture and greenhouse operators to maintain water quality, optimize resources, and support sustainable production.
Discover all Water Management Trends, Technologies & Startups
Water management is evolving through digital innovation and sustainable infrastructure. Technologies like digital twins now simulate water networks in real-time to offer improved system oversight. Smart metering enhances consumption tracking and leak detection, addressing inefficiencies in water usage. Further, advanced membrane filtration improves treatment processes, while edge computing enables faster local decisions in remote systems.
The Water Management Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.
![Dive into the Top 10 Water Management Trends & Innovations [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Water-Management-Trends-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)




![Dive into the Top 10 Utilities Industry Trends & Innovations [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Utilities-Industry-Trends-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)




