The space launch industry has been consistently growing with over 130 space launches occurring in 2021. However, the industry faces challenges such as the high cost of launching payloads, overcrowding of space, sustainability concerns, and more. Innovations in space launch systems are solving these challenges and paving the way for future missions to the moon, mars, and beyond. This report provides an overview of launch system trends. They range from reusable launch vehicles and engine systems to automation and payload management. Read more to find out how these innovations advance space missions.
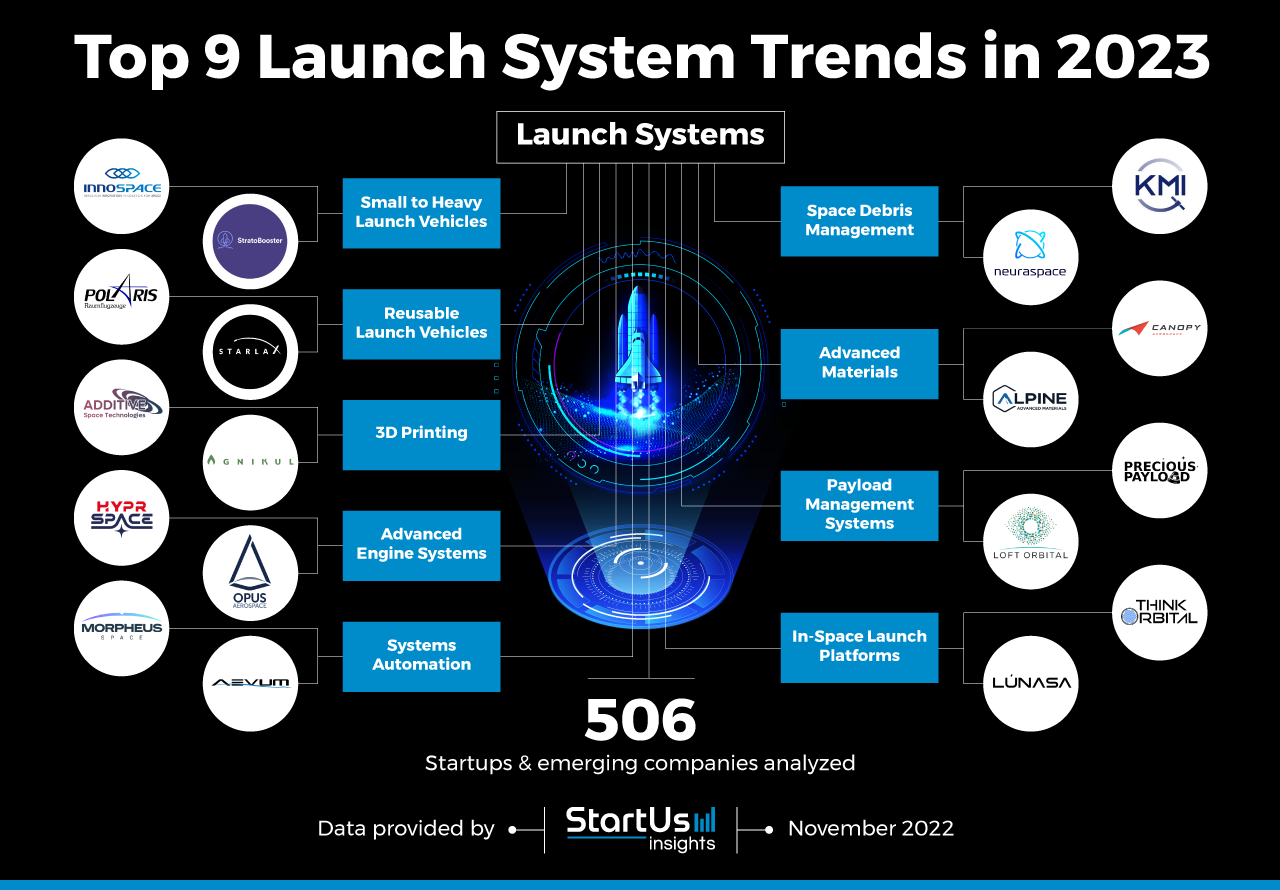
Innovation Map outlines the Top 9 Launch System Trends & 18 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Launch System Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 506 global startups & scaleups. The result of this research is data-driven innovation intelligence that improves strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging technologies & startups in the space industry. These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 2 500 000+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant startups, emerging technologies & future industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
In the Innovation Map below, you get an overview of the Top 9 Launch System Trends & Innovations that impact 506 companies worldwide. Moreover, the Launch System Innovation Map reveals 18 hand-picked startups, all working on emerging technologies that advance their field.
