Unlike emerging technologies – which are being developed and finding industry adoption – future technologies represent the next step. These future innovations (currently at nascent stages) will significantly improve business workflows, productivity, and worker safety within the next decade or more.
In this report, explore 16 future technologies that are set to advance 40+ industries. For example, see how neuromorphic computing imitates human brain structure and functions to accelerate computing workloads. We will dive into these technologies – outlining noteworthy advancements, financial forecasts, enabling technologies, and an emerging innovator in each field.
This article was last updated in January 2025.

Here is what this extensive report on 16 future technologies across 40+ industries will cover:
- Future Technology Trends: We’ll dive into technologies of the future that make business more productive than ever before.
- Industry Breakdown: How Future Technologies are Impacting Industries
- Heavy Industries: Think large machinery and equipment.
- Process Industries: Sectors like chemicals and food.
- Light Industries: Areas like electronics and apparel fall here.
- Service Industries: This includes sectors like finance and healthcare.
- The ‘Outliers’: Some industries like agriculture and packaging don’t fit neatly into any box but are vital players on the global stage.
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Explore the hurdles and societal questions arising from new technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Top future tech trends are quantum and neuromorphic computing, generative AI, hyperautomation, voice-activated technology, and autonomous vehicles. Other trends include nuclear fusion, battery technologies, synthetic biology, as well as preventative medicine and well-being, climate tech, zero-latency connectivity, and space exploration, among others.
- Impact & Use Cases of Future Technologies:
- Future tech in Heavy Industries: Quantum computing and hyperautomation improve production efficiency while generative AI automates design processes for autonomous factories, real-time process optimization, and sustainable energy integration.
- Future tech in Process Industries: Technologies like neuromorphic computing, synthetic biology, and hyperautomation improve product customization, the development of bio-based products, and enable automated quality control.
- Future tech in Light Industries: Generative AI, hyperautomation, and battery technologies provide rapid prototyping, streamline production lines, enable safer consumer products, and offer personalized consumer goods and automated logistics.
- Future tech in Service Industries: Generative AI, voice-activated technology, and digital trust solutions enhance customer interaction, service personalization, and data security for personalized healthcare treatments, automated financial advising, and enhanced retail experiences.
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Compatibility issues with legacy systems and costly upgrades are the major challenges. Safeguarding data privacy and ensuring bias-free technologies is also important.
How We Researched and Where this Data is from
- Analyzed our 3100+ industry reports on innovations to gather relevant insights and create a master technology-industry matrix.
- Cross-checked this information with external sources for enhanced accuracy.
- Leveraged the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, an AI- and Big Data-powered innovation intelligence platform covering 4.7M+ emerging companies and over 20K+ technology trends worldwide, to:
- Confirm our findings using the trend analysis tool and
- Identify companies for “Spotlighting an Innovator” sections.
Top 16 Future Technology Trends to Watch [2025 & Beyond]

- Quantum Computing
- Neuromorphic Computing
- Generative AI
- Hyperautomation
- Voice-Activated Technology
- Autonomous Vehicles
- Nuclear Fusion
- Battery Technologies
- Synthetic Biology
- Preventative Medicine & Wellbeing
- Climate Tech
- Zero Latency Connectivity
- Space Exploration
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
- Digital Trust Technologies
- Nanotechnology
1. Quantum Computing
Quantum computers solve complex problems beyond the reach of classical computers using the principles of quantum mechanics. They perform calculations at unprecedented speeds and accuracy. This allows logistics, pharmaceuticals, and finance companies to reduce data processing times and improve decision-making.
For example, quantum algorithms optimize routes and inventory levels in supply chain management while cybersecurity teams leverage them to implement quantum cryptography with unbreakable encryption.
Noteworthy Quantum Computing Advancements
- IBM’s Quantum Development: Businesses and researchers access quantum computers through the IBM Quantum Experience. It allows users to experiment with quantum algorithms using a cloud-based platform. Additionally, IBM unveiled its Quantum Roadmap, aiming to scale quantum technology and develop a 1000-qubit system by 2033.
- D-Wave’s Quantum Annealing: Specializing in quantum annealing, the company provides quantum computing systems to solve optimization and sampling problems. Its quantum annealer, the D-Wave 2000Q, has been used by Volkswagen to optimize traffic routing in congested urban areas.
Financial Forecast
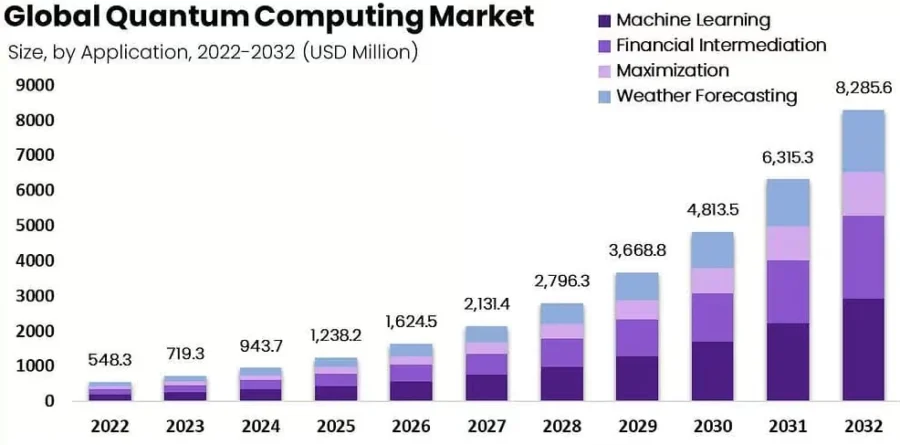
Source: Market.Us
- 2029: MarketsandMarkets predicts a market value of USD 5.3 billion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.7%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: QPerfect – Virtual Quantum Computer
QPerfect is a French startup that offers a virtual quantum computer to enable large-scale fault-tolerant computing. It allows researchers and developers to benchmark quantum hardware, create and test new algorithms, and develop quantum error correction codes.
Core Technologies Connected to Quantum Computing
- Quantum Error Correction: Quantum error correction is a suite of techniques that protects quantum information from errors due to decoherence and other quantum noise. This technology is essential for building reliable and scalable quantum computers.
- Cryogenic Engineering: Quantum computers require extremely low temperatures to function, often close to absolute zero (-273.15°C or -459.67°F), to maintain the quantum states of their qubits. The development of cryostats and other cooling systems is crucial to minimize quantum decoherence and ensure stable operations.
- Quantum Algorithms: These algorithms take advantage of quantum computing’s unique capabilities, like superposition and entanglement, to perform calculations more efficiently than classical algorithms. Prominent examples include Shor’s algorithm for integer factorization and Grover’s algorithm for database searching.
2. Neuromorphic Computing
By imitating human brain neural structures and functionality, neuromorphic computing handles complex, sensory-driven tasks with greater efficiency than traditional computing architectures.
The technology provides substantial benefits for businesses, particularly in sectors that necessitate adaptive learning and rapid data processing. This includes robotics, autonomous systems, and real-time analytics.
Noteworthy Neuromorphic Computing Advancements
- Intel’s Loihi Chip: It is a neuromorphic research chip that simulates neurons and synapses to enhance the efficacy of intricate tasks such as adaptive learning and pathfinding. It demonstrates a significant reduction in power consumption compared to conventional chips.
- IBM’s TrueNorth Processor: In an energy-efficient manner, IBM’s TrueNorth utilizes a network of neurons and synapses to execute pattern recognition, sensory processing, and decision-making tasks. It plays a critical role in the advancing applications that necessitate real-time processing, like speech recognition and computer vision.
Financial Forecast
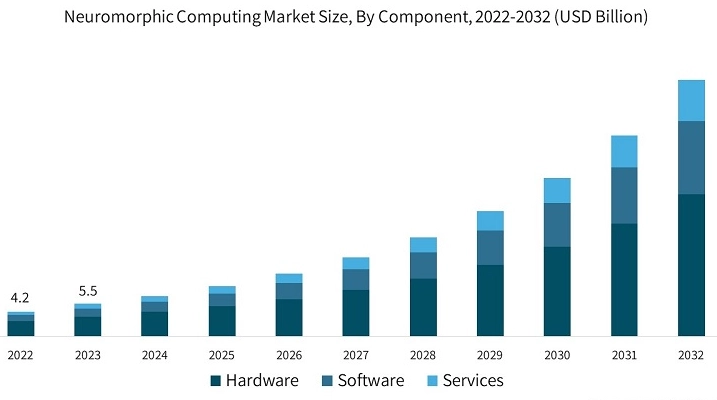
Source: Global Market Insights
- 2032: Global Market Insights forecasts a market value of USD 42.5 billion, with a CAGR of 25.5%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: ViVum Computing – Biological Intelligence
US-based company ViVum Computing provides biological intelligence for scalable AI. The company combines liquid time-constant networks (LTCs), reservoir models, continuous-time recurrent neural networks (CTRNNs), and ordinary differential equations (ODEs) to create AI systems.
