Technological innovations in satellites enable the majority of advancements in the space industry. The most significant satellite industry trends include small satellites or smallsats, that drive the next generation of satellite capabilities. Further, the low manufacturing cost of smallsats is paving the way for the mass production of satellites. Satellite Internet of Things (IoT) is another major trend enabling unprecedented connectivity across industries and empowering 5G and upcoming 6G capabilities.
Simultaneously, satellite manufacturers and operators are bringing technological innovations to ground stations as well as orbital services. Digitized payloads, propulsion systems, and technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) enable satellites to perform more complex functions autonomously.
This article was last updated in July 2024.
Top 10 Satellite Industry Trends in 2025
- Small Satellites
- Satellite IoT
- In-Orbit Services
- Advanced Ground Systems
- Artificial Intelligence
- Advanced Payload Systems
- Spacecraft Propulsion
- Very High Throughput Satellites (VHTS)
- Flexible Launch Services
- Additive Manufacturing
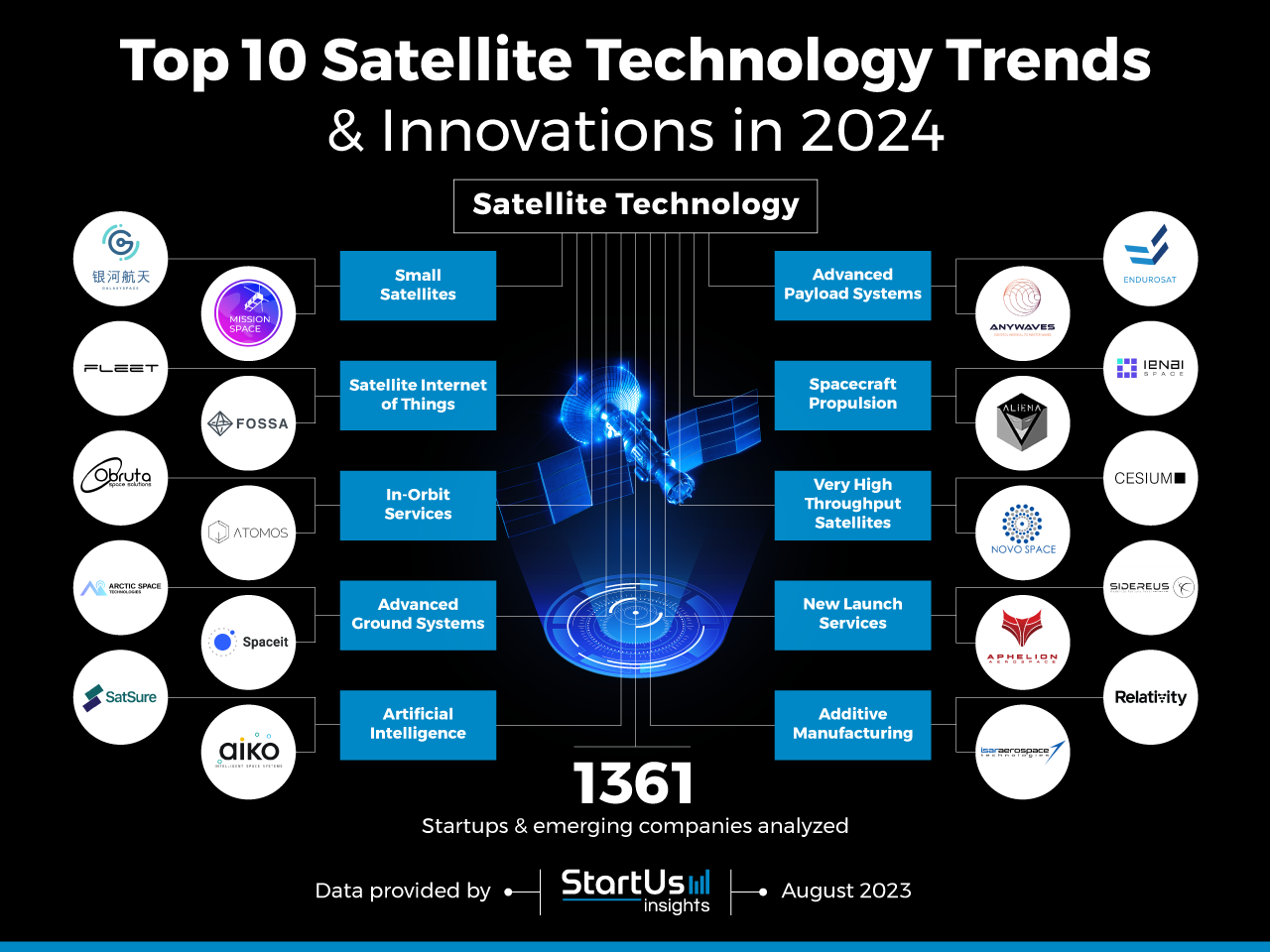
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Satellite Industry Trends Plus 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Satellite Industry Trends and Startups, we analyzed a sample of 1361 global startups & scaleups. This data-driven research provides innovation intelligence that helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging technologies in the satellite industry. In the Satellite Technology Innovation Map below, you get a comprehensive overview of the innovation trends & startups that impact your company.
