The advancements in data analytics, automation, and precision treatments are transforming biotechnology in 2025. Trends in biotechnology like Bioinformatics and generative AI are accelerating drug discovery and genetic analysis, with precision medicine and gene editing enabling personalized healthcare solutions.
Emerging technologies such as quantum computing improve computational biology, while lab automation simplifies research processes. Tissue engineering and bioprinting are also advancing regenerative medicine to offer options for organ replacement and innovative therapeutics.
What are the Top 10 Trends in Biotechnology in 2025?
- Bioinformatics
- Precision Medicine
- Synthetic Biology
- Generative AI
- Gene Editing
- Biomanufacturing
- Quantum Technology
- Tissue Engineering
- Bioprinting
- Lab Automation
Methodology: How We Created the Biotechnology Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 5M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our own startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the biotechnology industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the biotechnology innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Biotechnology Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top 10 Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 4500+ global startups & scaleups. The Biotechnology Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the biotechnology industry trends & startups that impact your company.

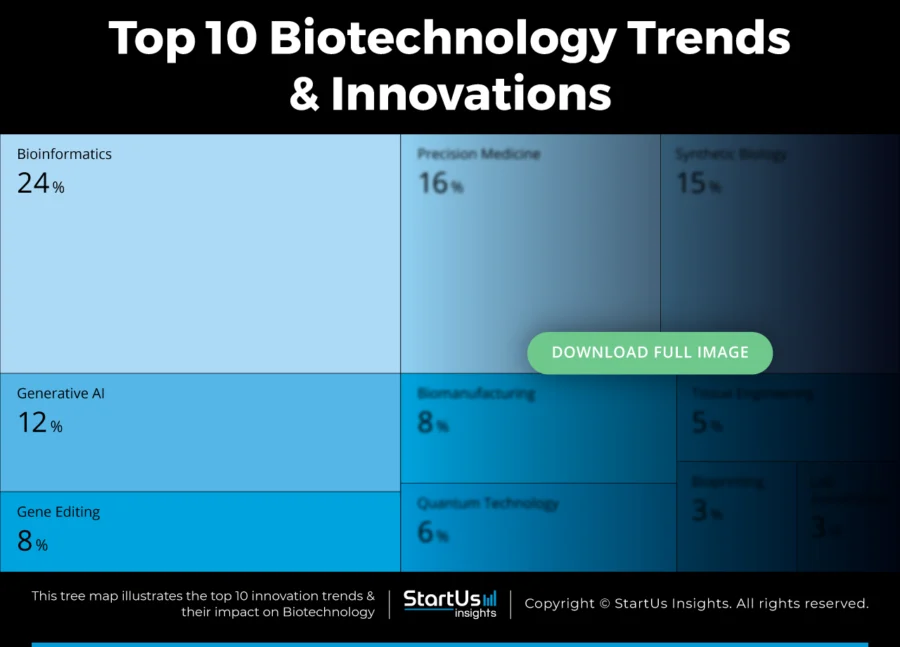
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Biotechnology Trends
The Tree Map below outlines trends shaping biotechnology in 2025, emphasizing research, medical progress, and industrial uses. Bioinformatics and generative AI accelerate genetic research by enabling faster data analysis and drug discovery.
Gene editing and precision medicine drive targeted treatments, and synthetic biology expands applications in bioengineering. Moreover, biomanufacturing changes how pharmaceuticals and bio-based materials are produced for increasing efficiency and scalability.
Global Startup Heat Map covers 4500+ Biotechnology Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 4500+ exemplary startups and scaleups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in Western Europe and the United States, followed by India. From these, 4500+ promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.

Want to Explore Biotechnology Innovations & Trends?
Top 10 Emerging Trends in Biotechnology [2025 and Beyond]
1. Bioinformatics
The global bioinformatics market reached USD 16.66 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass USD 52.01 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 12.05% from 2025 to 2034.