They map human-like perception and decision-making to improve the performance of machines and autonomous systems.
Core Technologies Connected to Neuromorphic Computing
- Advanced Materials: The development of neuromorphic computing heavily relies on advanced materials that mimic the electrical properties of biological neurons and synapses. Materials like memristors, which exhibit variable resistance based on the history of conducted current, are crucial.
- Microelectronic Engineering: Neuromorphic chip design and fabrication need precise microelectronic engineering techniques. This includes the integration of a very large number of synthetic neurons and synapses on a single chip while maintaining component functionality and efficiency.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Tailored algorithms take full advantage of the parallel processing capabilities of neuromorphic computers and ensure efficient data handling.
- Energy Efficiency Technologies: Since one of the primary advantages of neuromorphic computing is low power consumption, optimizing hardware and software to reduce power consumption while maintaining neuron-like activity is critical.
3. Generative AI
Generative AI is redefining how machines comprehend and produce content by creating text, images, audio, and video that resemble human-like qualities. The most popular genAI tools are ChatGPT4 for content creation and Midjourney and Stable Diffusion for image generation while GitHub Copilot facilitates coding workflows.
These solutions leverage sophisticated algorithms to acquire knowledge from a collection of data and subsequently produce new data that is both similar and unique. This way, generative AI inspires innovative strategies for customer engagement, marketing, and product development.
Noteworthy Generative AI Advancements
- OpenAI’s GPT-4: An autoregressive language model that uses deep learning to generate human-like text. Hence, it finds applications in a variety of business scenarios, including customer service automation, code generation, and writing articles.
- DeepMind’s AlphaFold: Google’s product accurately anticipates the 3D structures of proteins to provide a cost-effective and more precise alternative to conventional experimental methods. It has significant implications for drug discovery and understanding of biological processes.
Financial Forecast
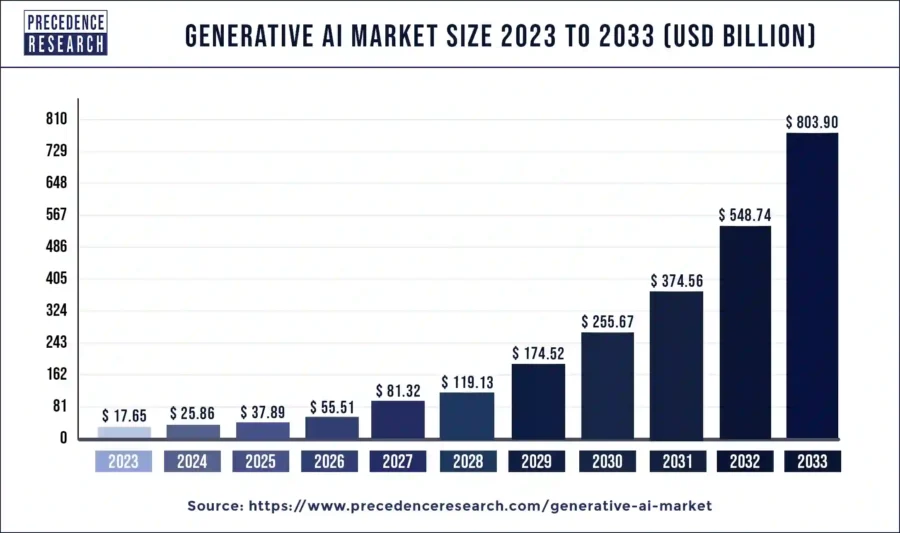
Source: Precedence Research
- 2032: Bloomberg Intelligence predicts a market value of USD 1.3 trillion, with a CAGR of 42%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Intrepid Fox – Automated Documents Collection
Intrepid Fox is a UK-based startup that automates document collection for banks and fintechs. The company’s generative AI-powered solution uses a chat interface to interact with customers and collect all documents. It then checks the details and asks for clarification from the customer if needed.
Further, the solution delivers a summary report and verifies data points to assist employees in decision-making.
Core Technologies Connected to Generative AI
- Advanced Neural Networks: Neural network architectures like generative adversarial networks (GANs) and variational autoencoders (VAEs) are the backbone of generative AI. They learn deep representations of data to enable new, high-fidelity content generation.
- Big Data & Analytics: Generative AI requires large datasets to learn effectively. Technologies that facilitate the collection, storage, and processing of big data are crucial for training generative models.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): The training and operation of generative AI models require substantial computational power. HPC solutions, including graphical processing units (GPUs) and specialized AI processors, are essential to handle the enormous computational demands of these algorithms.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: As generative AI takes on more roles within businesses, establishing ethical guidelines and frameworks for responsible AI use is critical, particularly in areas involving content creation and personal data.
4. Hyperautomation
Advances in robotics, intelligent process automation (IPA), and other autonomous systems are pushing the boundaries of automation beyond routine tasks. Hyperautomation combines AI, machine learning, and more to streamline operations and create adaptable business processes.
This enables companies to automate entire workflows, encompassing both operational and strategic tasks. The result is a more competitive, innovative, and resilient organization.
Noteworthy Hyperautomation Advancements
- Tesla’s Gigafactories: Tesla’s Gigafactories are highly automated production facilities that manufacture electric vehicles (EVs) and battery packs. Robots handle various tasks, from assembling car bodies to installing seats and painting vehicles. This significantly increased production efficiency and consistency while reducing the need for human labor.
- Amazon’s Fulfillment Centers: Amazon leverages advanced robotics in its fulfillment centers to automate sorting, packing, and transportation. These automation systems significantly increase order fulfillment speed and accuracy to efficiently handle large orders.
Financial Forecast
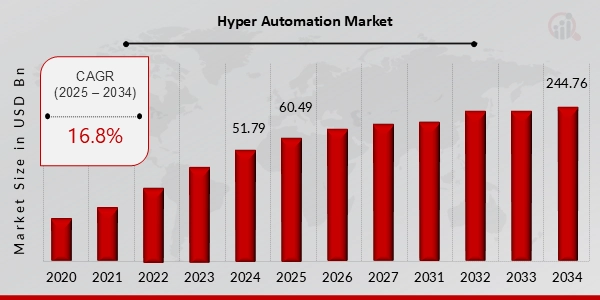
Source: Market Research Future
- 2032: Market Research Future forecasts a market value of USD 131.48 billion, with a CAGR of 16.8%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: augurai – Automated Error Detection
Indian company augurai develops an AI-based automated system for error detection in assembly line production. It incorporates robotics, special purpose machines (SPMs), cameras, and computer vision algorithms to detect defects inside products or components as well as on external surfaces.
The system also identifies missing and wrong components, damaged packaging, and incorrect labels. Therefore, it serves the automotive, aerospace, pharmaceutical, medical device, logistics, and food processing industries.
Core Technologies Connected to Hyperautomation
- Intelligent Process Automation: IPA builds on RPA by incorporating AI and ML to manage more complex tasks that require decision-making and problem-solving. This includes analyzing unstructured data, handling exceptions, and making autonomous decisions.
- Advanced Robotics: In physical automation, advanced robotics combines sensors and AI to perform dangerous, tedious, and high-precision tasks. These robots carry out high-strength tasks and precision assembly for the manufacturing industry.
- Integration Platforms: Ensure that different automated systems communicate and function cohesively by sharing data and insights across business functions. This streamlines workflows and decision-making processes.
5. Voice-Activated Technology
This technology enables users to interact with systems through voice commands and increases the accessibility, intuitiveness, and efficiency of digital services.
By using artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP), voice technology provides hands-free operations for workers to improve operational efficiency while delivering a more natural and engaging mode of interaction for end customers. Such systems find applications in industries, like retail, healthcare, automotive, home automation, and more.
Noteworthy Advancements in Voice-Activated Technology
- Open AI’s GPT-4o: This multimodal LLM supports text, audio, image, and video inputs. It understands and responds to natural language, and answers questions, provides detailed guides, generates creative content, and more. Developers integrate it into solutions, like smart speakers and customer service bots, to improve user experience.
- Honeywell Voice Solutions: Its voice-directed solutions for warehousing and logistics enable workers to interact with warehouse management systems (WMS). This hands-free, eyes-free system improves the efficiency, accuracy, and safety of picking, packing, and inventory management tasks.
