Restaurant chains integrate technology to enhance efficiency and customer experience. The adoption of AI-driven chatbots, contactless payments, and personalized marketing streamlines operations and engages customers. Digital menus and online ordering systems further offer convenience, reflecting a shift towards more seamless dining experiences. This industry research highlights the top 10 restaurant industry trends in 2025, including virtual reality (VR) dining experiences, sustainable waste management, and the use of locally sourced ingredients. These trends address the evolving demands of consumers and the market, positioning restaurants to innovate and thrive in a competitive landscape. Read more to explore each technology trend and how they advance your business.
This article was last updated in August 2024.
Top 10 Restaurant Industry Trends in 2025
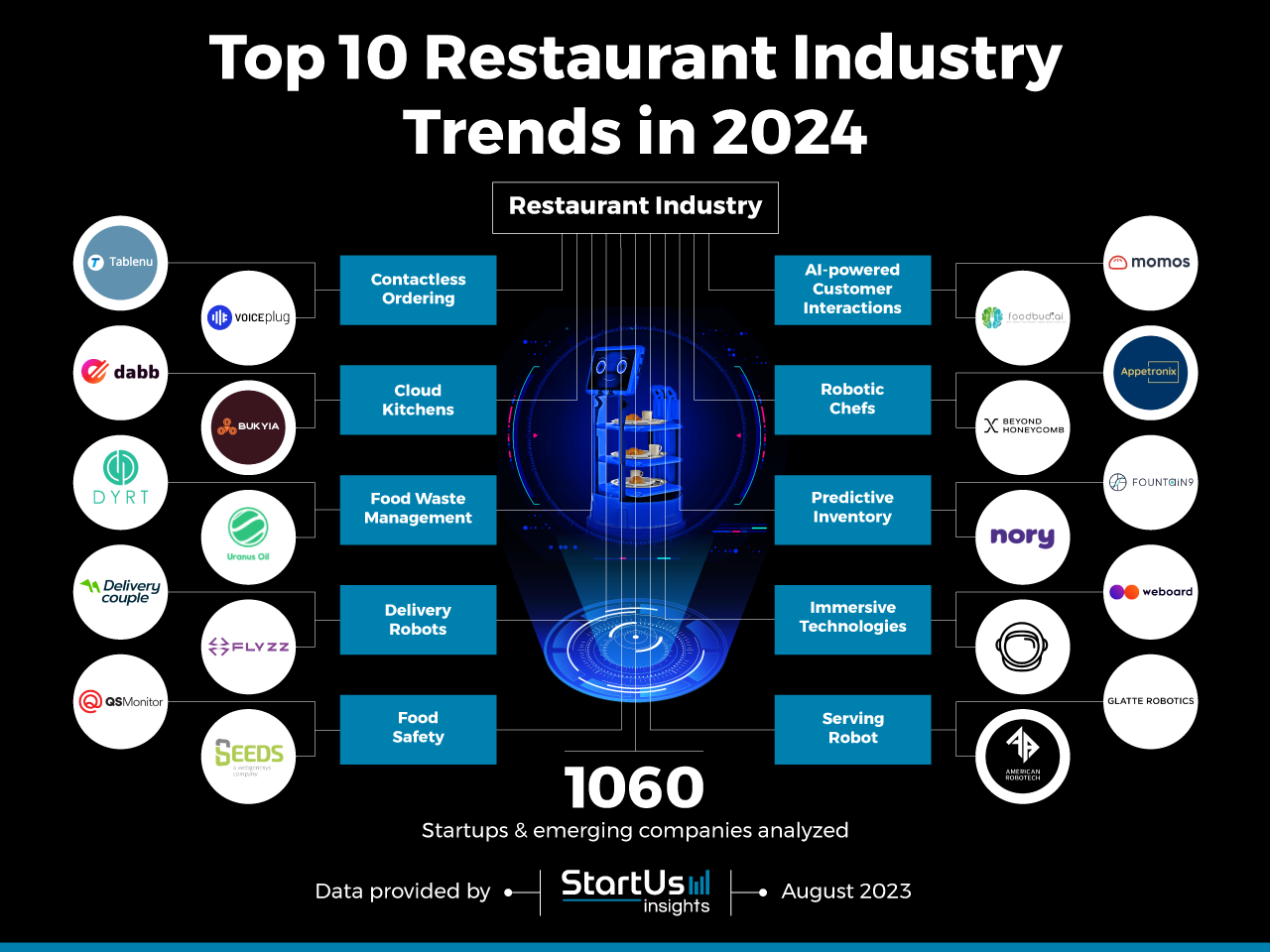
- Contactless Ordering
- Cloud Kitchens
- Food Waste Management
- Delivery Robots
- Food Safety
- AI-powered Customer Interactions
- Robotic Chefs
- Predictive Inventory
- Immersive Technologies
- Serving Robots
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Restaurant Industry Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Trends in the Restaurant Industry, we analyzed a sample of 1060 global startups & scaleups. This data-driven research provides innovation intelligence that helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging restaurant technologies. In the Restaurant Industry Innovation Map, you get a comprehensive overview of the innovation trends & startups that impact your company.