Top 9 Launch System Trends
- Small to Heavy Launch Vehicles
- Reusable Launch Vehicles
- 3D Printing
- Advanced Engine Systems
- Systems Automation
- Space Debris Management
- Advanced Materials
- Payload Management Systems
- In-Space Launch Platforms
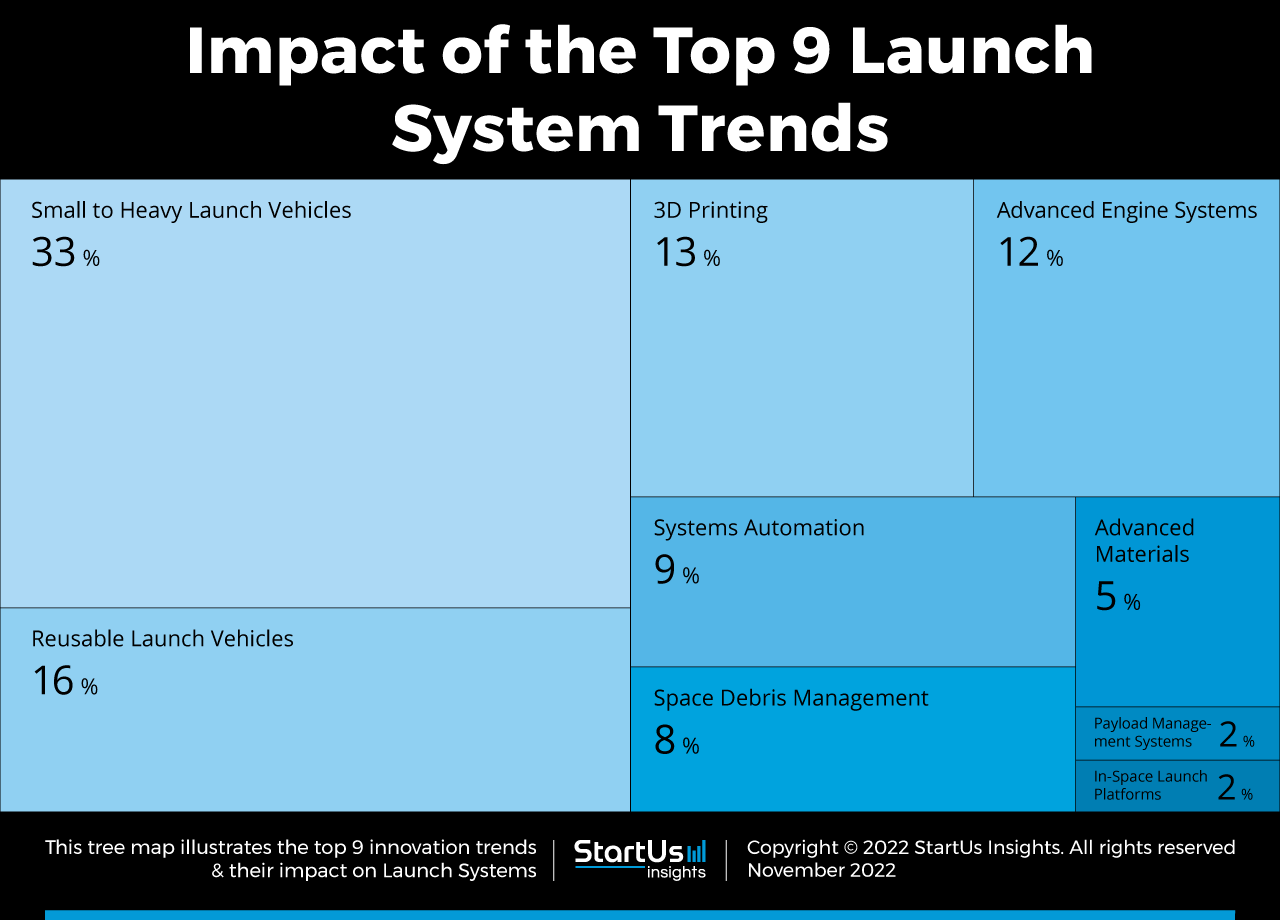
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 9 Launch System Trends
Based on the Launch System Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 9 Launch System Trends in 2023. Recent developments in small to heavy launch vehicles are advancing space missions, including low-earth orbit (LEO) experiments and satellite constellation deployment. Additionally, reusable launch vehicles promote sustainability and reduce the cost of subsequent space launches. Innovations in materials, 3d printing, engine systems, and in-space launch platforms improve launch efficiency for and beyond LEO applications. Moreover, systems automation leverages AI and autopiloting to make space travel safer and more accessible. Lastly, payload management systems assist in tracking component requirements while space debris management tackles the growing space junk problem.