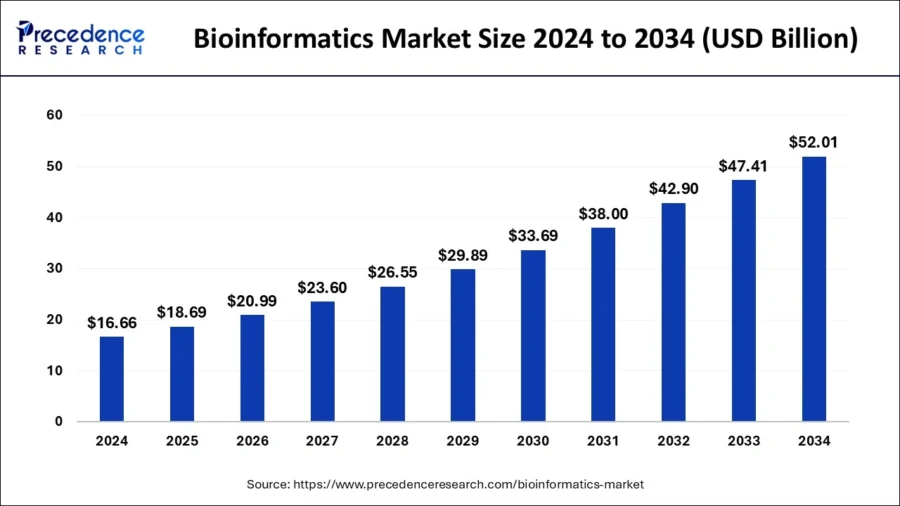
Credit: Precedence Research
Biotech venture capital funding grew in 2024, with USD 7.4 billion invested in Q1 and USD 9.2 billion in Q2, which totals USD 16.6 billion across 411 deals by midyear. These investments highlight confidence in biotech innovation, particularly in AI-driven bioinformatics.
AI transforms bioinformatics by accelerating drug discovery and development through molecular interaction analysis and predictive modeling of drug candidates.
Rising clinical trials and biomarker discovery efforts further promote AI adoption to improve trial efficiency and advance precision medicine.
Cloud computing and high-performance computing (HPC) offer scalable solutions for processing large biological datasets, which lowers entry barriers for smaller research organizations. The shift to cloud-based bioinformatics platforms is increasing access to computational tools that enable collaboration and speed up scientific discovery.
Further, next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies generate vast genetic data volumes that require bioinformatics for storage, analysis, and interpretation. These solutions support genomics, transcriptomics, and metagenomics research, with applications in diagnostics, precision medicine, and agricultural biotechnology.
PrecisionPhage advances Phage Bioinformatics
Finnish startup PrecisionPhage provides a platform Phagenomics for phage genome assembly, analysis, and comparison. Phagenomics guides users through genome assembly from raw sequencing data, performs automatic quality control, and selects contigs. It then offers annotation using advanced bioinformatic tools.
The startup’s platform’s interface removes the need for coding skills, which makes phage genome analysis accessible and reduces the time and costs of traditional methods. PrecisionPhage enables researchers and clinicians to analyze phage genomes, support therapeutic decisions, and advance phage-related studies.
Chromatin Bioscience enables Synthetic Promoters Design
UK-based startup Chromatin Bioscience designs synthetic promoters for diverse client needs. Its chromatinLENS platform analyzes multi-omics datasets and creates promoters for precise, cell-type-specific gene expression. It identifies short regulatory motifs active in specific cell types or environmental conditions to generate libraries of genetic parts that control gene expression.
The startup’s method enables the engineering of genetic circuits for controllable gene expression. It supports gene and cell therapies, biologics manufacturing, industrial biotechnology, and agricultural biotechnology.
2. Precision Medicine
The global precision medicine market is projected to grow to USD 207.80 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 10.8% during the forecast period 2024-2032.