Financial Forecast
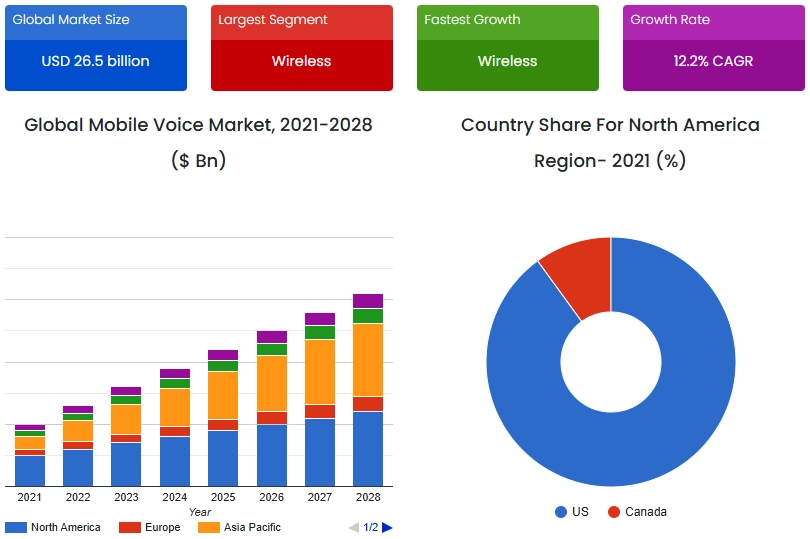
Source: SkyQuest
- 2030: SkyQuest predicts the market value of mobile voice to reach USD 59.3 billion, with a CAGR of 12.2%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Voam Technologies – Voice-Based Documentation
Voam Technologies is a Dutch startup that offers voice-based documentation for sales, recruitment, and technician administration. The company’s AI-powered app converts natural language into notes, provides summaries, and feature templates for common tasks, and integrates with existing systems.
This allows sales teams to ensure up-to-date customer relationship management (CRM) data, recruiters to mitigate manual data entry, and field technicians to spend more time on service.
Core Technologies Connected to Voice-Activated Technology
- Natural Language Processing: Enables machines to understand and process human language. Advances in NLP allow voice assistants to comprehend complex commands, engage in conversations, and provide relevant responses.
- Machine Learning & AI: Allows voice systems to learn from interactions and refine their responses over time. Machine learning algorithms analyze voice data to improve accuracy and personalize experiences, enhancing system performance.
- Speech Recognition: Converts spoken words into digital text. Advances in speech-to-text algorithms increase accuracy in voice recognition, even in noisy environments or across various accents and dialects.
- Cloud Computing: Crucial for the scalability and responsiveness of voice-activated systems. Cloud computing provides the necessary computing power and data storage solutions to process large volumes of data quickly and efficiently in real time.
6. Autonomous Vehicles
Previously considered a futuristic concept, autonomous driving systems now leverage advanced vision, AI, and machine learning to make self-driving vehicles a reality. They improve road safety and mobility for the elderly and disabled and reduce traffic congestion.
In the business world, autonomous vehicles are advancing logistics and delivery services, offering a more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable way to transport goods.
Noteworthy Advancements in Autonomous Vehicles
- Waymo’s Autonomous Ride-Hailing Service: A subsidiary of Alphabet, Waymo launched one of the first fully autonomous ride-hailing services. The Waymo One service utilizes a fleet of self-driving cars to showcase the practical application of autonomous vehicles in urban environments.
- Tesla’s Full Self-Driving Hardware: Tesla’s approach to incremental autonomy, with features like Autopilot and Navigate on Autopilot, has pushed the envelope on consumer expectations and acceptance of self-driving technology. This makes it one of the most effective examples of AV advancements.
Financial Forecast
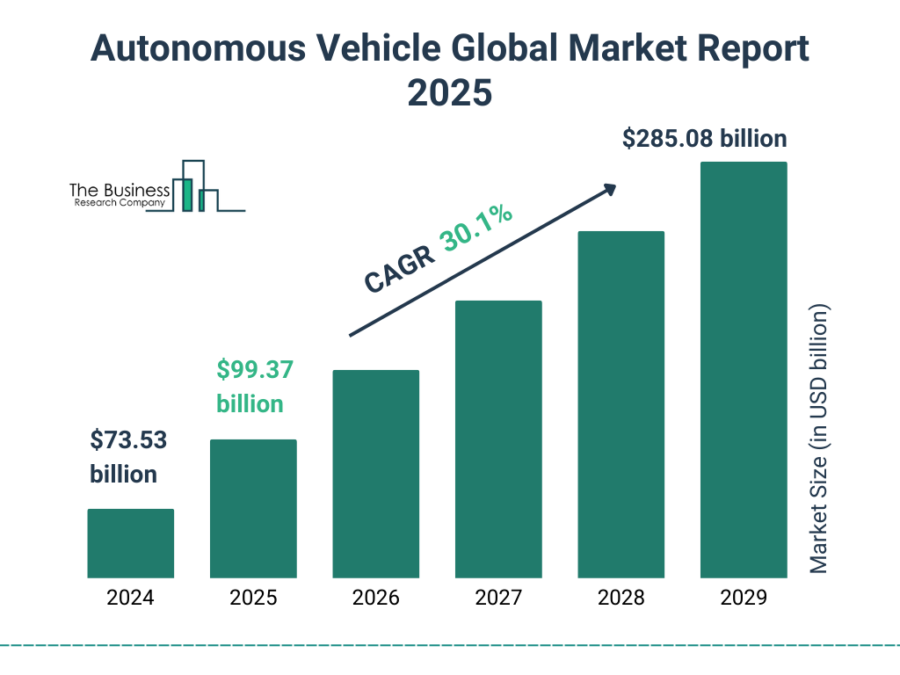
Source: The Business Research Company
- 2030: Fortune Business Insights forecasts the market value to reach USD 13632.4 billion, with a CAGR of 32.3%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Eight Knot – Autonomous Boat Navigation Platform
Eight Knot is a Japanese startup that develops an autonomous navigation platform for small vessels. Its AI analyzes sensor data to detect obstacles and other vessels. The platform also automates cautious maneuvering required for departure and docking.
Core Technologies Connected to Autonomous Vehicles
- Sensors and Vision Systems: Autonomous vehicles leverage a complex array of sensors, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, to navigate and understand their environment. They provide critical data to detect obstacles, monitor traffic conditions, and perform detailed environment mapping.
- AI and Machine Learning: Analyzes input from vehicle sensors to make real-time driving decisions. AI/ML algorithms improve decision-making capabilities over time, allowing vehicles to adapt to new scenarios and driving conditions.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X): Enhances situational awareness and prevents accidents by sharing information about road conditions, traffic, and potential hazards in real time.
- Cybersecurity: As autonomous vehicles rely on software and data exchange, cybersecurity measures are critical to protect against hacking and data breaches, in turn, improving passenger safety.
7. Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is frequently celebrated for its potential to provide an almost infinite supply of sustainable, clean, and secure energy. Unlike nuclear fission (which splits atoms), fusion combines light atomic nuclei such as hydrogen to form heavier nuclei.
During this process, a vast amount of energy is produced while generating minimal radioactive waste and carbon emissions. It thus strengthens energy infrastructures and economies by offering a scalable and stable energy source for industrial and technological advancements.
Noteworthy Nuclear Fusion Advancements
- International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER): 35 nations are collaborating in France to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion as a large-scale and carbon-free energy source. This international project aims to produce a self-sustaining fusion reaction to harness fusion power for commercial use.
- Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP): A program by the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) to develop and demonstrate the world’s first commercially viable fusion power plant by 2040. The project uses a spherical tokamak design to be more efficient and cost-effective than traditional designs.