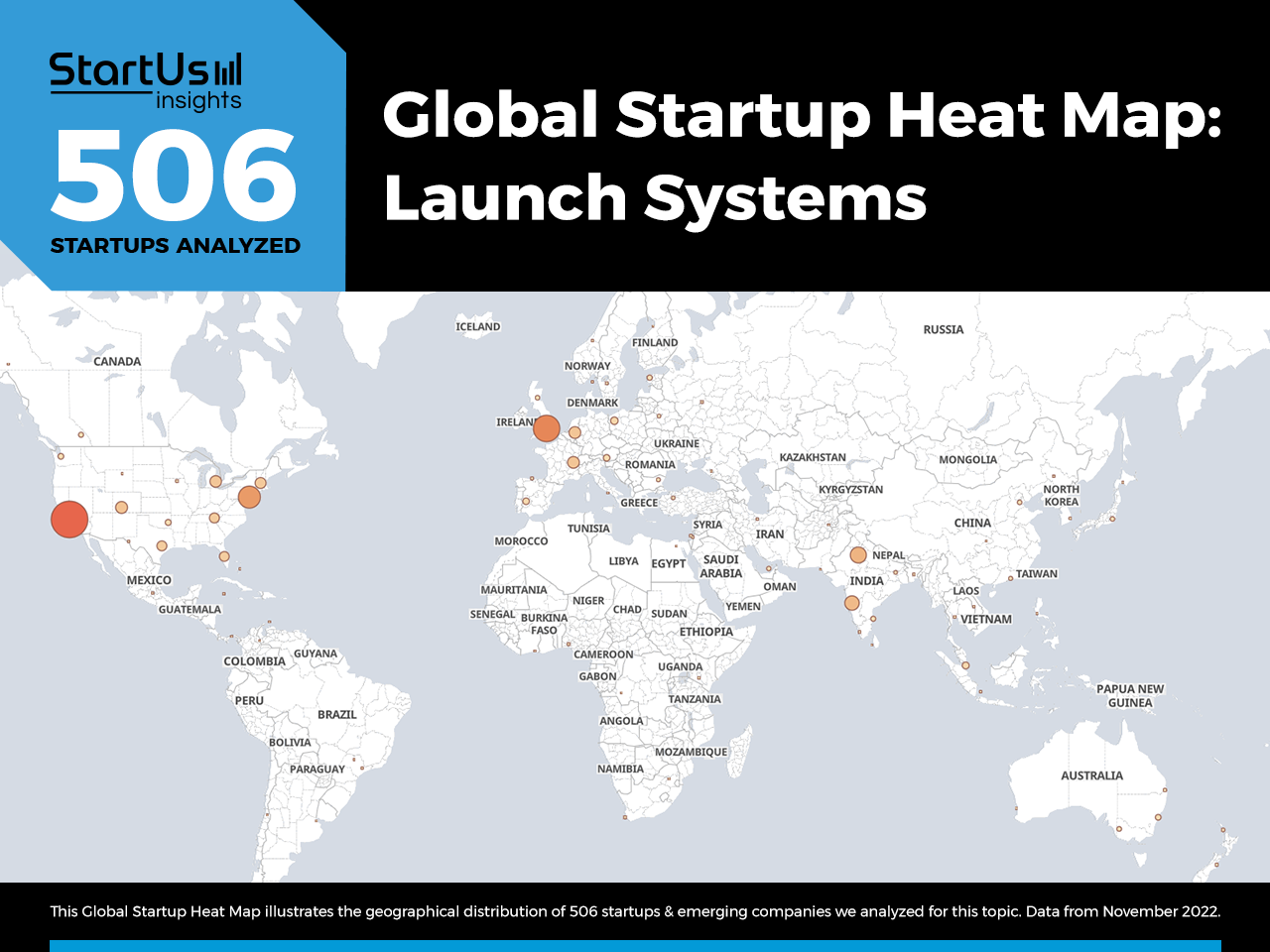
Global Startup Heat Map covers 506 Launch System Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 506 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals that the US sees the most startup activity.
