The maritime industry is leveraging technological advancements like robotics, autonomous vessels, and blockchain integration. These maritime trends improve logistics, maintenance, safety, and more across the sector.
Reflecting these trends, the global maritime market is projected to reach USD 2.92 trillion by 2035, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.69%.
This article explores the top 10 trends improving the maritime industry and highlights 20 emerging startups delivering such innovations.
What are the Top 10 Maritime Trends in 2025?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
- Green Energy & Energy Efficiency
- Maritime Robotics
- Cybersecurity
- Maritime Internet of Things (IoT) & 5G
- Blue Economy
- Tech-driven Safety & Risk Management
- Autonomous Vessels
- Blockchain Integration
- Smart Ports
Methodology: How We Created the Maritime Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 5M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our own startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the maritime industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the maritime innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Maritime Industry Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Maritime Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 1500+ global startups & scaleups. The Maritime Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the maritime industry trends & startups that impact your company.
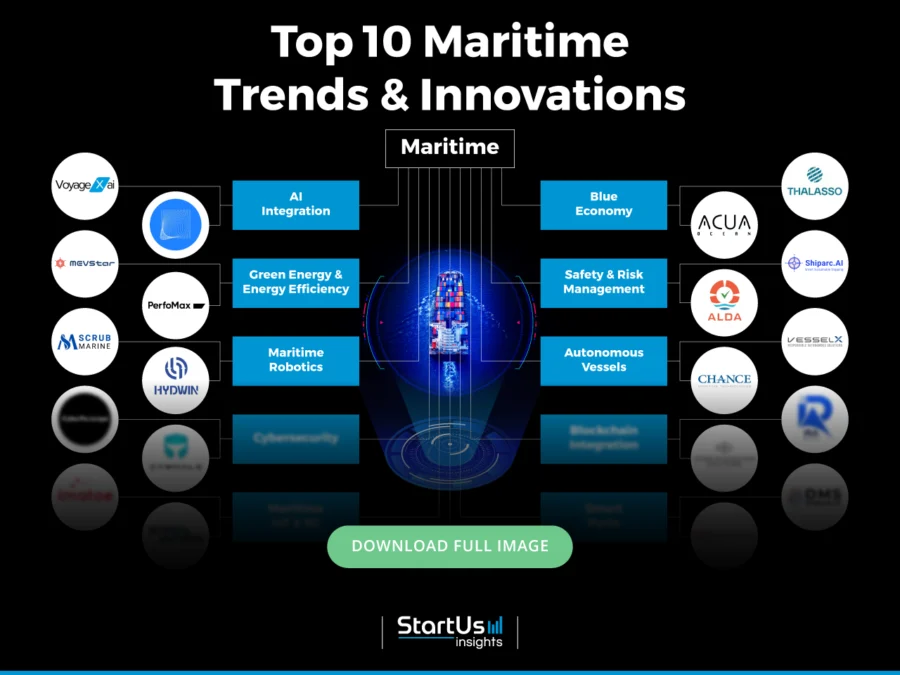
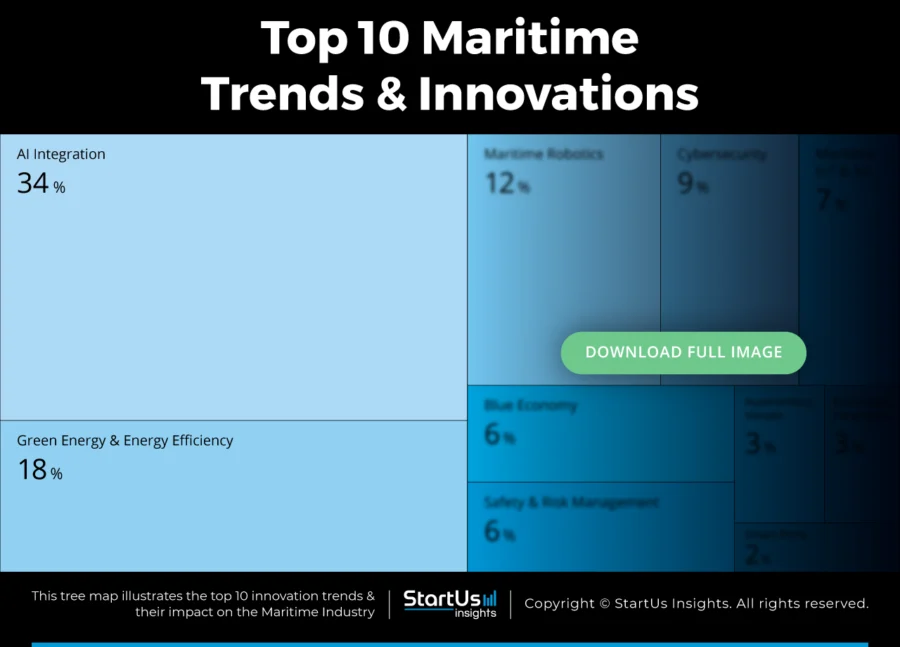
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Trends in Maritime
The Maritime Tree Map highlights the Top 10 Maritime Industry Trends shaping 2025. These include AI integration, green energy and energy efficiency, maritime robotics, and cybersecurity. It also includes maritime IoT & 5G, blue economy initiatives, tech-driven safety and risk management, autonomous vessels, blockchain integration, and smart ports. They improve maritime operations, vessel design, and port management to drive sustainable growth and advance the global maritime industry.
Global Startup Heat Map covers 1500+ Maritime Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 1500+ exemplary startups and scaleups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in Western Europe and the United States, followed by India. From these, 20 promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.
Want to Explore Maritime Innovations & Trends?