Financial Forecast
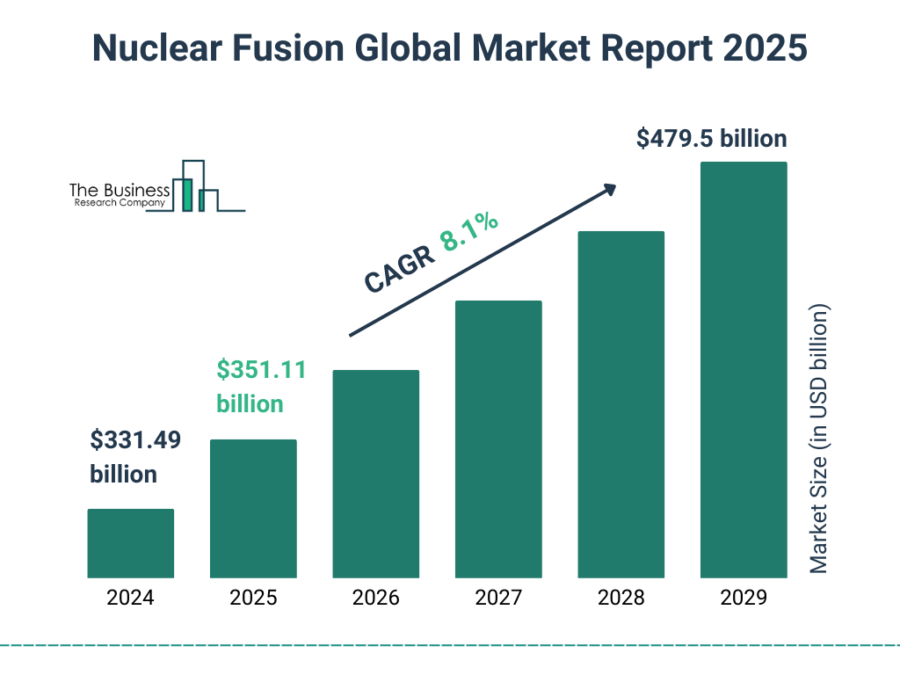
Source: The Business Research Company
- 2029: The Business Research Company predicts the market value to reach USD 479.5 billion, with a CAGR of 8.1%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Proxima Fusion – QI stellarator-based Nuclear Fusion
Proxima Fusion is a German startup that constructs fusion power plants using advances in stellarator optimization, computational design, and superconductivity. The company utilizes quasi-isodynamic (QI) stellarators to mitigate plasma currents and high-temperature superconductors with high magnetic field strengths.
It also leverages a simulation-first approach driven by neural networks and machine learning to accelerate design finalization and construct surrogate models for testing. Proxima Fusion’s technology enables flexible designs and runs stably in continuous operation.
Core Technologies Connected to Nuclear Fusion
- Magnetic Confinement: Applies magnetic fields to confine the plasma (a hot, charged state of matter composed of fusion fuel). Tokamaks and stellarators are two types of devices using magnetic confinement, which is crucial for maintaining conditions necessary for fusion.
- Laser Inertial Confinement: Uses high-powered lasers to compress and heat fusion fuel to the required conditions. Facilities like the National Ignition Facility (NIF) in the USA use this technique to initiate fusion reactions.
- Superconducting Magnets: Efficient and powerful magnets create strong magnetic fields to confine the plasma in magnetic confinement fusion reactors.
- Advanced Diagnostics & Control Systems: Optimize the performance and safety of fusion processes to improve high-energy plasma manipulation and stability.
8. Battery Technologies
The demand for advanced battery technologies is increasing as the world transitions to electric mobility and renewable energy. Battery technology innovations improve energy density and efficiency while also prioritizing cost reduction, safety improvement, and environmental mitigation.
These solutions have a significant impact on various industries, like automotive, consumer electronics, and grid-scale energy storage. Further, battery storage addresses the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources to enable a more stable and reliable energy supply.
Noteworthy Advancements in Battery Technologies
- Tesla’s 4680 Battery Cells: These cylindrical cells are larger and have a tabless design to reduce internal resistance and improve thermal management. The 4680 cells are expected to provide higher energy density, greater range, and lower costs for Tesla’s electric vehicles.
- Solid-State Batteries by QuantumScape: Its solid-state lithium-metal batteries feature high energy density, fast charging capabilities, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. For example, the company’s solid-state separator reduces dendrite formation and avoids short circuits.
Financial Forecast
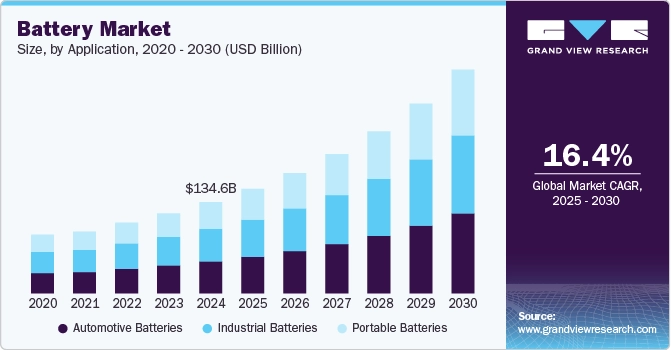
Source: Grand View Research
- 2030: Grand View Research forecasts a market value of USD 329.84 billion, with a CAGR of 15.8%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Janaenergy Technology – Sodium-Ion Battery
Janaenergy Technology is a Chinese startup that manufactures polyanion cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. The company’s biomass hard carbon materials feature high conductivity and energy density while being low-cost and environmentally friendly.
Core Technologies Connected to Battery Technologies
- Advanced Electrode Materials: The use of silicon in anodes and lithium-rich cathodes increases the capacity and efficacy of batteries. Advanced electrode materials store a greater number of ions and provide a higher energy density for prolonged battery life.
- Electrolyte Solutions: The safety and efficacy of batteries are significantly enhanced by advances in electrolyte chemistry, which includes the development of solid electrolytes for solid-state batteries. Solid electrolytes are non-flammable and offer increased ion conductivity at ambient temperature.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Control the environment by monitoring battery condition to balance and protect the battery. This enables cell-specific management of battery packs to improve the life and efficacy of battery systems.
- Recycling Technologies: Novel methods to recover valuable materials and mitigate environmental impact are increasing as the use of batteries increases. The efficient reclamation and reuse of components such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel is critical for sustainable battery manufacturing.
9. Synthetic Biology
By combining biology and engineering, synthetic biology is advancing environmental management, agriculture, and healthcare. It allows scientists and engineers to develop new biological components, devices, and systems by redesigning organisms.
This technology’s applications include the remediation of polluted environments, sustainable production of chemicals and fuels, disease treatment, and more. Moreover, each application represents a substantial commercial opportunity to establish new markets.
Noteworthy Synthetic Biology Advancements
- CASGEVY: A CRISPR/Cas9 gene-edited therapy for the treatment of sickle cell disease and transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia was authorized by the UK MHRA. It was the result of a collaboration between CRISPR Therapeutics and Vertex Pharmaceuticals.
- Lab-grown Meat by Upside Foods: The company recently received regulatory approval from the FDA to sell its cultivated chicken products in the USA. This approval marks a major milestone in the field of synthetic biology, demonstrating the feasibility and safety of producing cultured meat.
Financial Forecast
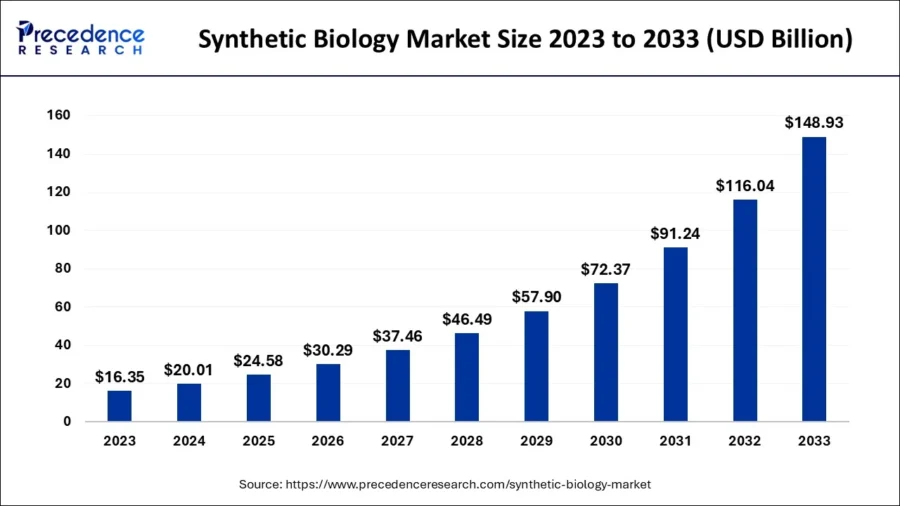
Source: Precedence Research
- 2033: Precedence Research predicts a market value of USD 148.93 billion, with a CAGR of 25%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Episteme Genomics – Automated Synthetic DNA Generation
Episteme Genomics is an Indian company that develops a biofoundry. Its automated benchtop instrument for numeric synthetic biology workflow, BioXp, allows researchers to generate synthetic DNA and mRNA from DNA sequences. This accelerates workflows, like gene synthesis, DNA cloning, and DNA amplification, for new biology discovery and vaccine development.
Core Technologies Connected to Synthetic Biology
- DNA Sequencing & Synthesis: Rapid advances in the field reduce the cost and increase the speed and accuracy of genetic information reading and writing. This is foundational for synthetic biology and enables the design and construction of new biological parts and systems.
- CRISPR & Other Gene Editing Tools: CRISPR, TALEN, zinc-finger nucleases, and other gene editing tools allow researchers to make precise modifications for adding, removing, or altering genetic materials to ensure desired traits or functions.
- Bioinformatics: Uses software tools and computational approaches to understand biological data to analyze large amounts of biological data for designing and modeling new biological parts or systems.