Below, you get to meet 18 out of these 506 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These launch system startups are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Top 9 Launch System Trends in 2023
1. Small to Heavy Launch Vehicles
Even though the frequency of space launches increases, the cost of launching their payloads remains extremely high. Moreover, building bigger rockets to carry more payloads only adds to the technical challenge and danger of space launches without economical benefits. This is why startups are developing launch vehicles based on payload size and orbital requirements. This makes space launches more economical and accessible to more institutions and organizations.
INNOSPACE manufactures a Three-Stage Launch Vehicle
South Korean startup INNOSPACE advances space mobility through its hybrid rocket technology. The startup’s 3-stage smallsat launcher, HANBIT-MINI, carries a payload of 500kg up to a 500km sun-synchronous orbit (SSO). Additionally, its cluster of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd stage thrust engines makes launch from multiple locations possible at wide azimuth and inclination angles. INNOSPACE’s faster manufacturing and efficient propulsion system also aid cost-effective and more frequent space launches.
Stratobooster specializes in High-altitude Balloon Rocket Launch
UK-based startup Stratobooster develops a high-altitude balloon launch rocket system for small satellites and payloads. It utilizes a balloon that lifts rockets to an altitude of 32km, where the thin atmosphere reduces the amount of thrust a rocket needs. The use of balloons to lift rockets reduces operating costs and ground infrastructure requirements. This enables organizations and institutions to economically launch smaller payloads into space while ensuring safer operations than traditional space launches.
2. Reusable Launch Vehicles
The cost of space launches is incredibly high due to the single-use nature of most rocket boosters. Discarded boosters also increase the quantity of space junk and pose the danger of falling from orbit onto a city. To prevent such risks and make space launches more frequent, startups are developing reusable launch vehicles where the primary boosters are recoverable. In addition, reusable rockets improve the sustainability of the space launch industry.
POLARIS Raumflugzeuge enables Hypersonic Space Launch
German startup POLARIS Raumflugzeuge makes reusable space launch and hypersonic transport systems. Besides being reusable, the startup’s reusable launch system supports take-off and landing on conventional runways while improving mission flexibility and scalability. It finds applications in space cargo transport, human spaceflight, hypersonic defense, and more.
Starlax Aerospace manufactures a Reusable Small-lift Launch Vehicle
Indian startup Starlax Aerospace offers Genesis, a reusable small-lift launch vehicle to deliver small satellites to low earth orbit (LEO). It features a payload capacity of up to 950kgs and a three-stage propulsion system. The reusable rocket also utilizes a second-state vacuum-optimized engine and a third-stage engine that delivers satellites at multiple altitudes and inclinations. The reusability of their launch vehicles improves the scope of spaceflights and deep space missions.
3. 3D Printing
The construction of space vehicles is highly challenging as even small errors in production may lead to catastrophic failure during spaceflights. As a result, current manufacturing methods are highly meticulous, taking months to years even for low-volume production runs. This leads to very high labor, supply chain, and energy costs, among others. Therefore, advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and 3D printing, are addressing these problems to make space launches safer and cost-effective.
Additive Space Techechnologies creates 3D Printed Aerospace Vehicles
US-based startup Additive Space Technologies specializes in 3D-printing aerospace structures including launch vehicles and habitation modules. The startup’s integrated additive manufacturing and assembly process, Aperture, uses machine learning, intelligent collaborative designs, and advanced material processing. Aperture also features a patented high-precision robotic collaborative wire-arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) and assembly cell. It is supported by multiple integrated 3D printers, milling machines, and tender robots. Together with its proprietary 3D welding technology, the startup significantly reduces rocket construction time and accommodates design changes on the fly.
AgniKul Cosmos offers 3D Printed Launch Vehicle Engines
Indian startup AgniKul Cosmos makes 3D-printed launch vehicle engines. The startup’s semi-cryogenic engine, Agnilet, produces 3kN of thrust and works alongside its fiber-based thin-wall high-pressure propellant storage tanks. AgniKul Cosmos also manufactures a highly customizable 2-stage rocket, Agnibaan, with a payload capacity of up to 100kg. Besides being lower cost and sustainable, the startup’s printing process replaces multiple individual components in a typical engine with a single 3D printed component.