Top 10 Emerging Maritime Trends [2025 and Beyond]
1. AI Integration
AI optimizes navigation, predicts failures, and reduces emissions. It drives efficiency, safety, and sustainability across the maritime industry.
AI-powered route optimization systems analyze weather, currents, and traffic to plot fuel-efficient routes.
Similarly, machine learning models predict equipment failures by analyzing sensor data from engines, pumps, and other machinery. For example, ABS’ My Digital Fleet monitors vessel health and alerts crews to potential breakdowns.
AI systems also support maritime operations with real-time decision-making. For instance, Wartsila’s smart prediction system utilizes AI to assist in ship movement by providing predictive insights based on real-time data.
Another example – Bearing AI uses predictive analytics on over 300 K-Line vessels to optimize fuel consumption, speed, and performance.
Presently, the AI market in the maritime transport industry alone is expected to grow from USD 6.24 billion in 2025 to USD 8.09 billion in 2029 at a CAGR of 6.7%.

Credit: The Business Research Company
Solutions like AI-driven robotic systems perform tasks such as hull cleaning and cargo handling. The NRMA’s Manly Fast Ferry implemented an autonomous hull cleaning system that led to a 13% reduction in diesel use by preventing biofouling.
In addition, the integration of IoT devices with AI facilitates real-time monitoring of vessel systems. For example, Orca AI developed a real-time data streaming platform that improves vessel performance and regulatory compliance.
Further, AI monitors and mitigates environmental impacts. It maps sea pollution and provides crucial data for environmental protection efforts.
AI-assisted annotation has also been employed to improve marine biodiversity observations from real-time video feeds.
VoyageX AI delivers AI-based Ship Management Software
VoyageX AI is an Indian startup that offers AI-driven maritime solutions to streamline and improve ship management.
Its vessel management software integrates core functions such as crewing, compliance, maintenance, and performance tracking into a unified platform to provide real-time insights.
Additionally, the crew management software automates processes like recruitment, certification tracking, scheduling, and payroll for efficient personnel management and regulatory adherence.
The planned maintenance system also uses predictive analytics to schedule and monitor vessel upkeep. The safety management software facilitates compliance with international safety standards by offering real-time tracking, incident reporting, and risk assessments.
Moreover, the marine procurement software automates requisitions, vendor selection, and inventory management for the timely procurement of supplies.

Further, the vessel performance system provides real-time data and actionable insights to optimize fuel efficiency, monitor emissions, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Harmony Maritime Solutions creates an AI-powered Robotic Platform
US-based startup Harmony Maritime Solutions develops Mantis Vision System, an AI-powered platform for maritime maintenance and security.
It integrates imaging and machine learning algorithms to perform automated barnacle cleaning, hull crack detection, and continuous surveillance of vessels and maritime facilities. Moreover, it removes barnacles from hulls using eco-friendly robotic systems to reduce fuel consumption and improve vessel efficiency.
Besides, its AI-driven sensors detect micro-cracks and structural weaknesses in real time to support timely maintenance and regulatory compliance. The platform further employs AI-powered cameras to monitor underwater and surface activity while providing continuous security coverage for docks, marinas, and ships.
2. Green Energy & Energy Efficiency
Maritime transport accounts for 2–3% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Hence, implementing green energy solutions, such as alternative fuels and renewable energy sources, as well as energy efficiency technologies, is critical to reduce the environmental footprint.
Additionally, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) targets full shipping decarbonization by 2050. This is also driving the adoption of green energy solutions to meet compliance regulations.
Energy-efficient technologies reduce fuel consumption and lead to cost savings. For instance, wind-assisted propulsion systems offer annual fuel savings of about 5-20%.
Highlighting these developments, the global marine vessel energy efficiency market size is expected to reach USD 5.28 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 12.13%.
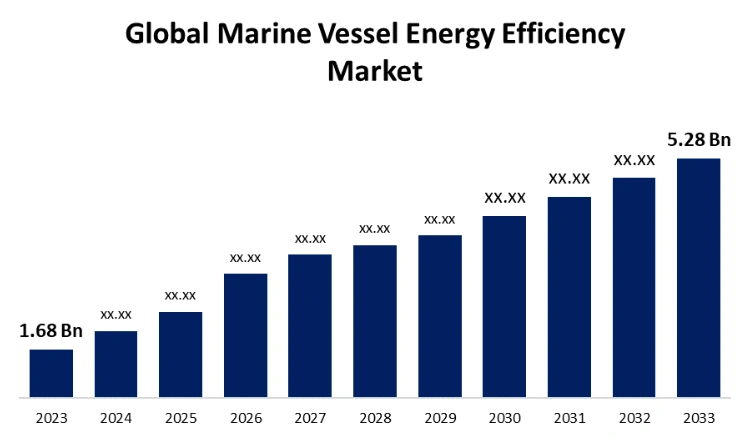
Credit: Spherical Insights
The adoption of low-carbon fuels such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), hydrogen, ammonia, and biofuels also produces fewer emissions. For instance, 169 LNG-powered ships were introduced to support the transition to net-zero emissions. Thus, operators deploy a total of 641 LNG-powered ships worldwide.
Additionally, technologies like rigid sails and rotor sails use wind energy to reduce fuel consumption. For instance, the Oceanbird project targets to lower emissions by up to 90% using expandable wing sails.
Air lubrication systems also create a layer of air bubbles along the hull. These systems reduce friction between the ship and water and lead to fuel savings.
Silverstream Technologies’ ALS delivers fuel savings of 7% for LNG carriers, 6% for tankers and bulk carriers, and up to 6% for cruise ships and ro-ro vessels.
Moreover, Norway has mandated that cruise ships must be zero-emission by 2032 in its fjords. This has prompted the development of electric and hybrid vessels.