Want to explore all restaurant industry innovations & trends?
These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 4.7M+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant technologies and industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
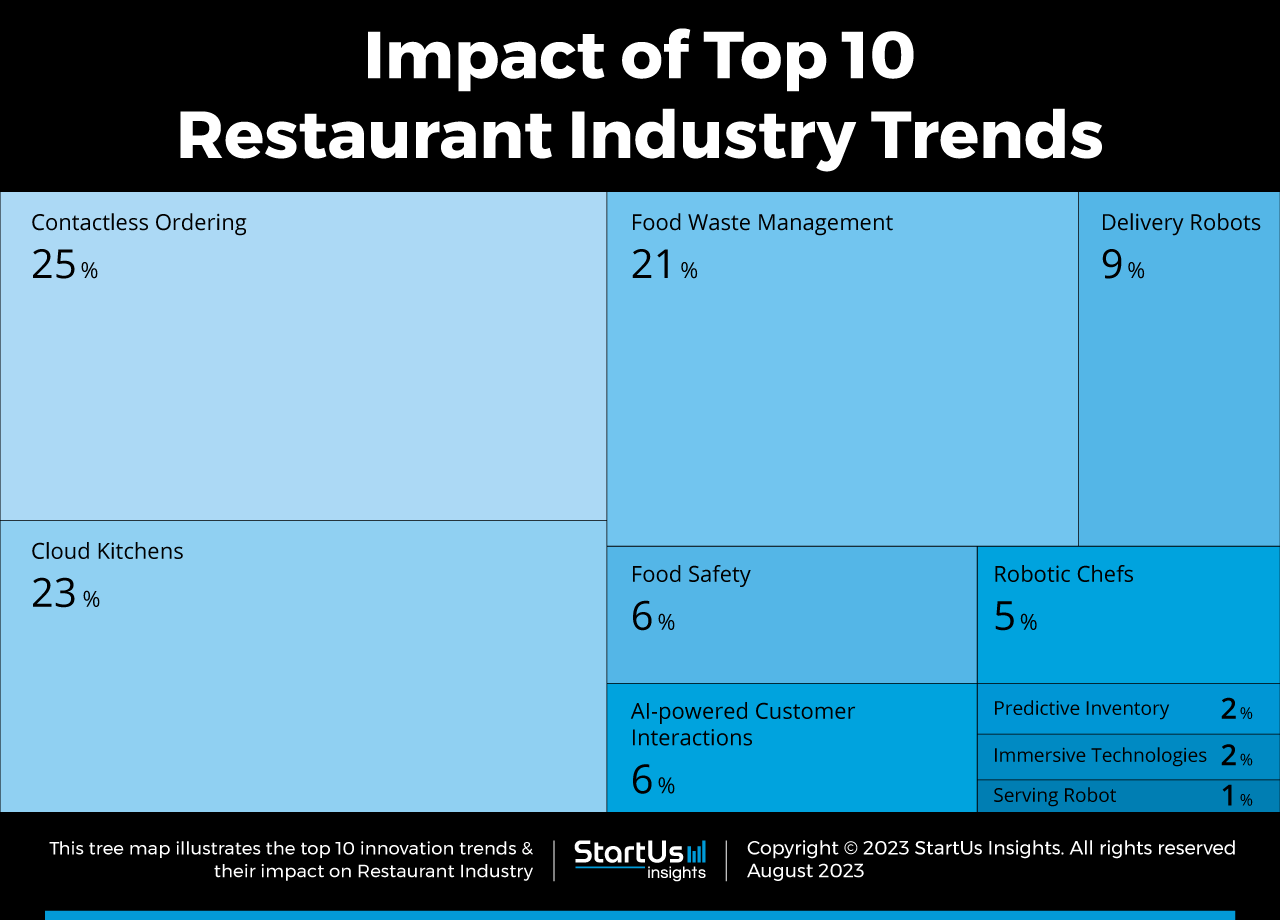
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the 10 Latest Trends in the Restaurant Industry in 2025
Based on the Restaurant Industry Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 10 Restaurant Technology Trends in 2025. The COVID-19 pandemic propelled contactless ordering and cloud kitchens into the top trends in the restaurant industry. Food waste management is also a critical aspect of this sector – which is why food chains are integrating in-house organic waste management systems. Further, food businesses are incorporating robots for delivery, kitchens, and serving.
Immersive technologies and AI are augmenting interaction between customers and restaurants to improve their satisfaction and convenience. Additionally, technologies for food safety are being integrated to avoid food poisoning while predictive inventory minimizes food wastage and costs. These innovations improve the overall efficiency of restaurant management and reduce carbon emissions.
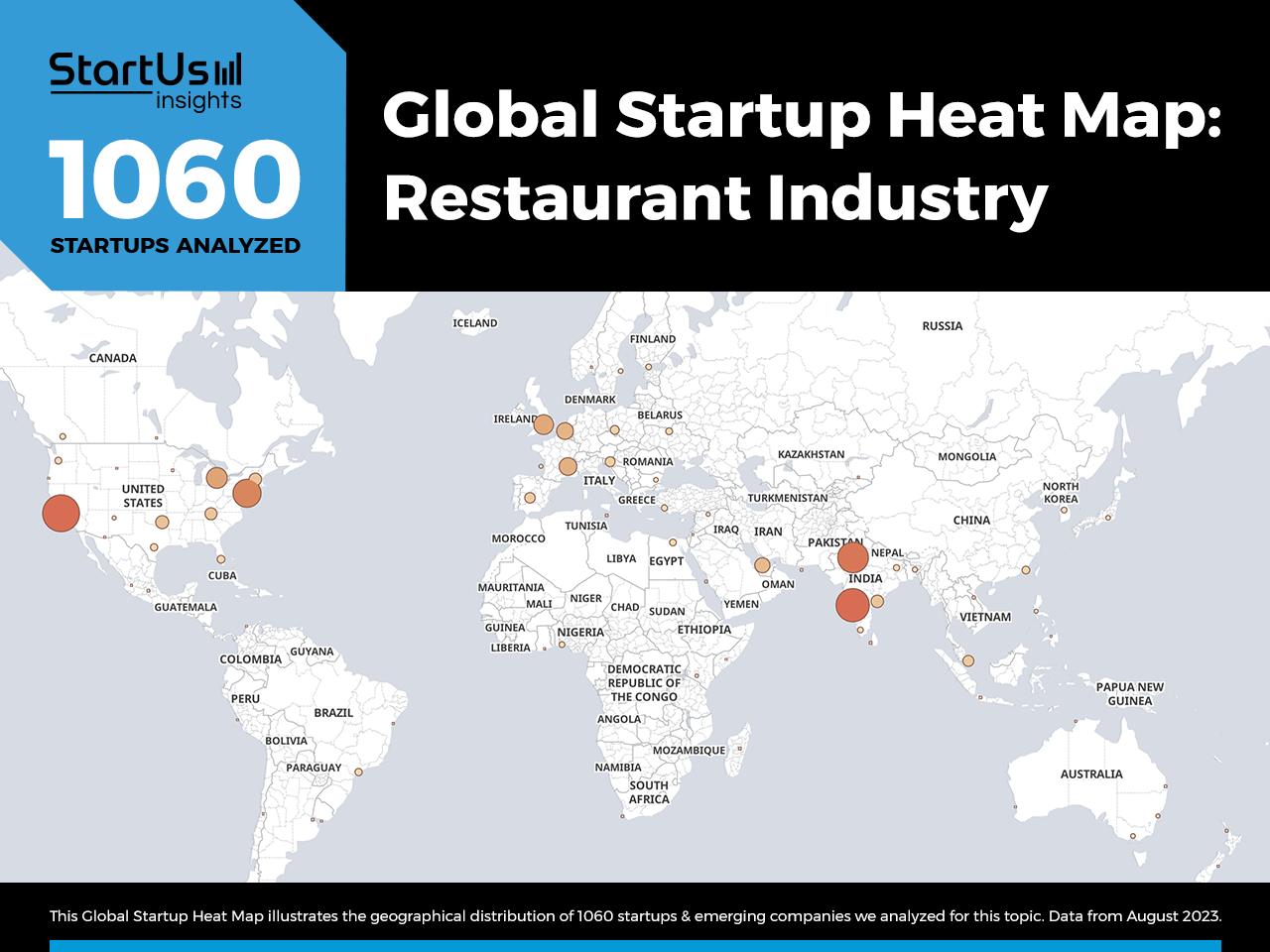