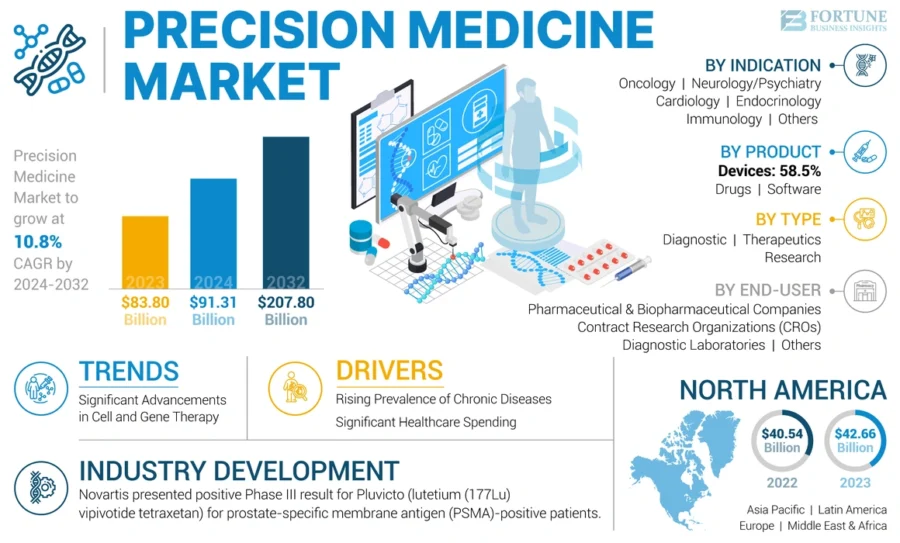
Credit: Fortune Business Insights
Besides, the precision medicine software market is growing, expected to reach USD 3.50 billion by 2029 with a CAGR of 12.57% from 2024 to 2029.
Cloud-based analytics, AI-driven insights, and advanced patient data integration platforms are streamlining personalized treatment approaches.
Regulatory approvals in 2024 reflect the rising adoption of precision medicine. The FDA approved 48 precision medicine indications, including 35 biomarker-indicated drugs, eight autologous cell therapies, and five gene therapies.
Significant milestones include the first two autologous cell therapies for solid tumors and the first FDA approval for treating NRG1 fusion-positive tumors.
Further, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences provided a five-year, USD 11.4 million grant to the Kansas Institute for Precision Medicine to develop genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic-based therapeutic innovations.
Technological progress is also improving genome sequencing efficiency and affordability, which accelerates the identification of genetic mutations linked to diseases and supports targeted drug development.
As precision medicine grows beyond genomics, metabolomics is emerging as a vital field and is expected to gain momentum in 2025. It measures metabolites and low-molecular-weight molecules to offer insights into disease mechanisms and biomarker discovery.
Montara Therapeutics facilitates Brain-targeted Therapeutics
US-based startup Montara Therapeutics develops BrainOnly, a platform for brain-selective therapies targeting central nervous system diseases. The technology uses a two-drug combination: a brain-penetrant, target-specific drug, and a non-brain-penetrant universal peripheral blocker.
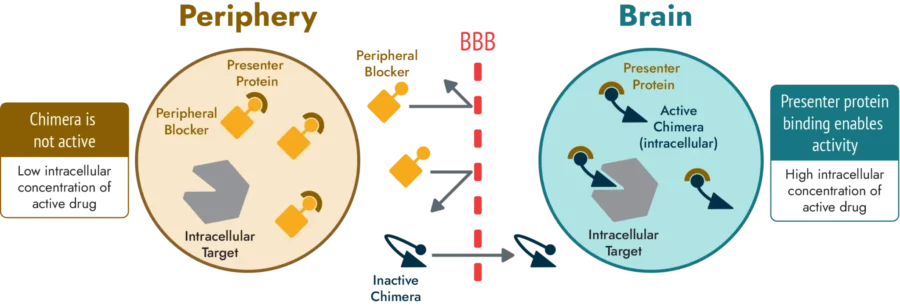
The peripheral blocker saturates presenter proteins outside the brain to prevent the target-specific drug from binding peripherally and reducing side effects. After crossing the blood-brain barrier, the target-specific drug binds to presenter proteins in the brain to improve therapeutic effectiveness. BrainOnly enhances the safety and efficacy of treatments for neurological diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and brain cancers.