Further, shore power adoption in ports is allowing ships to turn off auxiliary engines while docked, thus reducing emissions.
AI and autonomous systems also enable vessels to operate with minimal human input while optimizing routes and improving fuel efficiency.
MEVStar makes a Silicon Carbide (SiC) Converter
Danish startup MEVStar manufactures a silicon carbide MOSFET-based converter that improves power efficiency in maritime energy systems. The converter integrates with medium voltage batteries to manage alternating current (AC)/direct current (DC) power conversion.
It operates at high switching frequencies by reducing system size and weight while increasing efficiency. The converter also supports voltages up to 10 kV for optimal performance in space-constrained environments.
MEVStar also provides shore power and ferry charging solutions that accommodate medium to high-voltage applications. It also incorporates renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to enhance sustainability.
The converter systems enable flexible integration with existing vessel infrastructure and expand utility through electric vehicle (EV) charging stations at ports.
PerfoMax offers Vessel Monitoring and Optimization Platform
Singaporean startup PerfoMax delivers a digital platform that monitors and optimizes vessel operational efficiency using AI and digital twin. The platform collects data through non-invasive sensors by enabling rapid digitization of vessels without altering existing piping or wiring.
It also creates a sensor-based digital twin tailored to each vessel and its machinery to generate accurate performance predictions through adaptive models and normalized estimations.
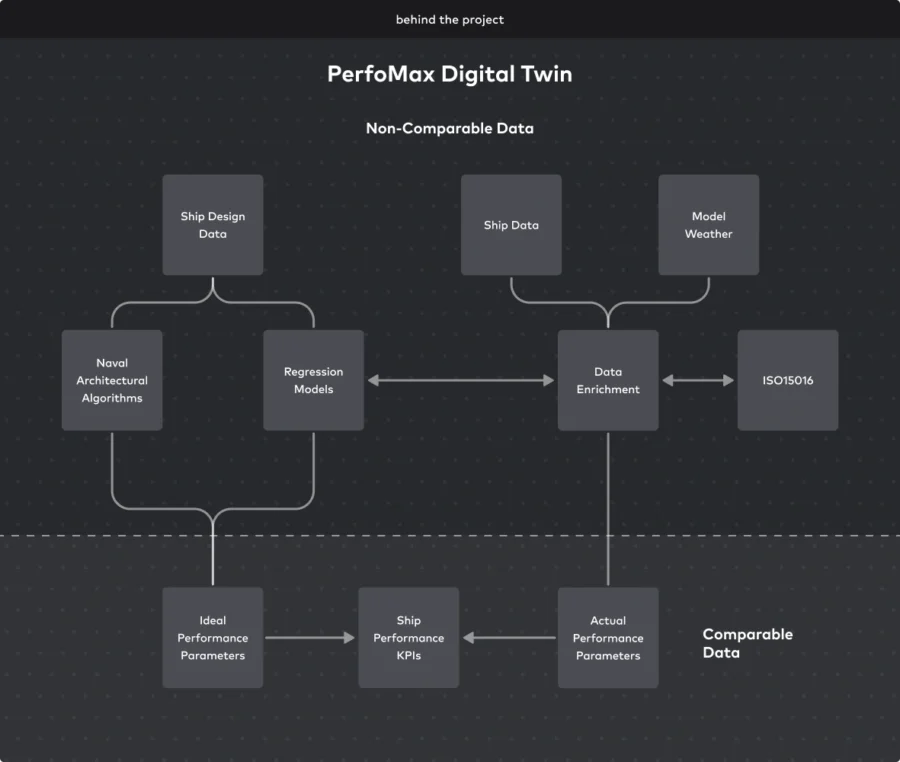
Moreover, PerfoMax’s AI co-pilot continuously monitors vessel operations to identify discrepancies and communicate insights in human language. The platform also tracks fuel consumption and emissions and provides dashboards and investigation analytics.
3. Maritime Robotics
The maritime sector involves hazardous tasks that pose major risks to human workers. Robots mitigate these dangers by taking on high-risk operations while enhancing operational efficiency.
For example, the US Navy is developing robotic crawlers to detect and neutralize underwater mines. This reduces the exposure of personnel to life-threatening situations.
Maritime robotics also automates tasks and reduces operational costs. The NRMA’s trial of the autonomous hull cleaning system resulted in a 13% reduction in diesel consumption for their Manly Fast Ferry fleet.
Moreover, unmanned systems improve naval capabilities without risking human lives. NATO’s Task Force X utilizes naval drones to protect undersea infrastructure and counter potential threats. This showcases the strategic importance of maritime robotics.
Maritime activities often require continuous environmental data collection to support research and monitoring efforts. Robotics simplifies this process by enabling constant and precise data gathering.
Currently, the global underwater robotics market is estimated to grow from USD 4.53 billion in 2025 to USD 7.14 billion in 2029 at a CAGR of 12.0%.

Credit: The Business Research Company
Organizations are now deploying autonomous surface vessels (ASVs) for surveillance and environmental monitoring. ThayerMahan’s SeaPicket buoys and outpost uncrewed surface vehicles autonomously monitor vast ocean areas.
Additionally, unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs), such as Boeing’s Orca and DARPA’s Manta Ray, operate autonomously for prolonged periods underwater. These UUVs improve intelligence gathering, protect undersea infrastructure, and counter threats.
Collaborative robotics (cobots) are also utilized in shipyards to assist human workers in tasks like welding and assembly.
Mobile manipulator robots further perform tasks such as material handling and equipment maintenance on ships.
Also, swarm robotics enables data collection over vast ocean areas and improves the monitoring of marine ecosystems.