Global Startup Heat Map covers 1060 Restaurant Technology Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 1060 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals high startup activity in India, followed by the US. Below, you get to meet 20 out of these 1060 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These startups offering innovative restaurant technology solutions are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Top 10 Restaurant Industry Trends in 2025
1. Contactless Ordering
With the onset of COVID-19, the need for minimizing physical contact became paramount. As a result, contactless ordering for restaurants is a fast-growing trend, spurred by health and safety concerns. Leveraging technologies like mobile applications, QR codes, and self-ordering kiosks, restaurants now minimize direct physical interactions between staff and customers.
Third-party delivery platforms, such as Uber Eats and DoorDash, further expand contactless dining options. Such digital platforms open new revenue streams and make home delivery more accessible while redirecting infrastructure costs for restaurants. They also play a significant role in driving personalization and convenience in the contactless ordering process.
From customization to saving preferences, contactless ordering solutions enrich the dining experience while aligning with sustainability goals. Moreover, advances like voice commands or facial recognition further refine the contactless ordering experience.
Glyde makes a Contactless Ordering System for Restaurants
Glyde is a US-based startup that offers a contactless ordering platform for on-premise service models. The technology allows customers to browse menus, place orders, and pay directly from their mobile devices without physical interaction. The platform also integrates with existing systems to avoid downtime and enhance customer experience. This increases efficiency, reduces wait times, and improves safety by minimizing contact points.
Voiceplug enables Voice Commerce for Food Ordering
Voiceplug is a US-based company that develops an AI-powered voice commerce solution for food ordering. It integrates with the restaurants’ existing phone systems, call centers, drive-thrus, or online ordering platforms to enable conversational and interactive ordering.
The startup’s contactless ordering app allows restaurants to quickly upsell or cross-sell as well as reduce labor requirements for orders, lowering the cost per order. This, in turn, reduces customer abandonment rate and lost orders while increasing repeat orders.
2. Cloud Kitchens
Cloud kitchens, also known as ghost or virtual kitchens, are commercial kitchens that prepare food exclusively for delivery. They primarily exist in industrial or commercial spaces, where chefs prepare meals that are then delivered to customers through third-party services like Uber Eats, DoorDash, or Zomato.