Primo Biotechnology advances Radiopharmaceuticals
Taiwanese startup Primo Biotechnology builds radioligand theranostics (RLT) for precision medicine, combining PET diagnostics with targeted radioligand therapy to treat cancer.
Its approach involves a targeting molecule that binds to specific tumor receptors, enzymes, or proteins, and a linker that ensures the drug’s biological stability. It also includes radionuclides, such as positron emitters (18F or 68Ga) for imaging and alpha or beta emitters (177Lu or 131I) for treatment.
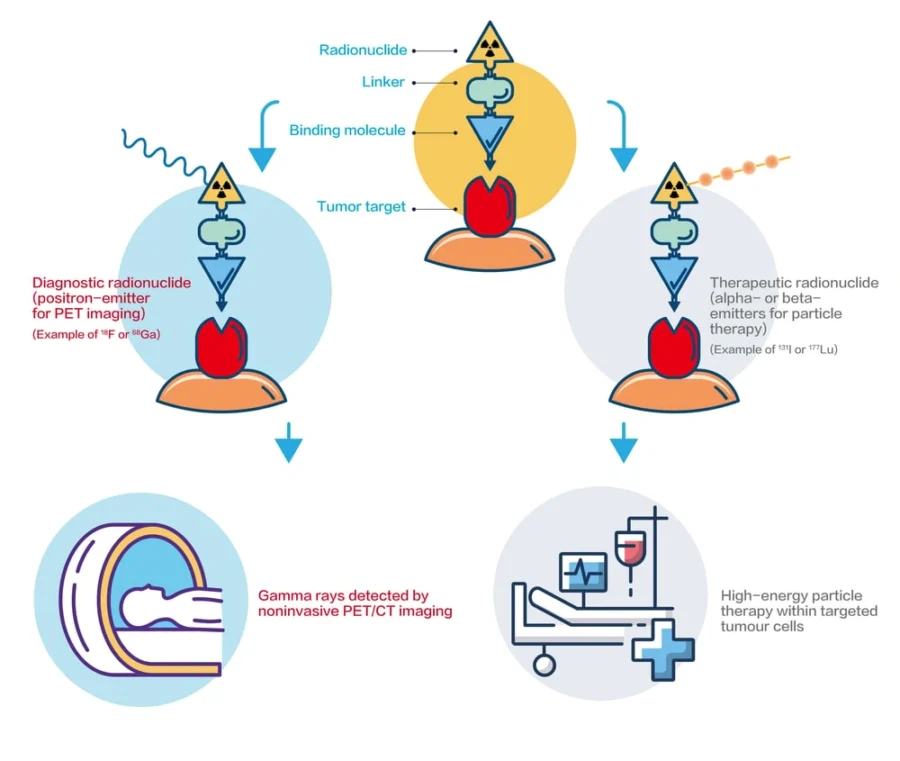
Physicians use startup’s RLT drugs in an image-guided process. They begin with non-invasive imaging to detect the cancer’s presence, location, and cell count. Based on the results, they decide whether to proceed with RLT-specific therapy, conventional therapy, or a combination.
Moreover, to address the increasing prostate cancer cases in Taiwan, Primo Biotechnology partnered with ABX to prepare for the introduction of PB01 to the Taiwanese market.
3. Synthetic Biology
The global synthetic biology market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20.6%, reaching USD 31.52 billion by 2029 during the forecast period 2024 to 2029.