For example, the EONIOS project off the coast of Ayia Napa, Cyprus, employs a swarm of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) to monitor 3D-printed artificial reefs.
Swarm robotics is also used for surveillance and defense. The US Department of Defense is developing autonomous swarm robots that travel up to 1000 nautical miles, carry 1000-pound payloads, and intercept vessels of interest.
ScrubMarine provides a Cavitation Cleaning Robot
UK-based startup ScrubMarine builds a submersible robotic system, ScrubMarine. It removes biofouling from vessel hulls using cavitation cleaning technology to reduce hull resistance and improve fuel efficiency.
The robot operates underwater without dry-docking, diver intervention, or chemical treatments. This allows vessels to undergo maintenance while remaining in service.

In addition, ScrubMarine automates hull cleaning using an environmentally friendly method that avoids releasing harmful substances into marine ecosystems. It reduces fuel consumption and promotes more sustainable practices in maritime operations.
Hydwin builds Hull Coating Removal Vehicles
Chinese startup Hydwin develops a robotic system that automates hull coating removal using ultra-high-pressure (UHP) water jet technology.
The company’s Treatment Carrier D10 and Treatment Carrier X25 platforms integrate AI-driven algorithms with UHP components for surface preparation on ship hulls. Both systems conform to WJ-2 / Wa 2½ standards for near-white metal cleaning quality without relying on chemicals or abrasive blasting.
Further, Hydwin reduces maintenance time, improves coating performance, and supports sustainable ship maintenance through high-pressure water jet technology and adaptive AI control.
4. Cybersecurity
Maritime operations depend on essential infrastructure like undersea cables, which are susceptible to sabotage. For instance, undersea fiber-optic cables connecting Finland to Germany were mysteriously severed. This raised concerns about a potential sabotage and highlights the need for improved cybersecurity measures in maritime.
Also, the integration of automation and digitalization in maritime operations improves efficiency and introduces vulnerabilities in operational technology (OT) systems. At the same time, the growth in connected devices within the industry increases the attack surface.
The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) is actively addressing these evolving cyberthreats. This agency is emphasizing the need for cybersecurity measures across critical infrastructures, including the maritime sector.
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and take automated actions to prevent potential threats in the maritime sector.
Additionally, businesses and devices authenticate and authorize before accessing network resources by implementing zero-trust security models.
For instance, Rakuten Symphony’s maritime cybersecurity service, Rakuten Maritime, integrates zero-trust-based technologies to improve vessel security.
Further, digital twins create virtual replicas of physical systems for enabling real-time monitoring and threat detection. For example, the TwinPot system employs digital twin-assisted honeypots to improve cybersecurity in smart seaports.
Moreover, AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms analyze patterns in network traffic to identify anomalies indicative of cyber threats. Blockchain also ensures data integrity and transparency in maritime operations by securing data-sharing platforms in the maritime sector.
Besides, maritime security operations centers (SOCs) tackle limited bandwidth challenges by using local caching and data compression. These features ensure effective cybersecurity measures are maintained, even with connectivity constraints.
Cyber Periscope enables Unified Maritime Cybersecurity
Indian startup Cyber Periscope builds a cybersecurity platform that secures maritime operations using AI-driven anomaly detection, blockchain auditing, and quantum-resistant protocols.
The platform employs real-time threat response and adaptive policy enforcement to prevent data loss. Its immutable logging system further leverages distributed ledger technology and smart contracts to ensure regulatory compliance.
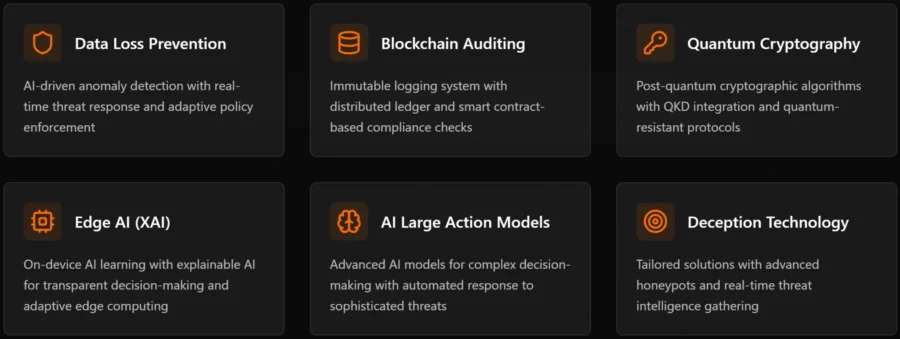
It also integrates post-quantum cryptographic algorithms and quantum key distribution (QKD) to secure communication against emerging threats. Cyber Periscope incorporates edge AI with explainable decision-making and deploys large action models (LAMs) to automate responses to complex cyberattacks. Further, the platform features tailored honeypots and real-time threat intelligence to identify and counter intrusions proactively.
Cywhale simplifies IT & OT Monitoring for Anomaly Detection
Israeli startup Cywhale offers a plug-and-play cybersecurity system that monitors and protects information technology (IT) and OT networks on maritime vessels.
It utilizes anomaly detection algorithms and deep analysis of National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA) protocols to identify cyber threats in real time. This enables continuous monitoring of critical onboard systems and transmits immediate alerts via satellite to both ship crews and onshore operations.
Cywhale secures vessel operations by providing real-time monitoring, sending automated alerts, and overseeing assets. It enables shipping companies to control their digital infrastructure and maintain operational resilience.
5. Maritime IoT & 5G
Maritime operations prioritize safety, operational efficiency, environmental protection, and crew welfare. Implementing 5G’s high-speed, low-latency connectivity facilitates real-time data transmission between ships and onshore operations to enable automation and more efficient vessel management.