These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 4.7M+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant technologies and industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
Want to explore all Satellite Technology innovations & trends?
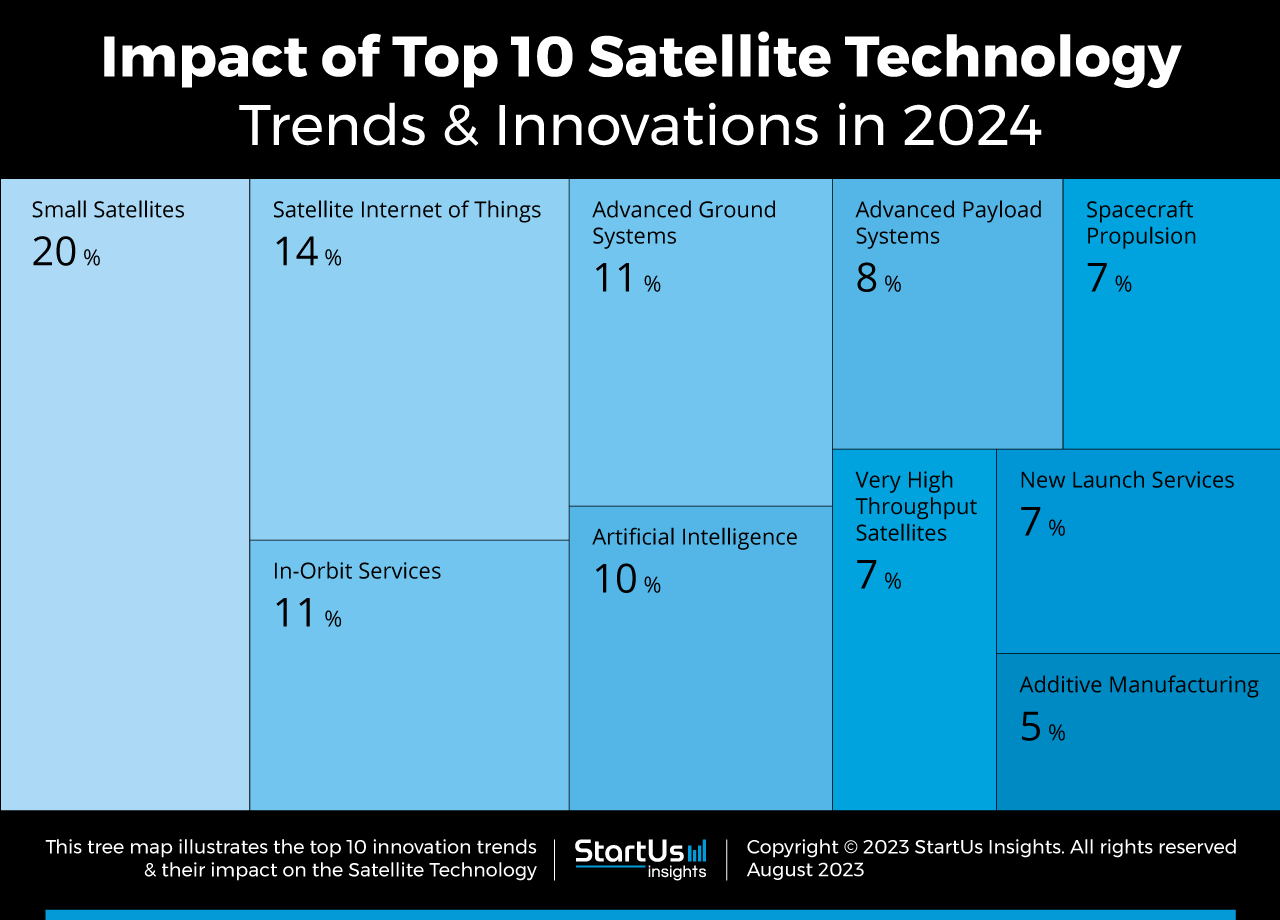
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Satellite Industry Trends
Based on the Satellite Technology Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 10 Satellite Industry Trends. Startups and scaleups are deploying small satellites in low-earth orbit (LEO) constellations for greater internet connectivity and speed. They also meet this need using very-high throughput satellites in LEO and geostationary orbits (GEO). Satellite IoT enables improved cloud computing, IoT networks, and backhaul for existing terrestrial systems. In-orbit technologies such as mission extension and service robotics are the other emerging satellite technology trends.