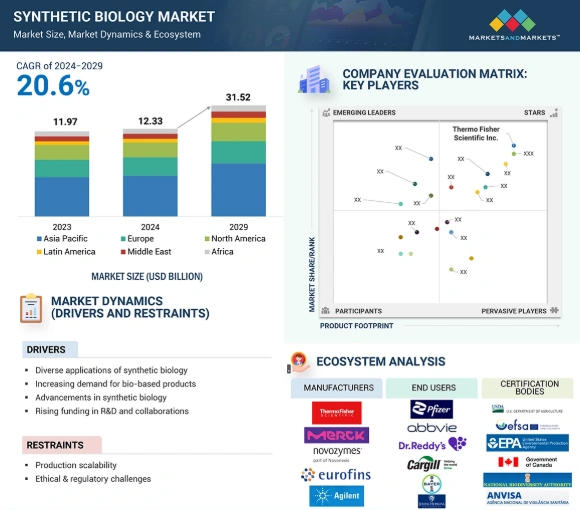
Credit: Markets and Markets
North America is projected to hold 42.3% of the global market share in 2025. This dominance stems from investments in research and development by biotechnology firms in the United States and Canada, which is supported by government funding and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
Besides, the OECD’s 2025 synthetic biology technology roadmap highlights the sector’s development over different timeframes. In the short term, AI-assisted design and fermentation advancements are expected to reduce the cost of bio-based products to improve their commercial viability.
Further reductions in DNA synthesis costs, cellular biosensors for real-time monitoring, improved biocontainment methods, and engineered living materials will shape the field in the medium term.
Lastly, in the long term, breakthroughs in whole-genome design and full-organism engineering are anticipated to drive progress in biofabrication and synthetic life sciences.
Also, the expansion of healthcare and life science facilities is enabling broader use of synthetic biology in therapeutics and diagnostics. The applications across pharmaceuticals, agriculture, energy, and materials science are encouraging adoption.
PhaBuilder makes Polymer Material Application
Chinese startup PhaBuilder offers PHAbrary platform for polymer material applications derived from polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA). This platform uses synthetic biology technology that aligns market demand with research and development to maintain a database that allows global customers to create PHA-based solutions.
The startup’s platform delivers refined modification options and detailed chemical property data to support various applications. This includes medical materials, catering supplies, food packaging, cosmetic packaging, beverage packaging, travel accessories, daily necessities, agricultural products, 3D printing, fiber textiles, and electronics packaging.
Novel Bio produces Plasmid DNA
Canadian startup Novel Bio develops the NBX, a microbial system for plasmid DNA production. This platform outperforms standard E. coli systems by producing higher yields, reducing run times, and improving quality. It integrates easily into existing workflows and remains compatible with E. coli infrastructure, which allows adoption without major process changes.
NBX lowers endotoxin levels and scales efficiently from research to clinical-scale production and provides a solution for large-scale plasmid DNA manufacturing. Novel Bio supports gene and cell therapy, RNA therapeutics, and nucleic acid vaccine development to improve drug development efficiency and address capacity challenges in biopharmaceutical production.
4. Generative AI
The global generative AI in biotech market is projected to reach USD 472 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 24.9% from 2023 to 2032.
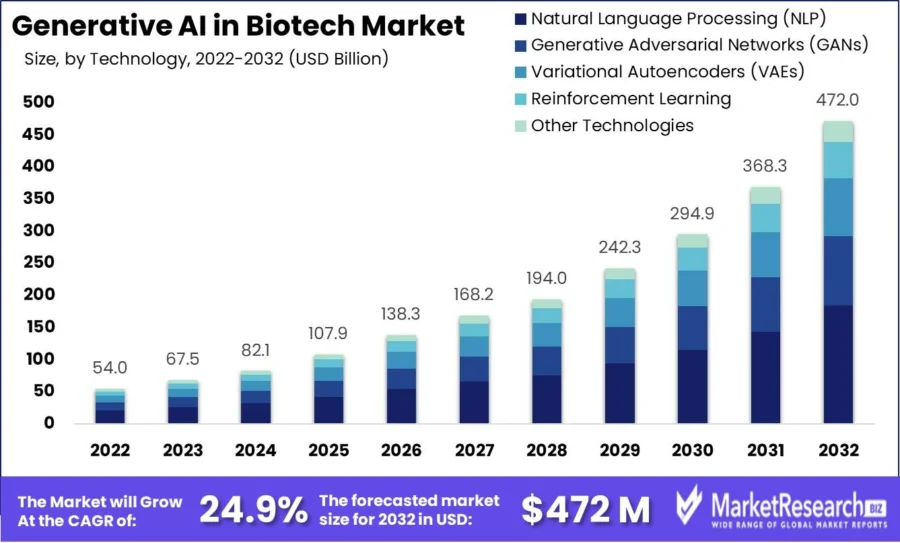
Credit: MarketResearch.biz
Investment in biotech AI rose sharply in 2024, reaching USD 5.6 billion, nearly tripling from previous levels. This funding reflects confidence in AI-driven biotech solutions, particularly for drug discovery, genomic data analysis, and clinical trial optimization.