For example, VTT, in collaboration with partners in the 5G-ROUTES project, successfully trialed a multi-hop 5G solution that provides real-time video transmission between vessels and virtual reality (VR) collaboration tools.
Also, maritime operations encounter unexpected equipment breakdowns. This necessitates optimized maintenance schedules. Operators monitor engine performance and fuel consumption in real time by installing IoT sensors on maritime equipment.
Additionally, port operators use IoT and 5G technologies to develop smart ports by tracking cargo in real time, operating automated equipment like cranes and guided vehicles for loading and unloading. These technologies also improve operations and traffic management.
Highlighting these innovations, the global marine IoT market is expected to reach USD 2.41 trillion by 2032.
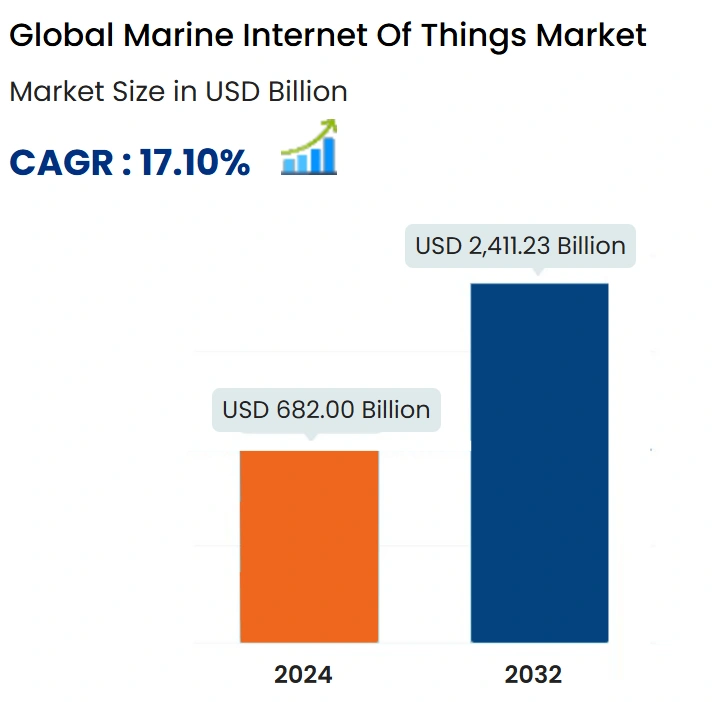
Credit: Data Bridge Market Research
Hybrid cellular (NTN) IoT networks are a combination of terrestrial and satellite networks that offer reliable connectivity in remote maritime areas. Eutelsat, in collaboration with Airbus and MediaTek, conducted a successful trial of a 5G NTN connection using OneWeb’s low Earth orbit satellites.
Moreover, AI algorithms process data from IoT sensors to optimize navigation routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve safety by predicting and avoiding potential hazards.
Deploying edge computing devices onboard also allows for local data processing while reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
Further, satellite-based IoT connectivity ensures uninterrupted connectivity for maritime operations. For instance, OQ Technology has partnered with O2 Telefonica to provide global 5G IoT services for maritime applications.
Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) also allows multiple devices to share the same frequency band by allocating different power levels. This is beneficial in maritime IoT networks where sensors and devices operate simultaneously.
imatoe offers IoT & AI-based Marine Automation Solutions
UAE-based startup imatoe provides marine automation solutions that combine IoT and AI to improve vessel performance, safety, and efficiency. The startup’s solutions offer real-time onboard equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, and intelligent decision-making to optimize fuel consumption and navigation accuracy.
AI-based route optimization supports efficient voyage planning, while collision detection and crew safety systems improve operational security. Additionally, imatoe provides asset reliability services, including vibration analysis and thermography, to extend machinery lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
The startup’s ship automation solutions cover alarms, and electrical, pneumatic, and hydraulic control systems. imatoe further offers cybersecurity audits for maritime IT and OT systems to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance.
Delta Digital offers a Sustainable Industrial IoT (IIoT) Platform
Dutch startup Delta Digital delivers DeltaOS, an IIoT platform that connects, monitors, and manages machines, installations, and vessels in real time. The platform processes data from sensors, edge devices, and building management systems (BMS) using protocols like ModBus, BACnet, and MQTT.
Additionally, it provides secure data storage and enables businesses to visualize performance metrics through reporting tools. Automated triggers and alerts also facilitate immediate action based on real-time conditions.
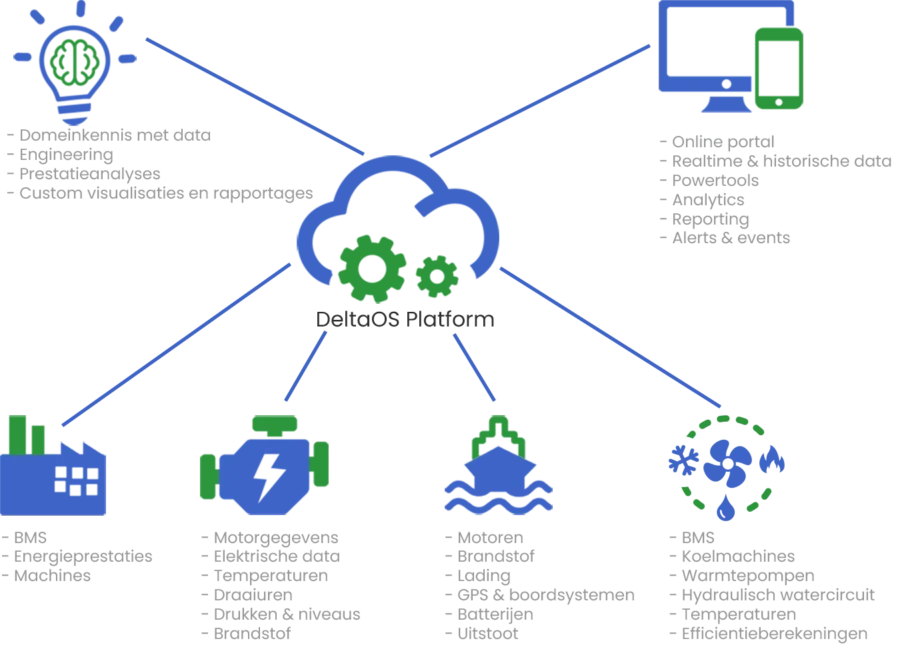
Further, DeltaOS integrates with ERP systems and maintenance software through its web application programming interface (API) to simplify data flow.