AI, for example, enables autonomous satellite operations and increases data processing power. Further, satellite bus designs now accommodate reconfigurable payloads, smart power systems, and onboard propulsion systems. Satellite launch costs are also decreasing with improvements in reusable rockets and flexible launch sites. Lastly, additive manufacturing equips satellite startups to assemble large space structures both in space and on Earth.
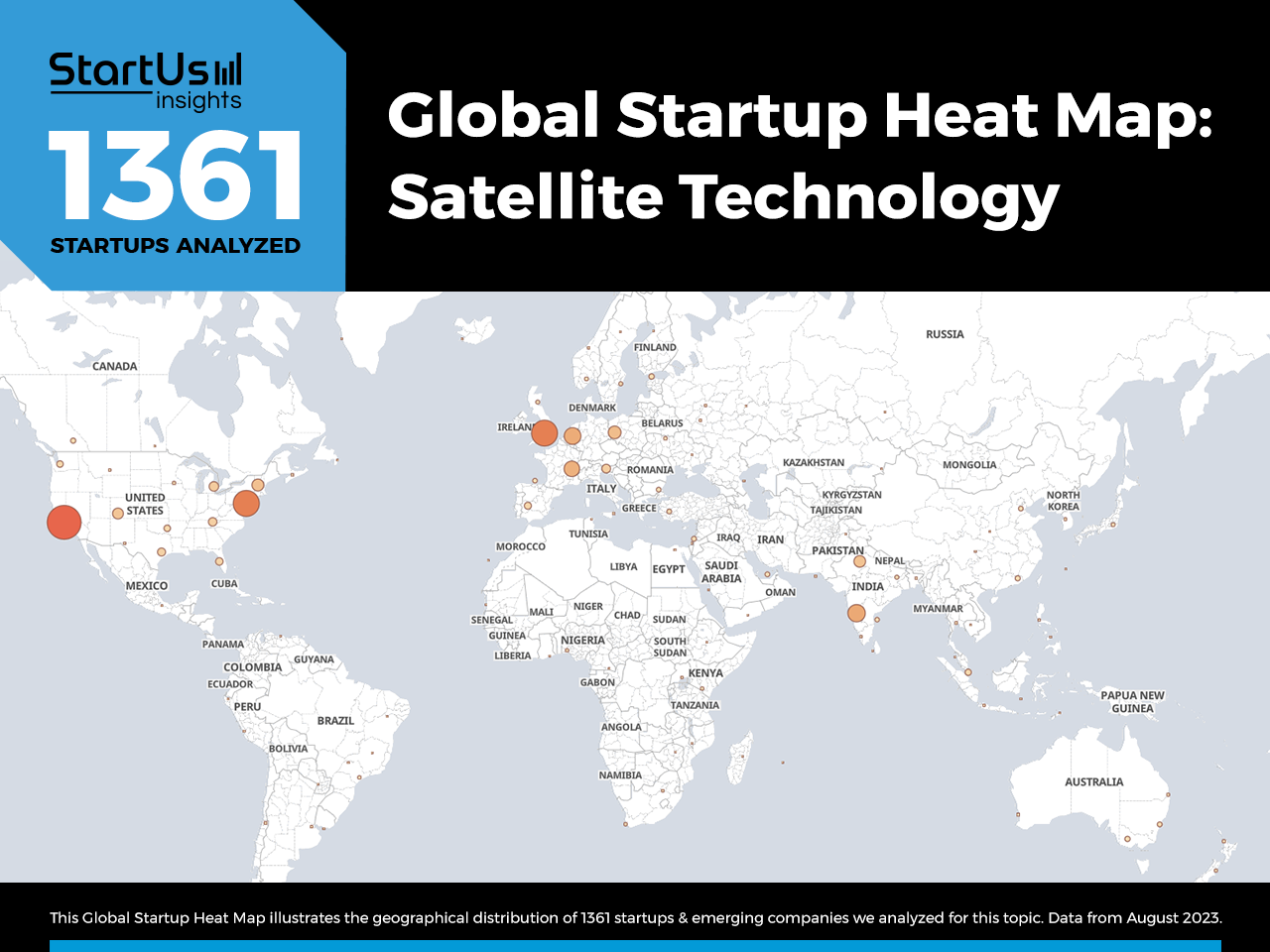
Global Startup Heat Map covers Satellite Technology Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 1300+ exemplary startups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals high startup activity in the US and UK, followed by Europe and India.