- Automated Biological Foundries: Also known as biofoundries, they utilize automation and robotics to construct and test synthetic biological systems rapidly and accurately for high-throughput synthesis and testing.
10. Preventative Medicine & Wellbeing
Preventative medicine and well-being are becoming important elements of healthcare. The increasing burden of chronic diseases and healthcare costs are the driving forces behind this transition to a more preventive approach.
It enables healthcare professionals to identify health hazards early, implement effective interventions, and maintain long-term health. This provides opportunities for the development of new services and products that range from advanced diagnostic tools to wellness programs.
Noteworthy Preventative Medicine & Wellbeing Advancements
- Apple’s Wearable Health Monitors: Apple’s smartwatches feature continuous blood glucose monitoring, sleep tracking, and enhanced heart health metrics like early detection of atrial fibrillation (AFib) and other irregular heart rhythms.
- Grail’s Early Cancer Detection: Its multi-cancer early detection test combines genomic sequencing and machine learning to detect 50+ cancers from a single blood draw. This enables early diagnosis and timely treatments to improve survival rates.
Financial Forecast
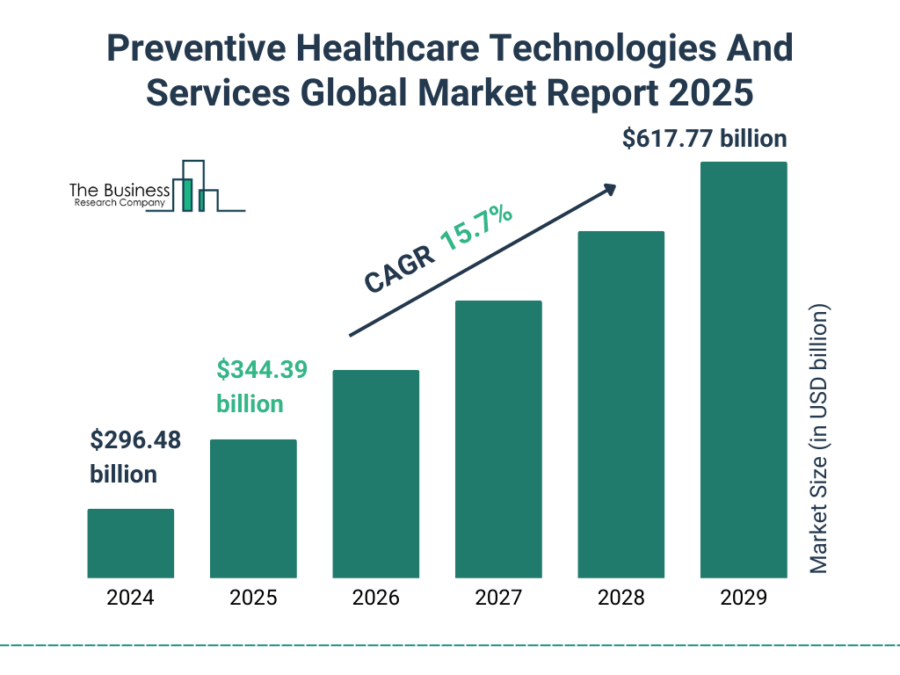
Source: The Business Research Company
- 2029: The Business Research Company forecasts the market value of preventive medicine to reach USD 617.77 billion, with a CAGR of 15.7%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: CheckEye – Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
Ukrainian company CheckEye provides a cloud-based solution for diabetic retinopathy detection. It utilizes AI and machine learning to analyze photographic images of the eye fundus to enable early detection of diabetic retinopathy. This provides decision support for healthcare professionals and enables them to deliver proactive patient care.
Core Technologies Connected to Preventative Medicine & Wellbeing
- Big Data & Analytics: Analyze large volumes of health data from electronic health records (EHRs), wearables, and genetic tests to inform preventative medicine. They enable healthcare providers to identify trends, predict disease outbreaks, and develop personalized treatment plans.
- Telemedicine & Digital Health Platforms: Facilitate remote health monitoring and consultations to improve access to healthcare and deliver continuous support.
- AI & Machine Learning: Predict health risks and outcomes based on complex datasets. These technologies detect subtle patterns that human analysts might miss and provide support for early diagnosis and preventative care.
11. Climate Tech
Climate technology combines various solutions to mitigate the effects of climate change and address environmental challenges. It includes solutions for enhancing energy efficiency, carbon capture systems, regenerative agriculture, and more.
Businesses, governments, and consumers are increasingly emphasizing such solutions to foster a more sustainable future as global awareness of environmental issues grows. In the business sector, implementing climate-positive solutions improves compliance with environmental regulations, reduces energy costs, and increases operational efficiencies.
Noteworthy Climate Tech Advancements
- Climeworks’ Direct Air Capture (DAC) Plant: The company’s plant has an annual capture capacity of 4000 tonnes. It represents a scalable solution to reduce atmospheric CO2 levels to meet global climate targets.
- LanzaJet’s Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF): The company’s alcohol-to-jet (ATJ) fuel is derived from renewable ethanol sources. This significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional jet fuel.
Financial Forecast
Source: Dataintelo
- 2032: Dataintelo predicts a market value of USD 130.9 billion, with a CAGR of 23.8%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Captivate Technology – Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)
Captivate Technology is a New Zealand-based company that offers MUF-16, a metal-organic framework. This sponge-like adsorbent captures carbon dioxide with high selectivity and reduces costs associated with modular capture units.
This enables an energy-efficient means for carbon-intensive industries, like cement manufacturing, natural gas combustion, and hydrogen production, to curb emissions at the source.
Core Technologies Connected to Climate Tech
- Advanced Energy Storage Systems: Lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, compressed air energy storage, and other emerging solutions ensure a consistent and dependable energy supply. This is critical to address the intermittency of renewable energy sources and accelerate the energy transition.
- Smart Grids: Detect and react to local changes in usage to improve the efficiency of electricity distribution. This is essential for integrating renewable energy sources into the grid and managing demand response programs.
- Geospatial Analytics: Utilizing AI and satellite imagery, geospatial analytics simplifies environmental monitoring and management. It allows businesses to track deforestation, water levels, and pollution patterns.
- Blockchain: Creates more transparent and efficient systems for trading carbon credits and tracking renewable energy generation to increase the accountability and effectiveness of sustainability initiatives.
12. Zero Latency Connectivity
Zero-latency connectivity facilitates real-time communication and interaction by enabling near-instantaneous data transmission. This is essential in sectors where timing is a critical factor – like telemedicine, autonomous driving, virtual and augmented reality (AR/VR), and high-frequency trading.
Zero-latency connectivity solutions thus increase operational efficiency and customer satisfaction by offering enhanced digital interactions and enabling real-time decision-making.
Noteworthy Advancements in Zero-Latency Connectivity
- 5G Standalone (SA) Networks by Verizon: Unlike earlier deployments that relied on existing 4G infrastructure, 5G SA networks operate independently to reduce latency and enhance performance. It supports applications requiring near-zero latency, such as real-time gaming and autonomous vehicles.
- Nokia’s 5G Edge Computing: Provides ultra-low latency connectivity for industrial and enterprise applications. It integrates with Nokia’s 5G technology with edge computing to bring processing closer to the data source and enable real-time data analysis and decision-making
Financial Forecast

Source: MarketsandMarkets
- 2035: MarketsandMarkets forecasts a market value of USD 85.9 billion for 6G, with a CAGR of 76.9%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: SpaceAlpha Insights – Near-Zero Latency Monitoring
Canadian company SpaceAlpha Insights enables near-zero latency monitoring and object classification using satellite communication. The company’s synthetic aperture radar (SAR) utilizes X and L bands and real-time processing to deliver ultra-high-resolution imagery of Earth’s surface.
This data allows authorities and businesses to improve precision agriculture, forest fire monitoring, in-field intelligence, pipeline monitoring, and more.
Core Technologies Connected to Zero-Latency Connectivity
- 5G: Provides high-speed data transmission capabilities and ultra-low latency for the development of real-time applications in various industries – like industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and consumer electronics.
- Edge Computing: Reduces the time required to process and return data by processing data closer to the source rather than relying on distant data centers and cloud computing.
- Advanced Network Infrastructure: New network protocols and upgraded fiber-optic communications are enabling zero-latency connectivity using fast data speeds and high bandwidth.
13. Space Exploration
Space exploration, long the domain of government agencies, is undergoing a renaissance driven by private-sector innovation and international collaboration. This new era of space exploration and tourism leverages technological, economic, and scientific advancements to improve efficiency and make space missions cost-effective.
In addition to discoveries, space exploration benefits industries on Earth by advancing telecommunications, weather forecasting, resource extraction, and more, opening up new markets.
