The rise of technology in the healthcare industry leads to new developments that challenge existing structures. Emerging technologies not only bring fresh opportunities to healthcare providers and suppliers but they also empower patients. Personalization is one of the factors rising in demand – an expectation that is met by eHealth technologies.
Moreover, healthcare companies use this demand to their advantage by upgrading treatment and preventive models and integrating them with connected devices to satisfy patients’ needs. As the supply chain recognizes these transforming perspectives the need to innovate becomes apparent.
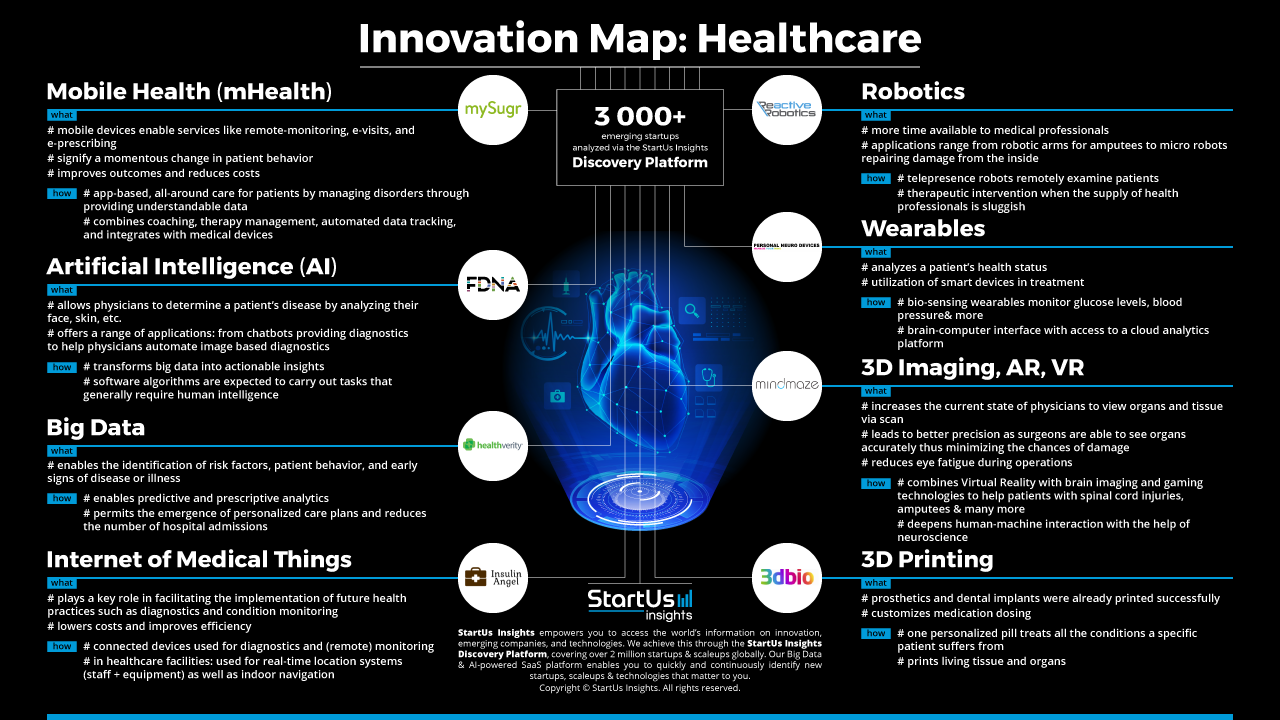
At StartUs Insights, we researched 3000+ startups to identify emerging technologies and business models, granting companies in the healthcare sector to gain a competitive advantage. The results of our proprietary innovation scouting approach are clustered in the Healthcare Innovation Map, revealing tomorrow’s key innovation areas and top disruptors:
Mobile Health (mHealth)
Currently, mHealth is perceived as the heart of the eHealth revolution as it is the signifier for a drastic shift in patient behavior. In 2017, 1.7 billion people have downloaded health-related apps, portraying the increased demand for such tools. Services such as remote-monitoring, e-visits, and e-prescribing are all enabled by mobile devices and applications. Though mHealth offers advantages such as improved outcomes and reduced costs, securing devices and apps will be a challenge. Startups working on security technologies help to improve confidence which is key to successfully implement mHealth solutions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Though artificial intelligence (AI) is not yet extensively employed in the healthcare industry, this technology will essentially alter the way patients are treated. Within the next decade, software algorithms will disrupt current practices by carrying out tasks that generally require human intelligence. From chatbots providing diagnostics based on symptom input and automation supporting physicians in image-based diagnostics and making smart diagnoses – AI effectively reduces the risk of human errors.