Below, you get to meet 20 out of these 1361 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These innovative satellite technologies are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Top 10 Satellite Technology Trends in 2025
1. Small Satellites
Equipped with smarter and compact subsystems, small satellites are replacing the need for large satellites and related infrastructure. Commercial satellite operators for connectivity services deploy constellations of smallsats in LEO to provide global coverage with low latency. For similar reasons, small satellites are increasingly positioned in LEO constellations for earth observation (EO) and remote sensing to generate superior insights.
Satellite startups advance this trend through mass production, rocket ride-sharing with other missions, modular commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware, and standardized satellite buses. Satellite operators and owners also minimize costs through vertical integration in satellite manufacturing.
Galaxy Space provides Communication Services via Smallsats
Galaxy Space, a scaleup from China, mass produces small satellites with modular components and small structures. The startup has already sent 1000 small satellites, equipped with innovative communication payloads, like constellations in the 500-1000km LEO. These constellations provide 5G network coverage and broadband services to users across the globe. They also serve industries such as aviation, marine, automobile, and manufacturing and are used for emergency response and ecological protection.
Mission Space predicts Space Weather using LEO Constellations
Latvian startup Mission Space deploys its own network of nanosatellite constellations, installed with custom sensors, to provide predictive space weather monitoring. The startup’s forecasting system measures near-earth magnetic and solar storms, in addition to charged-particle streams of up to 600km. This real-time satellite data is used across industries such as aviation, energy, and financial trading to prevent disruptions caused by space-weather radiation risks.
2. Satellite IoT
The demand for satellite-enabled Internet of Things is growing steadily owing to the extensive coverage provided by satellites compared to the existing terrestrial infrastructure. Governments and private sector investment in satellite technology for connected solutions are driving the technological advancements in satellite IoT. Commercial solutions deploy IoT sensors and devices for satellite-based, precise, and real-time asset tracking, monitoring, and remote surveillance around the world.
Current trends in satellite communication also enable a new range of cloud and edge computing capabilities. Some of the biggest advances in satellite IoT come from its application in the military and defense. For example, terrestrial communication networks suffer coverage limitations at extreme locations and often depend on land and sea cables. Startups provide hybrid services using satellite IoT as backhaul to existing terrestrial networks, improving the overall infrastructure.
FOSSA Systems offers Low-Cost Satellite IoT Solutions
FOSSA Systems, a Spanish startup, brings secure and optimized satellite IoT communications at a low cost. The startup uses dedicated picosatellite constellations to connect with IoT-enabled devices and facilitates strategic monitoring even at remote locations. The solution enables high-capacity vertically integrated industrial and commercial IoT services through its autonomous IoT sensors and platform. It is already improving productivity in agriculture, logistics, and industrial environments through its digitized solutions.
Fleet Space enables NanoSat-based IoT Solutions
Australian startup Fleet Space uses the LoRaWAN protocol of the low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) and LEO satellite constellations to provide bi-directional industrial IoT solutions. Its 6U NanoSatellites with 3D printed antenna and digital beamforming for LPWAN improve satellite-to-ground station connectivity. This provides more throughput for remote industrial monitoring. The startup’s integrated satellite and LoRaWAN gateway, The Portal, connects up to 1000 IoT sensors within a 15km range. The solution finds applications in the defense, utility, and mining sectors.
3. In-Orbit Services
Satellite technology companies are solving two major challenges impacting satellite performance in space – servicing orbiting satellites and decluttering space. The exponential rise in launches has led satellite operators to employ space situational awareness (SSA) for detecting and cleaning space debris. Self-destruction and other deorbiting technologies introduced by startups for decommissioning satellites are proving sustainable for the future of space.