The proliferation of food delivery services makes it more convenient for consumers to order meals from restaurants without leaving their homes. This trend accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic, when dine-in options were limited, causing a surge in demand for delivery.
Cloud kitchens thus allow restaurants to transition to food delivery-focused operations while reducing operating costs. They also enable businesses to control multiple virtual food brands from the same kitchen, diversifying their offerings and expanding their customer base.
Dabb offers a Ghost Kitchen Platform
Dabb is a Puerto Rican startup that provides a ghost kitchen platform. It allows traditional brick-and-mortar restaurants and food trucks to transform their business into scalable virtual kitchens. The platform also utilizes AI to deliver personalized recommendations to consumers.
Moreover, the company allows restaurants to avoid massive infrastructure costs, especially benefitting small businesses. The platform further features augmented reality (AR) that enables consumers to use smartphones to identify geotags and get rewards or offers, increasing revenue for restaurants.
Taster develops Cloud Kitchen Solutions
Taster is a UK-based startup that offers cloud kitchen solutions for creating delivery-first food concepts. The company designs delivery-optimized menus and franchises these concepts to aspiring restaurateurs. Taster’s technology integrates centralized kitchen operations where multiple brands and menus are prepared, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency.
The startup’s solution also ensures streamlined workflows, dynamic resource allocation, and comprehensive data analytics for menu optimization. Taster thus enables entrepreneurs to launch and scale food businesses with reduced overhead, while offering high-quality meals that meet the growing demand for delivery services.
3. Food Waste Management
Restaurants discard large quantities of edible food every day, representing a financial loss and contributing to environmental issues. That is why food retail outlets are transitioning to data-driven and innovative waste management strategies. These technologies include the Internet of Things (IoT), advanced analytics, AI, robotics, chemical recycling, and more.
By accurately tracking inventory and predicting varying customer demands, machine learning and predictive analytics enable restaurants to streamline resource utilization. This minimizes over-purchasing and reduces the chance of food spoiling. Further, food businesses deploy sensors to track food waste, which aids them in identifying patterns in food wastage.
Furthermore, food businesses deploy in-house waste management systems to control food waste at the source. For this, restaurants leverage advanced plastic recycling systems for managing packaging waste as well as food waste-to-energy (WTE) systems and composting. These measures, together, reduce the carbon footprint associated with restaurant operations.
Dyrt Labs advances On-Site, In-Vessel Composting
Dyrt Labs is a US-based food waste management company that offers an on-site, in-vessel composting solution. It processes food waste into compost on-site while eliminating the need for water for waste processing. The startup also offers a cloud-based dashboard to visualize and track the impact of composting.
The startup’s decentralized waste management mitigates trucking to offsite facilities and better aligns with ESG goals with CO2 tracking.
Uranus Oil enables Used Cooking Oil Recycling
Uranus Oil is an Indian startup that facilitates the conversion of used cooking oil into biodiesel. The startup sources used cooking oil from restaurants and moves the oil using its fleet. Once the procurement quantity reaches 12 tons, it informs biodiesel manufacturers for collection and upcycling.
The startup thus connects the otherwise disconnected restaurants and biodiesel manufacturers to streamline used cooking oil sourcing. This allows both food businesses and energy companies to optimize their supply chain and reduce their carbon footprint.
4. Delivery Robots
The convenience around food delivery and its growing demand in the industry forces restaurants to utilize delivery robots. They are autonomous delivery robots/vehicles equipped with GPS, cameras, sensors, and other technologies to navigate urban environments. For example, Uber Eats is partnering with Serve to scale robotic delivery operations.
Food delivery robots replace last-mile delivery persons to reduce labor costs and make on-demand delivery more affordable for customers. These robots also operate continuously without breaks and minimize human error. This reduces traffic congestion as fewer traditional delivery vehicles are needed on the roads.