A Google Cloud study found that 62% of healthcare and life sciences executives had implemented generative AI use cases, with 74% reporting positive returns on investment (ROI).
Besides, the key trends driving the adoption of generative AI are multimodal AI, AI agents, intuitive search tools, and AI-powered user experiences. These innovations enable efficient drug discovery, precision medicine, and research workflow automation while reducing reliance on traditional experimentation.
AI agents are expected to transform life sciences by automating tasks such as genomic data interpretation, biomarker identification, and clinical trial design by 2025.
Moreover, hybrid models integrating generative AI, quantum computing, and specialized machine learning are expected to gain traction.
Companies advancing this field include Model Medicines, whose GALILEO platform supports AI-driven antiviral drug discovery, and Insilico Medicine, which uses quantum-enhanced techniques to address complex oncological targets.
The integration of quantum-classical models is delivering precise molecular exploration and opening new pathways for drug development and therapeutic innovation.
NEBULA builds Physics-based Generative AI
French startup NEBULA develops a physics-based, dataset-free generative AI platform to map the 3D structural landscape of macromolecules under physiological conditions. This platform generates new conformations such as major transitions like opening, closing, activation, and deactivation, without using pre-existing datasets.
NEBULA identifies cryptic or transient binding pockets and novel sites for allosteric modulation to improve the accuracy of virtual screening and increase the likelihood of finding effective drug candidates. The startup integrates its technology into existing drug discovery processes, reducing development timelines and accelerating the delivery of treatments.
Silica Corpora develops Antibody Therapy Platform
German startup Silica Corpora builds an AI-based platform for de novo therapeutic antibody design. It uses protein large language models trained on millions of protein-protein interactions. The startup’s platform requires only amino acid sequences as input to generate novel antibodies without relying on in vitro or in vivo methods.
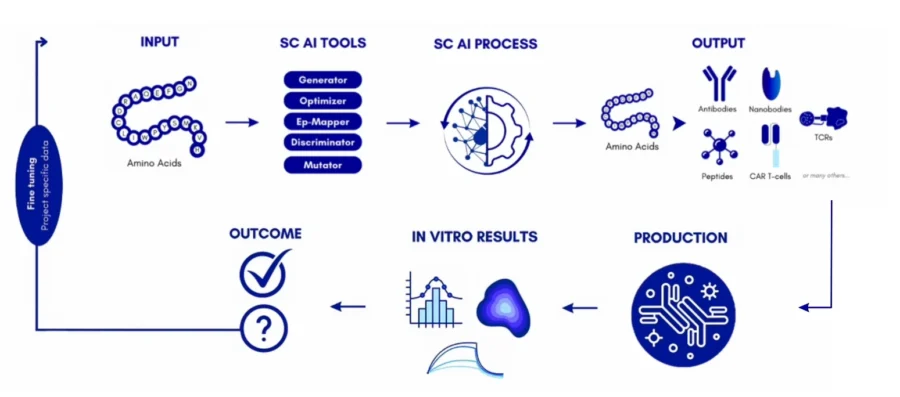
Silica Corpora Generator designs complementary-determining regions with a mean similarity of 85% to 98% to established therapeutics, which shows its accuracy in producing viable antibody candidates. Its Discriminator screens antibodies efficiently with a 98% success rate and distinguishes binders from non-binders within hours.
Further, the Optimizer tool improves binding affinity and other properties through sequence refinement. The Ep-Mapper predicts epitope amino acids with precision and recall values of 0.68 and 0.71, exceeding the performance of existing methods.