Another satellite technology to declutter space is by increasing the lifespan of existing satellites. For this, startups and scaleups use mission extension vehicles, also known as space tugs, to service or upgrade orbiting satellites. Other in-orbit services include orbital transfer vehicles, as well as payload and cargo delivery vehicles. Autonomous robotic technology further improves satellite maintenance efficiency by performing in-orbit satellite servicing and repairs.
Obruta provides Satellite In-Orbit Servicing
Canadian startup Obruta uses its proprietary service pods and systems to perform satellite servicing while in orbit. Satellites are either equipped with Obruta’s four-in-one service interface, Puck, or receive repairs through its service delivery pods. These technologies revive the satellite through refueling, repairing, recharging, relocating, deorbiting, data transfer, or life extension. This empowers satellite operators to increase mission duration and mitigate critical mission failures.
Atomos develops Orbital Transfer Vehicles (OTV)
US-based startup Atomos uses its Orbital Transfer Vehicle or space tugs for custom last-mile orbit insertion of satellites. Space tugs carrying satellites orbit the earth for precise satellite orbit insertion, orbit raising, phasing, and satellite plane changes. It does so by rapidly utilizing high-power electric propulsion and Atomos’ proprietary ubiquitous rendezvous operations. This allows satellite launchers to manage orbital transfers and satellite servicing at low costs.
4. Advanced Ground Systems
Innovation in telemetry, tracking, and command-to-control satellites make next-generation ground systems a top satellite technology trend. Ground stations use radio-frequency (RF) communication terminals, including electronically-steered and phased-array antennas, to track satellites with minimal human intervention. Similarly, the rise of satellite constellations requires modern inter-satellite links for coordinated constellation movement. For this, startups operating earth stations utilize smart RF and optical communication for better in-orbit relays during upstream and downstream data transfer.
In addition to existing stations, startups develop decentralized communications terminals for satellite connectivity in moving vehicles and remote locations. On the commercial end, ground stations are empowering software-defined satellites by enabling virtualized ground networks. These solutions enable satellites to autonomously reallocate, reconfigure, and handle massive bandwidth, as per demand, to support a growing number of end-users.
Arctic SpaceTech provides Decentralized Ground Station Services
Arctic SpaceTech, a Swedish startup, offers secure downstream satellite data handling by digitizing ground stations. Instead of using the cloud, the startup decentralizes satellite data processing next to the existing network of ground stations. It, therefore, enables low latency, real-time data processing while reducing bandwidth and storage requirements on the network for ground station and satellite operators.
Spaceit offers Mission Control-as-a-Service
Estonian startup Spaceit utilizes its platform to offer scalable mission control services from the ground. The platform integrates existing ground stations with satellite missions using telemetry, tracking, and command (TTC) protocols for real-time monitoring. The startup enables satellite operators to reduce operational costs by eliminating custom software development, hardware investments, and ground station licenses for satellite management.
5. Artificial Intelligence
The large volumes of data collected by satellites pose challenges in data handling, analysis, and timely resource management. Machine learning (ML) and AI enable the analysis of satellite data obtained from earth observation (EO), global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), and remote sensing. AI-facilitated data analysis on the cloud is paving the way for Ground-Station-as-a-Service solutions. Ground stations also use AI for ground-based SSA to command satellites for course correction and resource optimization. In space, AI is used for real-time orbit prediction and satellite tracking for enhanced space traffic management.
Further, big data and analytics empower onboard sensors with autonomous data processing capabilities in satellite subsystems, before downstream data transfer. AI-enabled subsystems also make autonomous satellite maneuvers such as relative navigation, pre-emptive communications correction, spacecraft rendezvous, docking, and satellite constellation operation possible.
SatSure provides Satellite Data Analytics
SatSure is an Indian startup that commoditizes data from remote sensing satellites. The startup’s open innovation platform, SPARTA, combines IoT, economic, and weather datasets with data gathered from EO satellites. It also uses machine learning algorithms and big data analysis for this purpose. SPARTA then produces actionable insights for banking, financial services and insurance (BFSI), agriculture, infrastructure, and climate sustainability for the locations in focus.