To quickly and cost-efficiently integrate delivery robots, restaurants are leveraging robot-as-a-service from startups and companies specializing in food delivery robots. This allows restaurant chains to mitigate expensive in-house product development and accelerate the time-to-market.
DeliveryCouple delivers Food Delivery Robot-as-a-Service
DeliveryCouple is a Polish startup that provides robots-as-a-service for food deliveries. The startup does a demo run for the robot and then activates it for operations once the billing is confirmed by food businesses.
The autonomous sidewalk robots allow businesses to offer deliveries for free or at reduced costs for their consumers as well as ensure timely deliveries. This increases consumer convenience and, in turn, revenue.
Ottonomy makes Autonomous Food Delivery Robots
Ottonomy is a US-based startup that offers fully autonomous delivery robots for food delivery. The company’s robots, Ottobots, use contextual navigation to create digital maps of serviceable areas and navigate autonomously. They also feature modular storage compartments, contactless delivery access via QR codes, and advanced maneuverability for navigating tight spaces.
Ottobots support various delivery applications, from curbside and last-mile deliveries to indoor services in airports and malls. The company allows retail and restaurant businesses to address staffing shortages and enhance delivery efficiency while reducing carbon emissions and improving operational safety.
5. Food Safety
The major risk factors affecting food safety are improper food-holding temperatures, inadequate cooking, contaminated equipment, food from unsafe sources, and poor personal hygiene. The heightened consumer awareness and stringent regulations thus make food safety a priority for restaurant businesses. To achieve this, they leverage technologies for food condition monitoring, improved sanitation, and responsible sourcing.
Real-time monitoring and tracking of food temperatures, humidity, and other essential factors allow food chains to drive countermeasures upon detecting issues. Tech-driven food safety training programs are also seeing interest, like computer vision-based staff monitoring systems, to improve food safety.
Restaurants are further integrating blockchain to track and trace the origin of ingredients and offer insights into sourcing, handling, and preparation methods. This immutable data fosters trust across all stakeholders in the food supply chain and engages consumers in the process.
QS Monitor offers AI-based Food Safety Risk Assessments
QS Monitor is a UAE-based startup that provides AI-based food risk assessments. It combines IoT devices, machine learning algorithms, and data analysis to monitor, track, trace, and ensure food safety across different stages of the global food supply chain.
The company’s supplier dashboard allows buyers, like restaurants, to access a vast food supplier database, which also features various filtering parameters and quality ratings. QS Monitor’s solutions and services enable food businesses to find responsible ingredient suppliers and ensure the safety of consumers.
SeedsBit improves Food Traceability
SeedsBit is an Italian startup that enhances food traceability. The startup aggregates information from the field, ingredient processing, distribution warehouses, supermarkets, and till the food reaches the consumer’s table. It stores this data on its proprietary blockchain-based platform.
The platform further allows restaurants and consumers to trace back the origin of their food items as well as allows food businesses to improve transparency in their operations. This increases the quality assurance of dishes and ensures food safety.
Find out how 10 emerging technologies shape your industry!
6. AI-powered Customer Interactions
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being leveraged in the restaurant industry to provide more interactive and customized consumer experiences. For instance, chatbots handle reservations and deliver personalized recommendations in food joints. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants also streamline customer inquiries and manage orders.
These tools interact with customers through websites, apps, or messaging platforms, offering 24/7 availability and immediate responses. By automating these interactions, restaurants improve efficiency and free up staff to focus on other areas of service. Customers also benefit from more personalized services and offerings, enhancing their experience in stores and satisfaction.
This trend in restaurants is further fueled by the integration of voice ordering and voice search systems. While it enables a hands-free experience for customers, the more important benefit is in making food ordering more accessible and inclusive.
Momos develops an AI-based Customer Care Platform for Restaurants
Momos is a US-based startup that creates an AI-powered customer care platform for restaurants. It combines all customer data in a single platform to offer a single source of truth. This allows restaurants to monitor performance, track interactions, and get real-time updates. The platform also features review management, feedback analytics, a unified inbox, and more.