Big Data & Predictive Analytics
Big data is crucial to the healthcare industry as it enables the accurate identification of risk factors, patient behavior as well as early signs of disease or illness. Through utilizing this technology, preventive measures become more effective as it builds the backbone of predictive and prescriptive analytics. Predictive analytics furthermore allow for the creation of personalized care plans, ultimately decreasing the number of hospital admissions.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
With current efforts to reduce costs, the Internet of Medical Things gains in significance as its connected solutions lower costs while improving efficiency. Moreover, the IoMT plays a key role in facilitating health practices such as diagnostics and condition monitoring. For healthcare providers and patients, this technology offers great benefits as connected mHealth devices used for diagnostics and monitoring ensure high quality at decreased costs. For healthcare facilities specifically, the Internet of Medical Things is significant in the context of real-time location systems (for staff and patients as well as equipment) and indoor navigation.
Robotics
Already implemented in healthcare today, the application of robotics in the healthcare industry range from robotic arms for amputees and micro-robots repairing damage from the inside to robo-assistants in surgeries. The next big step in this field is telepresence robots expected to examine patients in the coming years thus freeing up time from medical professionals.
Wearables
The increasing use of wearables enables two impactful use cases in the healthcare industry: real-time and remote patient monitoring. Making use of the data gathered by wearable devices grants the possibility to analyze a patient’s health status and even suggest the appropriate treatment. Examples of wearables range from devices monitoring blood glucose levels and blood pressure (bio-sensing wearables) to digital hearing aids and more. Wearables along with implantable sensors are key to integrating eHealth technologies in people’s lives seamlessly.
3D Imaging, Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR)
These technologies radically improve the current state of education, training, and treatment in the healthcare industry. In conjunction with AR and VR, medical professionals are enabled to view organs and tissue via scan, increasing the success of surgeries. Using 3D Imaging, virtual and augmented reality in a live environment leads to higher accuracy, ultimately minimizing the chance of damage. For surgeons specifically, these technologies in combination with enabled glasses reduce eye fatigue during an operation while surgeons in training benefit from a more advanced and effective educational experience.
3D Printing
The healthcare industry is expected to raise investments in 3D printing from 1.6% in 2016 to 20% by 2026. Though this technology has yet to have its breakthrough in the sector, prosthetics and dental implants have already been printed successfully. Moreover, 3D Printing allows for the creation of personalized medication dosing as well as personalized pills. Printed in various drug layers, patients could soon be taking only one instead of multiple pills. On top of these opportunities, the most ambitious goal for this technology is the creation of living tissue and organs – a goal expected to be reached within the next 20 years.
Disruptive Startups In The Healthcare Industry Include:
- Austrian mySugr specializes in app-based, all-around care for people affected by diabetes. The startup enables patients to manage the disorder by providing them with understandable data while also offering coaching, therapy management, unlimited test-strips, automated data tracking, and an integration with medical devices.
- BioTech startup FDNA allows physicians to determine a patient’s condition by analyzing their face through the Face2Gene app. Implemented using artificial intelligence, this startup makes use of deep learning to transform big data into actionable insights.
- Health Verity was founded in an effort to meet the growing demand for data in the healthcare industry. The cloud-based platform serves as a marketplace for data buyers and data providers with the aim to support clients in discovering, licensing, and linking patient data across a wide range of top-tier data providers.
- Berlin-based Insulin Angel leverages the Internet of Things (IoT) to offer a proximity and temperature device that notifies users before their medication reaches a critical temperature, reminds them in case they forgot to take their medication and sends an alarm in case they have lost their medication.
- Reactive Robotics develops an adaptive robotic system for critically ill patients. Thus, the German startup provides a new therapeutic intervention when the supply of healthcare professionals is sluggish while also tackling the inefficiency problem the industry currently faces.
- Personal Neuro Devices develops a brain-computer interface with access to a cloud analytics platform. The neuroscience startup’s solution Spark Headset keeps track of brain recovery after a concussion and treats associated symptoms.
- MindMaze aids patients who suffer from a stroke or spinal cord injury as well as amputees. The Swiss company combines VR with brain imaging and gaming technologies to deepen human-machine interaction with the help of neuroscience.
- Russian 3D Bioprinting Solutions already managed to print a mouse thyroid gland. The startup’s next goal is to create a functioning kidney. To accomplish this goal, the company relies on stem cells and hydrogels which are printed layer by layer.
From the innovation areas outlined in our Healthcare Innovation Map, it becomes clear that not only patients’ perspectives are changing but that the supplier side, too, realizes the need for innovation. In 2020, global healthcare spending is expected to reach €7.1 trillion, with digital technology accounting for the majority of it.
Technologies that support in self-managing (chronic) illnesses, give patients the possibility to self-diagnose and help medical professionals in coordinating better have a massive impact on the entire industry.
High costs from a decreasing relative productivity are counteracted with transforming technologies such as computer-aided diagnostics that free up time for medical professionals, wearables that provide an abundance of information, predictive analytics that estimate risks to take preventive action, and simulation learning that prepares medical professionals to work with humans – leading the healthcare industry towards a more cost-effective and sustainable future.

![AI in Healthcare: A Strategic Guide for Industry Leaders [2025-2030]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/AI-in-Healthcare-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)