AIKO enables Autonomous Satellite Missions
Italian startup AIKO provides E-4-level autonomy in satellites through its advanced flight software for both onboard and ground systems. The startup utilizes AI to create custom algorithms for autonomous mission command and data handling. It also engages AI for detection and reconfiguration of mission-critical events in satellites providing failure detection, data selection, and mission replanning. For satellite operators, it provides an efficient and cost-effective ground-based SSA solution.
6. Advanced Payload Systems
Payloads are the backbone of satellite missions and their advancement is, therefore, a top satellite technology trend. Startups find it profitable to use modular payloads instead of custom-made ones. Besides cost considerations, both startups and scaleups now use standardized payloads for enhancing satellite quality and capacity. Consequently, sophisticated COTS equipment such as high-resolution imaging and spectral sensors like synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and miniaturized transceivers such as foldable antennas are finding a place in satellite payloads.
Technological advancements also enable startups to make autonomous satellite payloads that perform tasks such as frequency and power allocation to high-demand beams and important subsystems. Payloads are also made reconfigurable using installed software to perform custom functions other than the satellites’ original purpose. This way, old satellites in orbit are repurposed for new missions rather than be decommissioned and added to space debris.
EnduroSat manufactures CubeSat Modules
EnduroSat is a Bulgarian startup that manufactures modular payloads for the CubeSat class of nanosatellites. The startup exercises a software-driven approach in its 1U to 6U-sized CubeSats modules to make multiple redundancies of data. The modules are also CubeSat standard-compliant and range from off-the-shelf transmitters and single or multiple-band antennas to custom CubeSat modules. This provides satellite operators with the flexibility to deploy their own satellites with minimal development costs.
Anyways provides COTS Antennas
French startup Anywaves builds custom and off-the-shelf miniature antennas for satellite constellations. Their antennas are operational in telemetry, tracking, and command (TTC), Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), and as onboard payloads. These antennas serve from the range of S- and X-band frequencies to all bands for GNSS. Anywaves’ COTS antennas are installable in satellites and enable time and cost-saving for satellite manufacturers and owners.
7. Spacecraft Propulsion
High-capacity power and propulsion systems that enable satellites to travel deep into space and perform complex maneuvers are becoming a staple in the industry. As a result, smart innovations such as high-power solar arrays and miniaturization of traditional fuel sources, like battery improvements, are incorporated into new satellites. Startups restructure low-weight thrusters for optimized performance and they make similar improvements in chemical propulsion for thrusters.
There is also a shift towards incorporating sustainable propulsion systems onboard satellites. Amongst the green propulsion technologies, startups and scaleups are primarily using electric propulsion instead of conventional systems. Other solutions include electromagnetic tethering, nuclear, solar, water, laser, and even Iodine-based propulsion.
Ienai SPACE develops Onboard Propulsion for Nanosats
Spanish startup Ienai SPACE makes mission-adaptable onboard electric propulsion for custom-form nano and microsatellites. The startup employs ionic propulsion for providing adjustable total and high specific impulse, 360-degree altitude control, and reaction wheel desaturation. The startup’s modular approach towards onboard propulsion maximizes payload occupation for satellite operators.
Aliena builds Green Space Propulsion Solutions
Singaporean startup Aliena manufactures miniaturized green propulsion systems for SmallSat mobility in space. The startup’s plasma thrusters are built with a high power-to-thrust ratio, specifically designed for low-power small satellites. It empowers small satellite operators to reduce fuel consumption while continuing to perform orbital services, constellation phasing, and maintenance.
8. Very High Throughput Satellites (VHTS)
Demand for satellite-based mobile and broadband communications is surging and GEO satellite network providers respond by increasing their strength and throughput capabilities. This implies that GEO satellites utilize advanced transponders and software-defined radios to transmit data at several hundreds of gigabytes or even terabytes per second. Software-defined radio equips the satellites to cater to fluctuating demands by beam hopping, changing shape coverage, and specifically targeting high-capacity areas. Increasing frequency in different frequency bands and using technologies like multi-spot beams allows service providers to cater to high demands.
They opt for Ku- and Ka-frequency bands for communications since these bands provide greater signal capacity and frequency reuse efficiency. With VHTS, connectivity over land, air, and sea for consumer, commercial, at military applications at unserved and underserved locations is now possible. LEO or non-GEO constellations also leverage VHTS data supply with low latency to serve the consumer market with greater flexibility.