Noteworthy Space Exploration Advancements
- SpaceX’s Reusable Rocket: The Falcon 9 reusable rocket has drastically reduced the cost of launching payloads into space. This allows for more frequent and cost-effective space missions, including plans for manned missions to Mars.
- NASA’s Artemis I Mission: An uncrewed mission that tested NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft around the Moon. The mission demonstrated critical systems and capabilities needed for future manned missions, including deep space navigation, communication, and re-entry.
Financial Forecast

Source: Precedence Research
- 2032: Spherical Insights predicts a market value of USD 486 billion, with a CAGR of 16.21%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: SpaceCopy3D – In-Situ Lunar Manufacturing
SpaceCopy3D is a Saudi Arabian startup that enables in-situ lunar manufacturing. The company’s multi-purpose interplanetary manufacturing device combines lunar regolith sampling, spectral data analysis, and 3D printing.
This allows space exploration and tourism companies to mitigate frequent payload service missions, reducing pollution and debris generated by continuous resupply missions.
Core Technologies Connected to Space Exploration
- Rocket & Propulsion Technologies: Essential for ensuring more cost-effective and efficient space travel. Reusable rockets, hybrid rockets, and ion propulsion systems are the major advancements in this sector.
- Satellite Technology: Miniaturization and improved efficiency of satellite technology increase satellite network deployment and management. These advances improve communication, navigation, Earth observation, and more.
- Robotics & AI: Conduct intricate tasks in space, such as structure assembly in orbit and planetary surface exploration. This improves the productivity of space missions by enabling more precise and flexible operations while ensuring astronaut safety.
- Advanced Materials: Innovations in lightweight, high-strength materials and thermal protection systems are enabling longer and more ambitious missions. They enable a more resilient space infrastructure.
14. Brain-Computer Interfaces
Brain-computer interfaces combine technology and neuroscience to enable direct communication between the human brain and external devices. This technology enhances cognitive abilities, creates new forms of human-computer interaction (HCI), and restores lost functions for individuals with disabilities.
This technology has potential applications in various industries, including healthcare, entertainment, military, and beyond.
Noteworthy Advancements in Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Neuralink’s Brain Implant Trials: Neuralink received approval from the FDA to begin human trials of its brain implant. The device enables direct communication between the brain and computers using ultra-thin threads that connect with the brain to record neural activity and stimulate specific brain regions.
- Synchron’s Stentrode Implant: The company’s minimally invasive devices are implanted via the jugular vein to interface with the brain’s motor cortex. It enables patients with paralysis to control digital devices using their thoughts, and the company reported positive results from clinical trials.
Financial Forecast
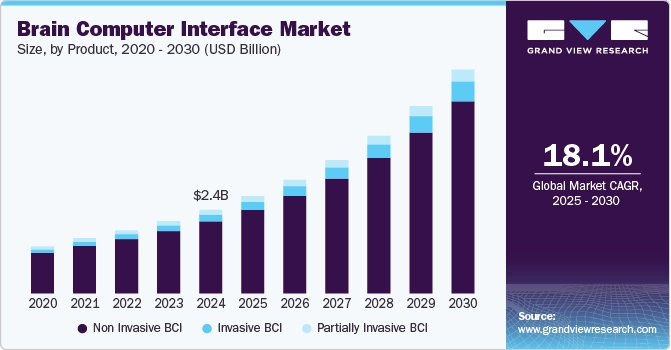
Source: Grand View Research
- 2030: Grand View Research forecasts the market value to reach USD 6.2 billion, with a CAGR of 17.5%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Cenexum – Wirelessly-powered Neural Interfacing
Cenexum is a Danish company that develops a wirelessly powered neural interfacing solution. The company’s miniaturized implantable device locally records the data, processes it using AI and machine learning, and enables bi-directional communication.
Additionally, multiple implants connect to a common network to integrate data from different parts of the central and peripheral nervous system. This approach offers more effective neurostimulation and treats chronic pain, depression, movement disorders, Parkinson’s disease, and more.
Core Technologies Connected to Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Neuroimaging & Electrophysiology: Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG) are crucial for neural network analysis and brain activity mapping. They enable the development of algorithms that decode neural signals and convert them into actionable commands.
- AI & Machine Learning: Process vast quantities of data generated by BCIs to precisely interpret neural signals and enhance the functionality of BCIs over time.
- Microelectrode Arrays: High-density microelectrode arrays are safely implanted in the brain to capture detailed neural activity. These arrays are biocompatible, durable, and transmit high-fidelity signals to external devices.
- Wireless Communication: Facilitates more natural and seamless interactions between the brain and external devices as well as enables real-time data transmission.
15. Digital Trust Technologies
Digital trust technologies are a collection of solutions that establish, maintain, and improve trust in digital interactions. The security and integrity of these interactions are critical as businesses increasingly depend on digital platforms for communication, transactions, and data storage.
Emerging cybersecurity systems enable digital ecosystems by improving identity verification, data privacy, and malicious activity monitoring. Companies that prioritize digital trust establish more robust relationships with their customers and mitigate the risks of sensitive data leaks.
Noteworthy Advancements in Digital Trust Technologies
- Microsoft’s Azure Confidential Computing: Uses hardware-based trusted execution environments (TEEs) to encrypt data not only at rest and in transit but also while being processed in memory. This improves security for sensitive data and applications across industries, like finance, healthcare, and government.
- IBM’s Quantum-Safe Cryptography: IBM developed and implemented new cryptographic algorithms to be resistant to quantum attacks and ensure long-term security for sensitive information. These algorithms, part of IBM’s comprehensive Quantum Safe Roadmap, are integrated into their cloud services and are available to customers through IBM Cloud.
Financial Forecast
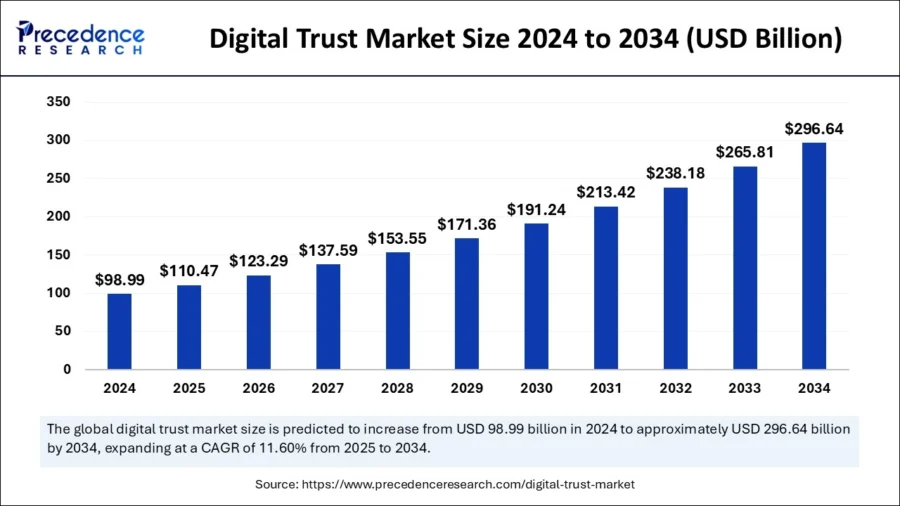
Source: Precedence Research
- 2034: Precedence Research predicts the market value to reach USD 296.64 billion, with a CAGR of 11.6%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: klearis – Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR)
Turkish company klearis’ content disarm and reconstruction technology protects businesses against file-borne threats. The company’s solution, Gryphon Engine, uses deep file inspection to identify the file’s true format.
It then deconstructs the file removes components that do not comply with international or vendor file type specifications, and re-builds a threat-free version. This allows organizations to protect their digital assets and neutralize potential threats while maintaining the usability of the original file.
Core Technologies Connected to Digital Trust Technologies
- Encryption Technologies: End-to-end encryption, homomorphic encryption, and advanced encryption standards (AES) are crucial for protecting sensitive information across databases, networks, and cloud platforms.
- Biometric Authentication: Retinal scanning, facial recognition, and fingerprint recognition offer a highly secure and convenient method for identity verification. They are used in many applications to authorize access to protected resources.
- AI & Machine Learning: Essential for the real-time detection and response to threats. These technologies identify unusual patterns and potential security breaches to enable proactive measures and mitigate risks.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Ensures the authenticity and integrity of digital communications by providing a framework for secure key exchange and identity verification – enabling secure email communication, digital signatures, and more.
16. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology manipulates matter at the atomic and molecular levels to produce materials with improved properties and capabilities – like strength, flexibility, and electrical conductivity. This discipline of science and engineering has significant implications for various industries, including healthcare, electronics, energy, and manufacturing.
Nanotechnology thus presents substantial opportunities for businesses to enhance existing products, develop new ones, and establish more efficient manufacturing processes.