5. Gene Editing
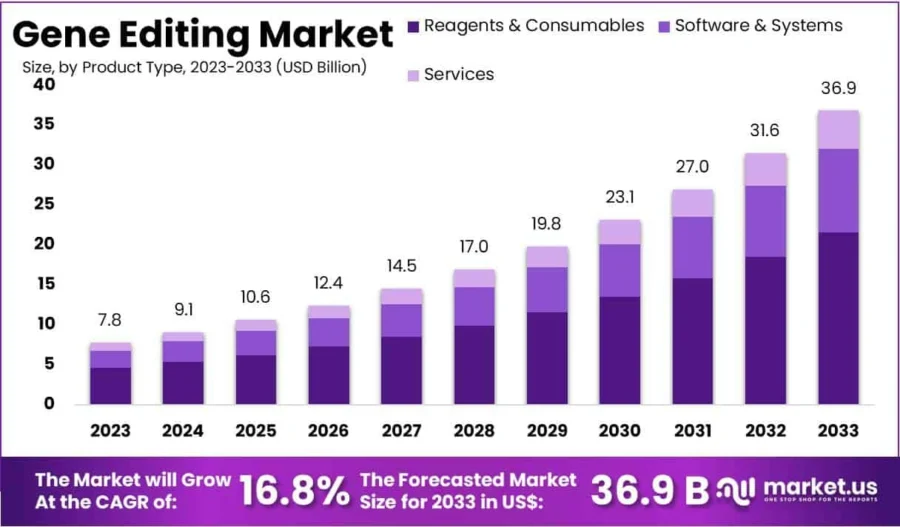
The global gene editing market is expected to reach USD 36.9 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 16.8% from 2024 to 2033.
Credit: Market.us
Within this market, the CRISPR gene editing segment is projected to expand from USD 4.77 billion in 2025 to USD 16.47 billion by 2034, reflecting a CAGR of 14.77% during this period.
The first CRISPR-based medicine, Casgevy, received approval for treating sickle cell disease and transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia in late 2023. It marked a significant step for genetic therapies targeting inherited blood disorders and signaled broader adoption of CRISPR-based treatments.
In March 2024, a study published in Nature Biotechnology by MIT researchers introduced a rapid gene-editing screen for assessing cancer mutations. This development enables faster identification of genetic drivers of disease.
Advanced CRISPR techniques, such as base editing and prime editing, now use modified Cas enzymes to make precise single nucleotide changes without causing double-strand DNA breaks and reduce the risk of unintended mutations.
Further, CRISPRa (gene activation) and CRISPRi (gene inactivation) use modified sgRNA/Cas complexes to target gene promoters and provide precise control of gene expression without altering DNA sequences.
Moreover, advances in non-viral and viral delivery methods are improving in vivo gene editing efficiency. New adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsids with enhanced tissue targeting abilities are increasing the specificity of gene delivery.
Meanwhile, non-viral delivery methods, such as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), are gaining popularity as safer, scalable alternatives to viral vectors.
Virostem manufactures CRISPR Gene Editing Products
Turkish startup Virostem designs lentiviral vectors for gene knockout, gene expression, and reporter assays. Its CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout Lentivirus includes three sgRNA/Cas9 all-in-one lentiviruses and a scrambled control. Each vector offers customizable selection markers, such as puromycin, blasticidin, neomycin, or GFP.
The Custom Gene Expression Lentivirus allows stable gene overexpression with user-defined selection markers, while the GFP Expression Lentivirus provides consistent fluorescent protein expression in target cell lines.
Besides, the Luciferase Expression Lentivirus supports bioluminescent reporting for functional assays. Virostem advances genetic research, drug discovery, and cell-based studies with tools for precise and efficient gene modulation.
Cimeio Therapeutics develops Immunotherapy for Hematologic Disorders
US-based startup Cimeio Therapeutics makes Shielded-Cell & Immunotherapy Pairs (SCIP), a method for treating hematologic diseases. This approach uses gene editing to modify cell surface proteins in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), which makes them resistant to depletion by paired immunotherapies while maintaining their function.