The startup’s platform allows restaurant businesses to automatically respond to customer queries and track customer feedback and sentiment. This allows them to make data-driven decisions in improving customer satisfaction and sales.
Foodbud delivers Personalized Food Recommendations
Foodbud is a UK-based startup that offers personalized food recommendations for customers. The startup’s machine learning-based platform provides suggestions based on food allergies as well as dietary and taste preferences. It also builds a personal food concierge that supplements consumers’ decision-making for dining out or cooking.
The startup’s ingredients data lake and AI further matches restaurants, cafes, and pubs to the right customers. This personalized matching ensures that the right customers reach specific restaurants, increasing chances of satisfaction and, in turn, sales.
7. Robotic Chefs
Robotic chefs are emerging as a transformative trend within the restaurant industry. These automated systems make dishes with high accuracy. From precise ingredient measurements to fast cooking times, a robot kitchen chef ensures consistent food items in terms of taste. This is particularly appealing to dining establishments that need a uniform brand image.
Moreover, robotic chefs tackle challenges like labor shortages and escalating personnel costs. By integrating robots into their operations, restaurants optimize workforce allocation by assigning human staff to roles demanding creativity, customer interaction, and supervision. This strategic reallocation enhances overall efficiency and leads to long-term cost savings.
Apart from these benefits, robotic chefs optimize ingredient usage to reduce food waste. Since they remove humans from food handling, robotic systems mitigate cross-contamination and improve food safety. To develop these systems, food companies and robot developers rely on advanced motor control systems and AI.
Dexai Robotics builds an Autonomous Robotic Chef
Dexai Robotics is a US-based startup that develops Alfred, an autonomous robotic chef for kitchen operations. The robot utilizes machine learning algorithms to accurately prepare recipes by identifying ingredients, measuring quantities, and cooking dishes.
It also features real-time inventory management, ingredient detection, and the ability to autonomously switch utensils for different tasks. The robot thus enhances culinary experiences by enabling kitchen staff to focus on creativity and customer service while ensuring a more efficient and sanitary food preparation process.
Beyond Honeycomb makes an AI Chef Grill Robot
Beyond Honeycomb is a South Korean startup that builds an AI chef grill robot. The startup’s modular robot features a molecular sensor that senses food quality even at higher temperatures. Its low footprint makes it suitable for low small spaces as well.
The robot further cooks various types of meat, including chicken, pork, beef, and fish, as well as is trained on a massive dataset. These features enable restaurants to make grilled meat products with consistent quality and increase customer convenience.
8. Predictive Inventory
Traditionally, restaurants rely on manual inventory planning to match stocking with consumer demands and avoid overstocking. On the other hand, predictive inventory management leverages advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to accurately forecast demand. This enables restaurants to proactively manage their inventory levels and streamline their operations for enhanced efficiency.
Predictive analytics solutions analyze historical sales data, seasonal trends, special events, and even external variables like weather patterns to forecast product demands. The insights from such analyzes guide purchasing decisions for restaurants to maintain optimal inventory levels while minimizing excess or shortage.
Consequently, predictive ordering and inventory management drastically reduce food waste by reducing the likelihood of unused items spoiling or being discarded. This aligns with sustainability goals and also translates into substantial cost savings for establishments.
Fountain9 aids in Predictive Inventory Planning
Fountain9 is a US-based startup that develops a solution for predictive inventory planning. The startup’s AI engine, Kronoscope, integrates with ERP systems, order management systems, and warehouse management systems to collect and analyze business data. It then uses a demand-sensing engine to forecast product demands based on holidays, anomalies, waste, cannibalization, and more.
The engine further allows restaurants to simulate prices and promotion scenarios to maximize revenue. All this data enables food businesses to optimize inventory planning and reduce food wastage.
Nory simplifies Food Inventory Management
Nory is an Irish startup that facilitates food inventory management. The startup’s AI predicts inventory usage in advance and creates accurate order guides and prep lists. It also offers real-time gross profit and waste analysis using smart counting and stock warning.