6. Blue Economy
The blue economy offers economic growth, improves livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of ocean ecosystems. This approach includes sustainable fisheries, aquaculture, marine biotechnology, renewable energy, and ecotourism that balance economic development with environmental sustainability.
According to the World Economic Forum, the blue economy market size is projected to double to USD 3 trillion by 2030.
Additionally, global temperatures exceeded 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels for the first time, with the World Meteorological Organization confirming it as the warmest year on record.
This rise highlights the urgent need to address climate change and protect biodiversity.
Hence, the blue economy plays a vital role in this by prioritizing the health of ocean ecosystems, reducing pollution, protecting biodiversity, and mitigating climate change impacts.
The emphasis on the blue economy also advances renewable energy initiatives, like offshore wind and tidal power, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Norway has mandated zero-emission operations for cruise ships in its World Heritage Fjords by 2032.
Solutions like AI-powered predictive analytics also optimize vessel routes and reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) implemented AI-driven ship monitoring to detect illegal fishing activities and oil spills.
For example, the Port of Rotterdam expanded its IoT infrastructure by using digital twins to improve supply chain efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
Additionally, underwater drones assess marine biodiversity, offshore wind farms, and seabed mining sites. The US Navy deployed AI-powered autonomous underwater drones for deep-sea mapping.
Thalasso advances Seaweed Management
Norwegian startup Thalasso offers autonomous harvesting and biorefinery technologies to manage sargassum blooms and leverage the economic potential of seaweed.
Its Ocean Harvester is a fully autonomous, electric-powered system that collects sargassum without harming marine life. It uses sensors and onboard AI to identify seaweed clusters, then deploys mechanical arms and conveyor systems to gather and store the sargassum.
Additionally, Thalasso deploys mobile micro biorefineries that convert harvested seaweed into valuable chemical compounds. These compounds serve industries like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, agriculture, and fashion.
These compact refineries are easy to install, enable on-site processing, and reduce transportation emissions while maximizing product yields.
ACUA Ocean advances Environmental Monitoring
ACUA Ocean is a UK-based startup that delivers unmanned surface vessels (USVs) for full open ocean operations. These USVs enable the deployment of modular sensors and system payloads.
Its H-USV measures 14.2 meters and provides the space, weight, and power capacity to carry payloads of up to 6.5 tonnes. It is also deployed from a 20ft ISO container through the moonpool.
Moreover, the vessel operates reliably in wave heights of up to 4 meters, which maintains stability and ensures safe deployment of equipment in challenging sea conditions.
Additionally, ACUA Ocean’s modular design supports persistent maritime operations, including ocean data collection and critical infrastructure monitoring.
7. Tech-driven Safety & Risk Management
Geopolitical tensions and port congestion lead to increased operational costs and fuel consumption in the maritime industry.
Instances like attacks by Yemen’s Houthi militia prompted maritime companies to divert vessels around the Cape of Good Hope to avoid the Red Sea.
Maritime crew members also face hazardous tasks such as handling heavy loads and exposure to toxic chemicals.
Automation and robotics undertake these dangerous tasks which reduce risks to crew safety.
Enhanced communication systems, including low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite networks, enable constant contact with shore-based support and family, thereby improving crew welfare.
Remote operated vehicles (ROVs) perform underwater inspections and maintenance that reduce the need for divers and increase safety during hazardous tasks.
Technologies like those of GoComet’s port congestion tracker, MarineTraffic provide real-time data on port congestion to assist in route planning and scheduling. This mitigates delay and reduces operational costs.
Autonomous surface vessels (ASVs) operate without human intervention to take over high-risk maritime tasks. They handle operations such as navigating pirate-prone waters and working in extreme weather conditions, reducing the danger to onboard crews.
The UK and France recently deployed an AI-powered mine counter measures system that uses autonomous drone boats to detect and neutralize naval mines.
Moreover, AI algorithms analyze data from vessel equipment to predict maintenance needs. This prevents unexpected failures and reduces downtime.
The global maritime safety system market size is expected to grow from USD 22.04 billion in 2025 to USD 26.29 billion in 2029 at a CAGR of 5.9%.

Credit: The Business Research Company
Shiparc.AI provides AI-driven Safety Insights
UAE-based startup Shiparc.AI delivers an algorithm-based software platform that increases safety through data-driven insights and predictive analytics.
This platform collects and analyzes real-time data from crew hazard reports, fatigue assessments, and vessel operations. It also identifies leading and lagging health, safety, and environmental (HSE) indicators across fleets.