4. Advanced Engine Systems
Spaceflight engines receive continuous improvements in their performance and capabilities to carry payloads to higher orbits more efficiently. Besides, rocket launches generate a tremendous amount of greenhouse gases, presenting environmental concerns for space missions. Advanced propulsion systems mitigate these issues by leveraging sustainable manufacturing and novel fuels. They include mixtures of solid and liquid fuels and green fuels, among other options. Improvements in engine systems also enable more resource-efficient deployment of payloads further in space.
HyPrSpace develops a Hybrid Rocket Engine
French startup HyPrSpace provides a hybrid rocket engine that uses liquid and soil propellants. It features a liquid oxidizer storage tank that feeds into the combustion chamber containing the solid fuel. Through this system, the oxidizer flow rate modulates the thrust and avoids explosion in the event of failure. HyPrSpace‘s engines are also less sensitive to operational conditions, unlike current kerosene engines, and provide better reactant regression rates.
OPUS Aerospace creates Launch System Combustion Chambers
French startup OPUS Aerospace 3D-prints aluminum combustion chambers for satellites and the last stages of launchers. The startup’s platform, EPERVIER, produces a low carbon-footprint engine by 3D printing aluminum components in a single piece. OPUS Aerospace also manufactures ecological and economical launchers to place small payloads in low earth and sun-synchronous orbits at 500km. This enables space launch vehicle manufacturers to integrate sustainable components in their launch systems.
5. Systems Automation
Space launches are highly complex due to the calculations involved in phases of flight, on-orbit operations, reentry, and mission planning, among others. These complications only increase as space becomes more crowded with operational and defunct satellites and parts. Moreover, astronauts for manned space flight require a considerable amount of training to operate space vehicle systems. On the other hand, the automation of spaceflight systems and integration of AI into space launch systems greatly reduces these problems. This also lowers the risk of errors and makes space travel more accessible to humans.
Morpheus Space provides a Propulsion System Autopilot
US-based startup Morpheus Space develops an autopilot that integrates into propulsion systems. It is a part of the startup’s ecosystem, SPHERE, that provides the capability for autonomous orbital maneuvers for satellites. This entirely removes the need for satellite operators to use custom-written hardware and software for orbital maneuvers. Moreover, the autopilot enables them to simply specify target orbits while it does the calculations.
Aevum offers AI-powered Space Transport
Aevum is a US-based startup that creates AI-based reusable launch systems for space transport. The startup’s AI-powered global network, Aether Transport System, offers spaceports that serve as payload drop-off and operations facilities. Aevum also offers a digital interface, Space Portal, to configure transport services. This enables organizations and space agencies to access Aevum’s autonomous space transport services and quickly launch their payloads.

6. Space Debris Management
As space traffic grows, tracking objects becomes increasingly difficult while escalating the risk of collision. Moreover, a collision in space creates a large number of high-speed projectiles that risk the safety of all space assets in their orbit. Innovations in space debris capture and traffic management are addressing this safety issue. Novel space launch systems integrate debris management solutions to better navigate through space and are actively preventing the Kessler Syndrome.
Kall Morris advances Active Debris Removal
US-based startup Kall Morris develops hardware and software solutions to actively remove orbital debris. The startup’s hardware solution, REACCH, is a mechanically articulated end effector with electrostatic and gecko adhesion that enables soft and secure capture of space objects. Likewise, its software module, TUMBLEYE, identifies objects in space using machine learning and observes targets on approach. Lastly, the startup’s other product, LAELAPS, facilities debris collection by establishing communication with ground stations. It also measures thrust variations on the way to a target orbit. Through these solutions, space exploring companies are able to ensure their asset safety.
Neuraspace enables Smart Space Traffic Management
Portuguese startup Neuraspace develops a scalable AI and machine learning platform for smart space traffic management. Its collision avoidance system uses data fusion and combines data from multiple sources with AI-based object behavior prediction. The platform also automates the process from data ingestion to maneuver suggestion with continuous monitoring of satellites and AI-based alert prioritization and classification.