The startup’s solution further features automated invoice and vendor management as well as centralized inventory and recipe management. It enables end-to-end inventory management for restaurants while allowing them to reduce food waste.
9. Immersive Technologies
Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) are innovative opportunities for restaurants to elevate their offerings and engage customers in novel ways. One of the key applications of immersive technologies is to enhance brand storytelling. Restaurants leverage AR and VR to craft compelling narratives that delve into the sourcing and creation of menu items.
By offering customers a visual and interactive journey through the culinary process, establishments establish a deeper connection with their audience. Through AR projections, dining spaces are transformed into immersive environments that complement the theme of the restaurant or the cuisine being served.
AR-enhanced menus overlay detailed information about ingredients, dietary considerations, and preparation methods. VR-powered interactive menus also allow customers to visualize dishes in a lifelike setting before placing orders. This offers customers a comprehensive understanding of their choices and increases consumer engagement.
WeBoard delivers VR-based Training for Restaurant Workers
WeBoard is a Czech Republican startup that offers a VR-based training platform for restaurants. It combines conversation AI-powered training bots and VR to create realistic simulations of real situations and train workers through a natural spoken conversation.
The startup’s solution finds use in sales and customer service, learning and assessments, risk and change management, and more. It increases the efficiency of training programs and better equip workers for realistic scenarios, improving customer satisfaction.
Space Food makes AR-based Food Menus
Space Food is an Irish company that creates AR-based food menus. The startup’s solution allows restaurant businesses to deploy AR-based menus that consumers access through QR codes. This provides a more engaging way for customers to order food in restaurants.
10. Serving Robots
The growing demand for contactless services, personalized interactions, and streamlined operations makes restaurants integrate food serving robots. In an era where hygiene and safety are paramount concerns, these robots minimize direct human contact with food and drinks, reducing the risk of contamination. They also create a talking point and social media buzz for restaurants.
With precision and accuracy, serving robots navigate through restaurant spaces to deliver orders directly to tables or designated pickup points. This contactless delivery ensures the safety of customers and staff as well as enhances the overall dining experience. Serving robots also address challenges related to labor shortages and operational costs.
The restaurant industry often grapples with staffing issues, particularly during peak hours. Serving robots complement human staff by taking on repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing human employees to focus on more value-added activities. They include engaging with customers and ensuring the overall quality of the dining experience.
Glatte Robotics manufactures Robot Servants for Restaurants
Glatte Robotics is a German startup that builds service robots for restaurants. They utilize invisible laser beams to scan their surroundings and determine their surroundings. Some of them feature voice output to interact verbally with workers or consumers as well as include tray shelves and closed cabins.
The startup’s robots enable restaurants to avoid in-house product development, thereby reducing capital expenses. These robots also allow food businesses to streamline food serving for diners and divert workers to deal with more complex tasks and customer handling.
American Robotech makes a Large Capacity Dish-Return Robot
American Robotech is a US-based startup that offers a large-capacity dish-return robot. It is an autonomous robot that features ultra-large capacity, paging function, gesture recognition, and voice control. The robot thus ensures a better turnover by moving utensils faster.
The robot also allows workers to call and assign tasks and ensure contactless operations. Further, its 6-array omnidirectional microphone enables the robot to locate sound sources in real time and navigate intelligently. This allows restaurants to optimize space utilization and improve productivity.
Discover all Current Restaurant Trends, Technologies & Startups
From the convenience of contactless ordering and the efficiency of cloud kitchens to the innovations in delivery robots, these trends are redefining how we engage with restaurants. The continued evolution of serving robots and the assurance of food safety will shape the way we dine, ensuring both efficiency and hygiene. A wider adoption of these technologies will further improve efficiency and sustainability. The Restaurant Industry Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.



![Food and Beverage Industry: Top 10 Technology Trends [2025 & Beyond]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Food-and-Beverage-Industry-Trends-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)