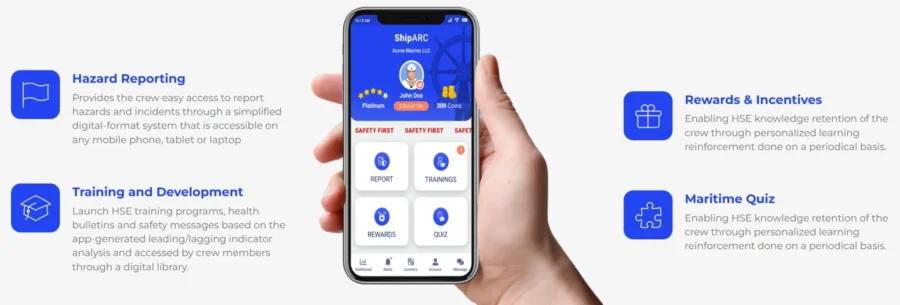
Moreover, the platform features AI-enabled predictive models that allow companies to assess potential risks. This enables proactive measures to prevent incidents, protect crew safety, and reduce environmental impact.
Additionally, Shiparc.AI tracks crew training and performance while providing insights into compliance and identifying peak performers and underperformers. Its centralized dashboard offers onshore teams and senior management access to live statistics and in-depth analyses.
Alda Oryggi develops a Fishing Vessel Safety Management Platform
Iceland-based startup Alda Oryggi builds a digital safety management platform that simplifies and increases safety practices on fishing vessels. It allows crew members to conduct safety training, complete inspections, and manage safety procedures directly from smartphones.
Moreover, this platform enables real-time engagement and ownership of onboard safety tasks while reducing the risk of accidents. Additionally, the startup’s web admin interface provides captains and safety managers with a real-time overview of safety performance like completed drills, inspections, and compliance.
8. Autonomous Vessels
Human error is a major factor in maritime accidents, accounting for approximately 75% to 96% of incidents. Also, crew-related expenses like wages, salaries, fringe benefits, etc, consume a major portion of a vessel’s operating costs.
Additionally, with global oil demand projected to grow by 1.1 million barrels per day in 2025, up from 870K barrels per day in 2024, hence, it is important to implement innovative strategies that reduce fuel consumption and lower operational costs.
Yara Birkeland, operates the world’s first fully electric, autonomous container ship to transport fertilizer from its Porsgrunn plant to the port of Brevik in Norway. The vessel replaces about 40K diesel truck trips each year and reduces CO₂ emissions significantly.
Advanced sensor systems like radar, lidar, sonar, and optical sensors enable autonomous vessels to accurately perceive surroundings and ensure safe navigation.
Further, autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) perform tasks, like hull inspections and environmental monitoring. This reduces the need for divers and improves safety.
For instance, the Manta Ray AUV, developed by DARPA, supports extended-duration missions without human intervention.
The autonomous ship market size is estimated at USD 8.99 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 12.79 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.3% during the forecast period 2025-2030.
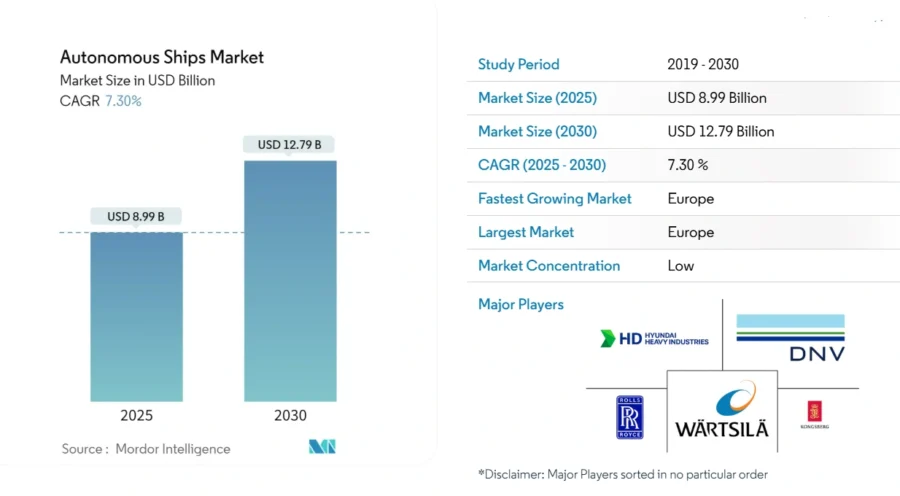
Credit: Mordor Intelligence
Vessel X provides a Small-Craft Water Surface Cleaning Vessel
Vessel X is a Turkish startup that develops Vatoz, an autonomous small-craft vessel that collects floating waste from water surfaces in marinas and ports.
The vessel operates using AI and supports autonomous and remote control modes. Moreover, it features a low-draft design that also allows waste collection in shallow water areas and runs on rechargeable electric batteries to ensure zero emissions.
In addition to waste collection, Vatoz monitors water quality and provides valuable data to support environmental management efforts.
Chance Maritime Technologies deploys Uncrewed Surface Vessels
US-based startup Chance Maritime Technologies offers a fleet of long-endurance uncrewed surface vessels for autonomous maritime operations.
Its USVs, including MC29, MC40, and LR30, are engineered for extended missions ranging from hydrographic surveys to fisheries monitoring and ocean depth data collection.
Moreover, the MC29 operates continuously for over 20 days and features a configurable moon pool for custom payloads. The MC40 also extends endurance to over 90 days and includes a large aft mission bay and gyrostabilizer for stable data collection in higher sea states.
Further, Chance Maritime Technologies offers modular payload options and reliable data collection without requiring capital investment in vessel ownership. This allows maritime companies to access ocean data collection capabilities and improve their operations without incurring high ownership and maintenance costs.
9. Blockchain Integration
Blockchain features self-executing smart contracts with terms directly embedded into code to automate processes like cargo release and payment settlements. This reduces the need for intermediaries and minimizes administrative overhead.
Additionally, decentralized applications (dApps) facilitate direct interactions between stakeholders, which improves transparency and reduces delays in the maritime sector.