7. Advanced Materials
Outer space is an extremely hostile and harsh environment as well as poses a number of structural challenges for space vehicles. Moreover, space vehicle designers are restricted by weight limitations. Space vehicles also experience extreme temperature and pressure conditions twice, once when exiting the atmosphere and then on re-entry. Innovations in material engineering are enabling manufacturers to build space vehicles that are lighter, more resilient, and more economical.
Canopy Aerospace engineers Heat Shields
US-based startup Canopy Aerospace develops heat shields that protect spacecraft during re-entry. The startup’s thermal protection system (TPS) features a software solution that optimizes aerothermal conditions for different trajectories. It also automates the design of protective materials and provides cost reports. Further, Canopy Aerospace’s smart TPS composites contain multimodal sensing to detect anomalies at any stage of flight. The applications of their shielding include reusable rockets, orbital spaceflight, hypersonic travel, and more.
Alpine Advanced Materials creates Engineered-Composite Parts
US-based startup Alpine Advanced Materials manufactures high-performance engineered-composite parts for space vehicles. The startup’s nanocomposite material, HX5, offers the strength of aluminum with just half the weight. Besides, it performs well in hot and cold temperature extremes, has low shrinkage, high dimensional stability, and is corrosion resistant. The parts developed from HX5 are thus optimal for space-bound missions.
8. Payload Management Systems
Although rockets have a fixed payload capacity, the payloads have varying shapes and sizes depending on their mission. Payload components and materials need to adhere to mission designs and therefore have the risk of incompatibility. Besides, payloads play a vital role in determining the aerodynamics of rocket launches. For these reasons, startups are developing solutions that enable payload manufacturers to better tailor their payloads for specific missions. They also allow rocket launch operators to integrate payloads without any issues.
Precious Payload develops a Payload Supply Chain Platform
German startup Precious Payload offers a suite of products to optimize payload-related workflows. The startup’s software, Payload.ctrl, lets payload manufacturers manage their supply chains and identify component and subsystem suppliers. Additionally, it runs professional requests for information and proposals across payload and satellite component manufacturers. This enables payload manufacturers to keep their suppliers up to date with the latest revision of mission requirements.
Loft Orbital provides a Payload Integration Interface
US-based startup Loft Orbital makes software and hardware products to simplify space launch mission operations. The startup’s universal interface, Payload Hub, enables rapid integration of payloads without adding any constraints to their development. It also controls payloads and manages the communication and resources between payloads and the satellite bus. This reduces the complexity of constantly managing payloads to ensure that they meet mission parameters.
9. In-Space Launch Platforms
Launching objects into space requires a tremendous amount of energy to reach the escape velocity. Moreover, launching larger payloads means more cost, complexity, and greenhouse gas emissions. Space servicing costs are also high as servicing missions require launching repair vehicles from the earth. Therefore, in-space manufacturing and launching rockets and satellites from space remove nearly all drawbacks associated with traditional space launches. Additionally, launches from space make missions into deeper space easier.
ThinkOrbital offers Scalable Space Infrastructure
US-based startup Think Orbital provides scalable infrastructure for versatile space stations. They protect the habitat from orbital debris and thermal radiation as well as supports in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing (ISAM) activities. The service module also uses the international docking standard, making it simple to dock and launch space vehicles. Besides, the platform’s robotic arm features an electron beam welder for optimal operation in the vacuum. Think Orbital’s in-space infrastructure finds multiple applications including on-orbit storage, refueling, space tourism, research, and more.
Lunasa Space delivers Orbital Maintenance
UK-based startup Lunasa Space offers in-space maintenance services through a constellation of reusable and automated miniature orbital maintenance stations. The startup’s miniature space station, VIA, offers ridesharing and life-extension services for satellites in LEO. It also assists satellites in changing orbital planes and high-precision LEO altitude deployment while making satellite launch costs affordable.
Discover all Launch System Trends, Technologies & Startups
Reusable launch vehicles see increasing adoption as the number of space launch increase each year. More launches also drive the importance of space debris management to prevent collision and protect space assets. Further, advanced manufacturing methods are reducing production times while maintaining a zero error rate through automation. Advanced materials, such as self-healing materials, are protecting long-term space assets and their inhabitants. These solutions also make space tourism safer and cost-effective.
The Launch System Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Among others, reusable launch systems, energy-efficient propulsion, and deep space exploration will transform the sector as we know it today. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage. Get in touch to easily & exhaustively scout startups, technologies & trends that matter to you!