Noteworthy Nanotechnology Advancements
- CytImmune Sciences’ Cancer Treatment: Aurimune is the company’s nanoparticle-based cancer treatment. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is delivered at high precision to cancer cells via gold nanoparticles in this treatment, increasing the drug’s efficacy while reducing side effects.
- Nanoseen’s Water Filtration Technology: NanoseenX is its nanomembrane that filters water from impurities like viruses, bacteria, and heavy metals. It is an economical means to produce drinking water in places where access to clean water sources is limited.
Financial Forecast

Source: Precedence Research
- 2034: Precedence Research expects the market value to reach USD 115.41 billion, with a CAGR of 33.14%.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Peptina Biotech – Portable Chemical Analysis Device
Peptina Biotech is a Brazilian company that offers Biotab, a nanotech-based portable chemical analysis device. It detects and quantifies several analytes and is a cost-effective alternative to chromatography instruments.
The device enables real-time chemical analysis, allowing food and beverage companies to simplify their quality control processes while enabling farmers to implement on-site soil analysis.
Core Technologies Connected to Nanotechnology
- Nanofabrication Techniques: Electron beam lithography, atomic layer deposition, and nanoimprint lithography are necessary to build materials at the nanoscale. They precisely regulate the characteristics of materials and create the intricate nanostructures required for biomedical devices, electronics, and more.
- Characterization Tools: Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) are crucial for the investigation of nanoscale materials. They provide researchers with detailed images and measurements to better comprehend their properties and behavior.
- Self-Assembly Processes: Enables the automated development of nanoscale materials and devices. Scientists are able to create new materials with customized properties for applications in electronics, photonics, and medicine by using the principles of self-assembly.
- Computational Nanotechnology: Computational models facilitate the comprehension of complex interactions and the development of materials with the desired properties, accelerating the discovery and optimization of nanomaterials and nanodevices.
Impact of Future Technologies on 43 Industries Globally

Impact of Emerging Technologies on Heavy Industries
In a world where innovation continually redefines the norm, heavy industries are not exempt from the transformative wave of disruptive technologies. From the sprawling fields of manufacturing to the precise nature of aerospace, technological advances are shaping the way we produce, construct, and operate.
Let’s explore how modern tools and methodologies are sculpting a new era for these vital sectors.
Manufacturing
- Hyperautomation: Intelligent automation streamlines production lines and reduces operational costs.
- Generative AI: Improves product design and customization through AI-driven modeling and simulations.
- Nanotechnology: Use of high-performance materials to enhance the efficacy and durability of products.
Construction
- Generative AI: Employs sophisticated AI algorithms to optimize building design while taking into account factors such as climate and utilization patterns.
- Nanotechnology: Facilitates the development of more sustainable, lighter, and more durable materials.
- Climate Technology: Implements energy-efficient systems, sustainable materials, and more to reduce the environmental impact.
Oil and Gas
- Quantum Computing: Accelerates the processing of geological data for exploration and decreases the expenses associated with the discovery of new reserves.
- Digital Trust Technologies: Enhance the security of automated drilling operations and remote monitoring.
- Hyperautomation: Improves safety and efficiency by automating complex extraction, refining, and distribution processes.
Utilities
- Battery Technologies: Energy storage solutions that facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources and provide off-grid power.
- Nuclear Fusion: Offers a virtually limitless and potentially pure energy source.
- Digital Trust Technologies: Enhance grid security and reliability by implementing advanced cybersecurity measures.
Automotive
- Autonomous Vehicles: Improve road safety and vehicle efficiency by leveraging self-driving technologies.
- Battery Technologies: Enhance the capabilities of electric vehicles by utilizing batteries that are more durable and support fast charging.
- Generative AI: Optimizes vehicle design and manufacturing processes.
Mining
- Hyperautomation: The automation of hazardous tasks improves productivity and safety.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Unmanned vehicles and drones facilitate safer and more efficient exploration and extraction.
- Generative AI: Allows companies to enable predictive maintenance and optimize extraction processes.
Energy
- Nuclear Fusion: Provides a novel method of power generation with minimal environmental impact.
- Battery Technologies: Enable more efficient storage solutions to regulate the fluctuating outputs of renewable energy sources.
- Climate Technology: Enhances energy efficiency and reduces carbon footprint using renewables and energy-efficient integrations.
Steel
- Nanotechnology: Creates more corrosion-resistant and stronger materials.
- Hyperautomation: Improves production processes by utilizing automated and precise manufacturing.
- Generative AI: Enhances the performance of alloy compositions and thermal treatments.
Aerospace
- Nanotechnology: Offers high-performance and lightweight materials for harsh environments.
- Synthetic Biology: Biomaterials for in-flight structures and life support systems in extended space travel.
- Quantum Computing: Enhances the precision of material and flight simulations to improve performance and safety.
Railroad
- Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous control systems in railroads enhance scheduling and safety.
- Zero-Latency Connectivity: Allows for real-time monitoring and control, improving productivity and minimizing bottlenecks.
- Hyperautomation: Automating maintenance and operational duties enhances efficiency and minimizes downtime.
Shipbuilding
- Generative AI: Enables shipbuilders to simplify vessel design and improve sustainability.
- Nanotechnology: Advanced materials improve the durability and efficacy of vessels.
- Climate Technology: Reduces emissions and enables companies to adhere to environmental regulations.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Process Industries
Process industries are known for their role in the production of necessities like chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food products. These sectors, integral to the backbone of global supply chains, are characterized by complex and large-scale production processes.
As such, they are prime candidates for the integration of future technologies. From gen AI optimizing production lines to novel connected devices ensuring real-time monitoring and quality control, the impact of these technologies is far-reaching. Explore how these advancements are streamlining operations and catalyzing a new era in the process industries.
Food and Beverage
- Synthetic Biology: Lab-grown proteins and engineered crops improve sustainability and nutrition.
- Generative AI: Advanced data analysis and predictive modeling enhance the development of recipes and food safety protocols.
- Nanotechnology: Improves the preservation and packaging of food using smart packaging and nano-encapsulation.
Chemical
- Quantum Computing: Accelerates the discovery of new materials and chemical reactions.
- Hyperautomation: Robotic assistance and automation systems optimize chemical production processes.
- Climate Technology: The adoption of sustainable chemical production methods reduces carbon emissions.
Pharmaceuticals
- Synthetic Biology: Enables personalized medicine and novel drugs through biomanufacturing and genetic engineering.
- Preventative Medicine & Wellbeing: Promotes early detection of diseases and personalized health management.
- Nanotechnology: Advanced diagnostic instruments and targeted drug delivery systems to facilitate more effective treatments.
Materials
- Quantum Computing: Identifies novel materials with better properties through quantum simulations and optimizations.
- Nanotechnology: Creates advanced materials with improved conductivity, flexibility, and strength.
- Hyperautomation: The automation of material production and quality control processes enhances efficiency and decreases costs.
Textiles
- Nanotechnology: Enables fabrics that are more durable, stain-resistant, and have smart textile capabilities.
- Generative AI: AI-driven insights offer novel patterns and optimize production processes.
- Climate Technology: Sustainable textile production reduces waste and environmental impact.
Semiconductor
- Quantum Computing: Explores the limits of semiconductor performance and capabilities.
- Nanotechnology: Facilitates the creation of more effective, faster, and smaller semiconductor devices.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Enables near-real-time visibility into production to improve precision and avoid wastage.
Cosmetics
- Synthetic Biology: Bioengineered ingredients for producing more effective and safer cosmetic products.
- Generative AI: Customizes skincare and cosmetic solutions through tailored formulations and recommendations.
- Nanotechnology: Nano-sized ingredients are more effective in absorbing into the epidermis and delivering them to target areas.
Water & Wastewater Management
- Climate Technology: Advanced water purification and recycling technologies mitigate water scarcity and pollution.
- Nanotechnology: The use of nano-materials in filtration systems improves the efficiency of water purification.
- Hyperautomation: Automating water infrastructure monitoring and maintenance enhances efficiency and decreases operational costs.
Impact of Future Technologies on Light Industries
The world of light industries, often associated with everyday products and consumer goods, is undergoing a silent yet profound revolution. These sectors, while differing vastly in products, share a common thread: they cater directly to end consumers.
Thus, the stakes are high for innovation, customization, and efficiency. Dive into the myriad ways emerging technologies in businesses are reimagining the fabric of these industries.
Apparel
- Nanotechnology: Intelligent fabrics that feature improved moisture-wicking and self-cleaning properties.
- Generative AI: Optimizes fashion design and market trend prediction.
- Climate Technology: Sustainable production methods and environmentally favorable materials reduce the environmental impact.
Publishing and Printing
- Digital Trust Technologies: Blockchain and encryption guarantee secure and verifiable digital content distribution.