Blockchain-based shipment tracking also enables real-time shipment monitoring by ensuring data immutability and transparency. This allows stakeholders to monitor cargo movements accurately.
For instance, the port of Shanghai implemented a blockchain-based platform to streamline logistics and improve cargo handling efficiency.
Moreover, blockchain’s decentralized architecture and cryptographic security protect against cyber threats like phishing attacks and malware. This safeguards sensitive maritime data.
Tokenizing physical assets, such as cargo or vessels, into digital tokens on a blockchain facilitates the secure and efficient transfer of ownership and value.
Further, the transition to blockchain-secured digital bills of lading reduces the risk of document fraud and streamlines the documentation process in the maritime sector.
iRA Blocks advances Maritime Asset Tokenization
UAE-based startup iRA Blocks builds a blockchain-based platform that facilitates the fractional tokenization of high-value maritime assets. It converts physical maritime assets, like vessels, into digital tokens that enable investors to purchase fractional shares and gain exposure to the maritime industry.
Through secure smart contracts and blockchain technology, iRA Blocks offers transparent ownership records, streamlined transactions, and enhanced asset liquidity.
Its native iRB Token simplifies transactions and offers additional utilities like staking and rewards.
Further, by lowering investment entry barriers and enabling diversification across vessels and markets, iRA Blocks improves access to maritime investments.
Ceres Blockchain Solutions builds a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN)
Serbian startup Ceres Blockchain Solutions offers blockchain-based platforms that support decentralized applications. It focuses on digital asset management, sustainability, and maritime operations.
The startup’s DePIN, Pont Network, converts maritime record-keeping by creating secure, tamper-proof, and transparent ship histories on the blockchain.
10. Smart Ports
Ports use IoT, AI, robots, and more to streamline cargo handling, reduce vessel turnaround times, and improve resource management.
For example, the port of Rotterdam uses a digital twin to monitor operations in real-time, predict bottlenecks, and support faster decision-making.
Additionally, implementing smart technologies reduces ports’ environmental impact. The port of Hamburg uses sensors and smart traffic systems to reduce congestion and pollution.
Ports also face safety and security breaches. For instance, the Liberian-flagged oil tanker Delta Blue was attacked twice by militants using rocket-propelled grenades and missiles. However, deploying drones and IoT devices enables authorities to inspect infrastructure, detect anomalies, and prevent accidents.
High-speed 5G networks further enable real-time data transmission to support smart port applications. The Port of Valencia is implementing a 5G network to advance digital transformation and become a model smart port by 2027.
Moreover, AI analyzes data to predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules. This allows ports to improve resource management.
For instance, the port of Busan implemented an AI-based logistics metaverse to increase productivity, environmental sustainability, and safety in port logistics.
Blockchain also offers secure and transparent transactions, which provide cargo security and reduce fraud. Singapore plans to mandate digital bunkering services with electronic bunker delivery notes to streamline ship fueling processes and reduce fraud risks.
Currently, the smart port market is projected to grow from USD 24.46 billion in 2025 to USD 61.17 billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 10.72% during the forecast period.
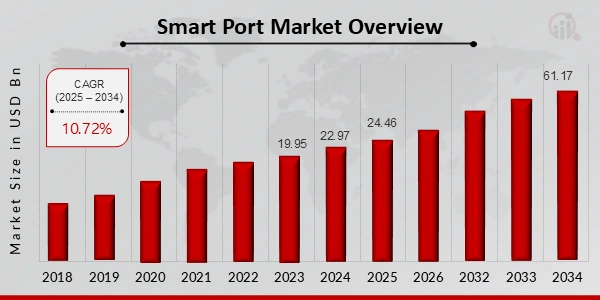
Credit: Market Research Future
DMSLOG.Ai builds an AI-powered Operations and Optimization System
US-based startup DMSLOG.Ai develops an AI-powered platform that converts container terminals into smart ports by optimizing operations, decongesting gates, and reducing emissions through integrated technologies.
The platform integrates data from terminal activities and applies machine learning algorithms to generate accurate predictions for container movement and resource allocation.
Its plug-and-play vehicle booking system (VBS) automates daily appointment quotas and coordinates truck arrivals to streamline terminal gate operations and reduce waiting times.
Additionally, the AI-based resource planner estimates container handling volumes, calculates required equipment and labor, and aligns deployment with HR policies.
DMSLOG.Ai also includes a satellite-view interface for real-time yard and block monitoring. This enables businesses to track container locations and navigate historical movement data. They also customize views based on operational parameters such as container type, storage duration, and scheduled pickup or delivery times.
TacticFlow advances AI-powered Autonomous Port Optimization
Spanish startup TacticFlow offers TFlow, an AI-powered software platform to optimize in-port traffic operations. The platform uses autonomous decision-making and real-time data analysis to improve scheduling and port efficiency.
Additionally, the platform employs intelligent agents to monitor variables like ship arrivals, weather conditions, and traffic flow. These agents automate scheduling and dispatching for tugboats, pilots, and mooring services.
The platform also adjusts berthing schedules to minimize vessel idle time and streamline port traffic. This increases operational efficiency and reduces congestion. Further, TFlow improves port capacity and shortens turnaround times while lowering operational costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Discover all Maritime Trends, Technologies & Startups
The maritime industry drives its future with resilience, interoperability, and large-scale decarbonization. Innovators deploy underwater wireless communication, digital twins, edge computing, and hydrogen propulsion to improve fleet operations. These developments shape a fast-evolving, tech-driven maritime ecosystem that is ready to meet the demands of a changing planet.
The Maritime Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.






![15 Top Defense Companies and Startups to Watch in Europe [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Defense-Companies-in-Europe-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)