Cesium Astro facilitates High-Throughput (HTP) Payloads
By developing high-throughput communication payloads, US-based startup Cesium Astro enables telecommunications satellite operators to serve this emerging market. The startup’s multi-beam active phased array (APA) system, Vireo, is designed for HTP satellites with size, weight, payloads, and cost (SWaP-C) constraints. It provides users with HTP capabilities as well as control over power consumption, beam hopping, beam-weight storage, and constellation performance.
Novo Space provides HTP Computing for Large Satellites
US-based startup Novo Space empowers large satellites with SpaceVPX-standard HTP backplane electronics for onboard components. The startup’s radiation-tolerant components include onboard computers, signal processors, carriers, and mass memories with 10x Gpbs high-throughput interfaces. These standardized parts use proven technologies in hardware and software, thereby, mitigating risks and costs for satellite operators.
9. Flexible Launch Services
Unlike a decade ago, the size and number of satellites launched in a particular orbital flight determine the requirement of launch vehicles engaged for the job. Therefore, flexible and on-demand launches are sought-after by satellite owners due to increasing smallsats and overall satellites launched into orbit. Air launch to orbit and launch using spacecraft, balloons, autonomous launch vehicles, or drones are some flexible satellite launch techniques that startups and scaleups are innovating in.
Containerization of smallsats for easy launch to LEO constellations is another innovation in ground-based launch services. The biggest advancement in ground launch systems, however, is the use of reusable rockets for positioning satellites in any orbit. They drastically lower the launch costs of commercial satellites. Startups also develop large, small, and micro launch vehicles catering to all types of satellites.
Sidereus Space makes Single-Stage-to-Orbit (SSTO) Reusable Launch Vehicles
Utilizing its reusable launch vehicle, Italian startup Sidereus Space provides flexible satellite launch solutions from anywhere in the world. The startup’s multi-purpose launch vehicle provides satellite owners with the launch and orbital re-entry capabilities. It leverages miniaturized propulsion technology to provide SSTO for both LEO and sun-synchronous orbits (SSO) within a few weeks.
Aphelion Aerospace provides NanoSat Launch Services
US-based startup Aphelion Aerospace develops dedicated nanosatellite launch services. Its Helios launch vehicle is capable of putting spacecraft in any orbit suited to the mission, including polar and high-inclination orbits. The startup launches specific missions that do not involve ride-sharing or have complex launch requirements. This dedicated launch service accelerates orbital access for satellite missions without having to wait months for scheduled launches.
10. Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing lowers the production costs of satellites and their subsystems. Satellite buses, customized payloads, and even rocket engines in satellite launchers are now 3D printed by satellite manufacturers. Startups use 3D printing on a large scale to mass-produce satellites for LEO constellations. Digital twins of bespoke and complex satellite parts are created and 3D printed. This speeds up the prototyping and testing of satellites and their parts, in turn, reducing the manufacturing lead time and costs.
Likewise, 3D printing small parts of large space structures on the ground and assembling them in space significantly reduces the complexity of space manufacturing. This saves the cargo volume and fuel required to put large structures in space. In-space additive manufacturing facilitates the replacement of malfunctioned components and enhances in-orbit satellite upgrade missions.
Isar Aerospace 3D-prints Launch Rocket Parts
German startup Isar Aerospace uses advanced additive manufacturing and carbon composite materials to manufacture rockets for launching satellites. Additive manufacturing empowers the startup to build high-performance metals with precision and provide flexibility and speed to its stakeholders. Its in-house manufactured launch vehicle, Spectrum, is already putting satellites in the SSO for up to 700 Kgs and in LEO for up to 1000 Kgs.
Relativity Space builds 3D-printed Rockets
US-based startup Relativity Space employs additive manufacturing to produce its satellite launch rockets. The startup uses its 3D metal printer, Stargate, to produce rocket Terran 1 and reusable rocket Terran R. This reduces rocket production lead time from years to a couple of months. It also reduces radical part counts, enables quick design iterations, and optimizes quality control and inspections.
Discover More Satellite Trends, Technologies & Startups
Innovations in the satellite industry are happening at light speed. In addition to the smart subsystems and in-orbit services, space satellites utilize more advanced technologies as discovered in our research on satellite technology trends. Satellite avionics are also advancing towards miniaturized and radiation-tolerant systems.
The satellite industry trends and startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.



![15 Top Defense Companies and Startups to Watch in Europe [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Defense-Companies-in-Europe-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)