- Generative AI: Automates content creation and personalization for improving targeted marketing and consumer engagement.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Enhances real-time collaboration and digital printing capabilities for faster production cycles.
Consumer Electronics
- Neuromorphic Computing: Enables energy-efficient, AI-powered devices with human-like processing.
- Battery Technologies: Improves the efficacy and longevity of portable electronics.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Facilitates real-time interactions and seamless connectivity in IoT ecosystems.
Medical Devices
- Nanotechnology: Innovates minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic devices.
- Synthetic Biology: Bioengineered materials and sensors enable advanced medical diagnostics and interventions.
- Preventative Medicine & Wellbeing: Wearable health monitors and early disease detection tools promote proactive healthcare.
Furniture Manufacturing
- Hyperautomation: The integration of robotic assembly and automated systems optimizes production processes.
- Generative AI: Customizes furniture design and manufacturing to reflect consumer preferences and ergonomic data.
- Climate Technology: Energy-efficient production methods and sustainable materials reduce carbon emissions.
Leather Goods
- Synthetic Biology: Lab-grown leather substitutes promote ethical sourcing and sustainability.
- Nanotechnology: Nano-coatings and treatments improve the functionality and durability of leather products.
- Generative AI: Optimizes production workflows and customizes leather product design through AI-driven insights.
Jewelry
- Nanotechnology: Innovative jewelry designs improve properties like color durability and abrasion resistance.
- Generative AI: Enables the development of unique and complex jewelry designs.
- Digital Trust Technologies: Blockchain improves the authenticity and traceability of precious metals and gemstones.
Impact of Future Technologies on Service Industries
Service industries, recognized as the pillars of modern economies, are where many individuals directly encounter the benefits of new technologies. This arena is marked by its focus on consumer interaction, experience enhancement, and efficient service delivery.
In this rapidly evolving environment, future technology acts as both a disruptor and an enabler. Let’s explore how these innovations in technology are crafting a renewed vision for each sector within the service industries.
Retail and eCommerce
- Generative AI: Optimizes inventory management and personalizes purchasing experiences.
- Digital Trust Technologies: Blockchain and advanced encryption delivers secure and transparent online transactions.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Facilitates real-time support and consumer engagement.
Finance
- Quantum Computing: Revolutionizes financial modeling, risk analysis, and cryptography with advanced computational power.
- Digital Trust Technologies: Enhances cybersecurity and fraud prevention by utilizing advanced authentication and blockchain.
- Generative AI: AI-driven chatbots and analytics automate customer service and provide personalized financial advice.
Logistics
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving trucks and autonomous drones improve delivery efficacy and minimize expenses.
- Hyperautomation: Integrated automation systems optimize warehouse operations and supply chain management.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Enables the real-time monitoring and coordination of logistics activities to improve operational efficiency.
Tourism and Hospitality
- Voice-Activated Technology: Improves guest experience by providing concierge services and voice-activated room controls.
- Generative AI: Personalizes travel recommendations and itineraries to enhance guest experience.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Optimizes back-end operations in real time and provides visitors with seamless connectivity.
Transportation
- Autonomous Vehicles: Advances public and private transportation with self-driving cars, buses, and ride-sharing services.
- Battery Technologies: Facilitates the adoption of electric vehicles by providing more durable and longer-lasting batteries.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Enhances real-time data exchange to improve traffic management and vehicle communication.
Real Estate
- Digital Trust Technologies: Safeguard property transactions and ownership records.
- Generative AI: Improves market predictions and property valuations.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Facilitates real-time virtual property tours and smart home technologies.
Healthcare
- Preventative Medicine & Wellbeing: Wearable health monitors and AI diagnostics facilitate early detection and personalized treatment plans.
- Nanotechnology: Enables targeted drug delivery systems and minimally invasive medical devices.
- Digital Trust Technologies: Blockchain and advanced encryption secure digital health records and protect patient data.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Interdisciplinary Industries
While many industries can be grouped under broad umbrellas like heavy, process, or service industries, some stand out for their distinct nature and influence. These unique sectors often operate at the intersections of traditional categories, wielding the power to shape everything from our daily lives to global paradigms.
As technology permeates these sectors, it blends innovations tailored to their specific challenges and opportunities. Here, we spotlight five such industries: Agriculture, Biotech, Packaging, Telecom, and Smart Cities, and delve into the transformative power of future technologies within them.
Agriculture
- Synthetic Biology: Genetically engineered plants and bio-based fertilizers improve crop yield and resilience.
- Climate Technology: Regenerative agriculture and advanced climate monitoring reduce the environmental impact.
- Hyperautomation: Precision agriculture and automated machinery optimize agricultural operations.
Biotechnology
- Quantum Computing: Achieves faster drug discovery and genetic research using sophisticated computational models.
- Synthetic Biology: Biomanufacturing processes and innovative therapies for industrial and medical applications.
- Nanotechnology: Targeted drug delivery systems and advanced diagnostic instruments to improve healthcare outcomes.
Packaging
- Nanotechnology: Advanced packaging materials with more sustainable and improved barrier properties.
- Generative AI: Optimizes packaging design and logistics through AI-driven insights.
- Climate Technology: Utilizes energy-efficient production processes and environmentally favorable materials to reduce environmental impact.
Telecom
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Facilitates the transmission of data and communication at high speeds in real time for next-generation telecommunications services.
- Quantum Computing: Optimizes bandwidth management and improves network security.
- Digital Trust Technologies: Ensures secure data transfer and safeguards user privacy.
Smart Cities
- Autonomous Vehicles: Improve urban mobility and reduce traffic congestion.
- Zero Latency Connectivity: Improves communication and enables smart infrastructure management in urban environments.
- Climate Technology: Sustainable urban planning and energy-efficient solutions enable climate-positive cities.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Navigating the Double-Edged Sword of Disruptive Innovation
While these emerging technologies are driving unprecedented advances, they simultaneously cast shadows of challenges and ethical dilemmas. Like any powerful tool, these technologies carry hazards that might outweigh their enormous advantages if not used carefully.
This section dives into the challenges we face and the ethical quandaries that force us to consider the deeper implications of our technological pursuits.
Challenges
- Integration with Existing Systems: Merging new technologies into current systems often demands substantial adjustments and leads to compatibility issues with legacy systems.
- Skill Gap: As newer technologies emerge, there is a growing demand for skilled professionals. Many industries face the challenge of a skill gap where there aren’t enough qualified individuals to handle novel technologies.
- Security Concerns: The growing number of connected devices increases their vulnerability to cyberattacks and data breaches.
- High Initial Costs: Investing in cutting-edge technology requires a significant financial outlay before any return on investment (ROI) is realized.
- Reliability and Maturity: Not all emerging technologies have been tested at scale, leading to concerns about their reliability and long-term viability.
Ethical Considerations
- Data Privacy: As data becomes the new oil, concerns about who has access to this data, and how it is used, become paramount. Ensuring data privacy and informed consent is crucial.
- Bias and Fairness: AI and machine learning models unintentionally perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Transparency and Accountability: With systems making autonomous decisions, ensuring transparency in how they operate and holding them accountable becomes a significant concern.
- Job Displacement: Technological advancements render certain job roles obsolete, leading to economic and social implications.
- Environmental Impact: While many technologies reduce environmental harm, producing and disposing of tech products have detrimental environmental effects.
Emerging technologies, while holding promise for a brighter, more efficient future, come with their set of challenges and ethical dilemmas. Balancing innovation with responsibility will be the key to ensuring that these technologies benefit society at large without compromising on fundamental values and rights.
To Stay Ahead of the Technology Curve, it’s More Important than ever to be Proactive
Identifying and understanding technological advancements and developments is foundational to navigating the complexities of the business landscape, ensuring both relevance and resilience. However, broad awareness is just the starting point. Each sector faces unique challenges and opportunities shaped by future technologies, and a one-size-fits-all approach does not suffice.
Specialized innovation intelligence platforms cater to your needs and bridge the gap between knowledge and application. Take our AI- and Big Data-powered Discovery Platform, for instance. It covers over 4.7M emerging companies and over 20K tech trends globally – giving you a comprehensive and in-depth overview of the global startup ecosystem. Use it to efficiently identify startups and scaleups, tech trends, and emerging disruptive innovations before they become mainstream. Explore our Discovery Platform today and be at the forefront of technological change.



![AI Implementation | A Comprehensive Strategic Guide for Enterprises [2025-2030]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/AI-Implementation-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)
![AI in Agriculture: A Strategic Guide for Industry Leaders [2025-2030]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/AI-in-Agriculture-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)
![AI in Automotive: A Strategic Guide for Industry Leaders [2025-2030]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/AI-in-Automotive-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)