By safeguarding healthy cells, SCIP allows the safe use of immunotherapies that selectively target and eliminate diseased cells. This strategy offers therapeutic options for hematologic malignancies, autoimmune disorders, and genetic diseases, to provide effective treatments and improve patient outcomes.

6. Biomanufacturing
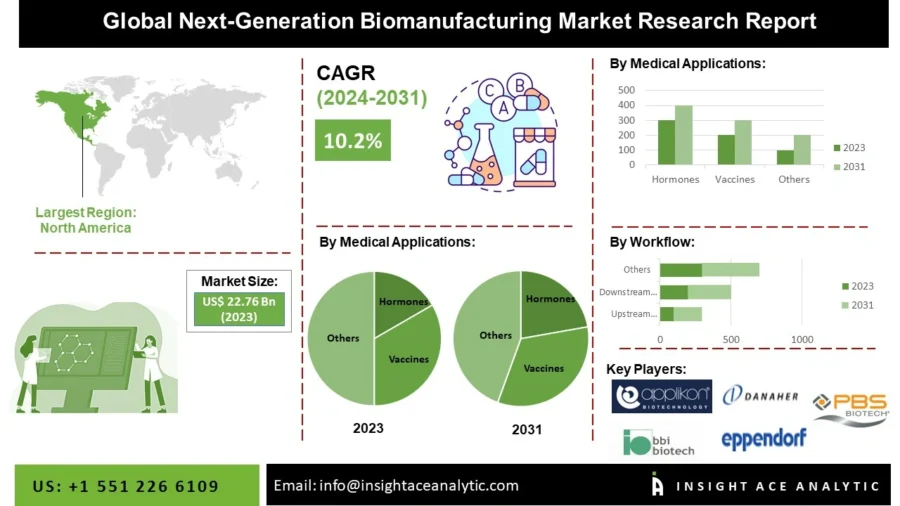
The next-generation biomanufacturing market is expected to reach USD 48.27 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2024 to 2031.
Credit: InsightAce Analytic
China invested USD 4.17 billion in biomanufacturing to advance innovation in bio-based chemicals, precision biotherapeutics, and sustainable biofuels in 2024.
Meanwhile, India introduced its first national biotechnology policy, Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment (BioE3), focusing on six strategic areas: bio-based chemicals and enzymes, smart proteins, precision biotherapeutics, climate-resilient agriculture, biofuels and carbon capture, and marine and space research.
Digital technologies are reshaping biomanufacturing, with AI, digital twins, and advanced process control systems optimizing production efficiency, improving quality control, and reducing process variability.
Digital twins, increasingly adopted for process optimization, facility design, and predictive analytics, allow manufacturers to simulate bioprocesses virtually before making real-world changes.
In addition, process analytical technology (PAT) is advancing in 2025, enabling real-time monitoring and control of biomanufacturing processes.
Automation is progressing through tools like Raman spectroscopy, chromatography, and mass spectrometry, which provide continuous monitoring of product quality.
Coastal BioTech manufactures Bio-Materials
Tanzanian startup Coastal Biotech produces bio-material ingredients from macroalgae to replace chemical inputs in agriculture and industrial processes. It cultivates regenerative ocean crops like Rhodophyta (red algae) and Chlorophyta (green algae), which help replenish ecosystems during growth.
The startup processes seaweed into organic fertilizers and biostimulants to improve soil health, improve crop yields, and enhance resilience to environmental stress. It also researches the use of micro-organisms and fungi in bio-agriculture to optimize industrial processes. Coastal Biotech lowers input costs for farmers, supports regenerative farming, and strengthens food security.
Cauldron advances Hyper-fermentation
Australian startup Cauldron builds hyper-fermentation technology to transform biomanufacturing. This system uses continuous fermentation with novel bioreactor designs, optimized growth media, and advanced protocols to address contamination, genetic drift, and production inefficiencies.
The startup’s ACE media ensures precise nutrient composition to prevent contamination and support various microorganisms. Its Hyper-Fermentation OS improves genetic stability and maintains long-term, efficient production, working like an assembly line for continuous output.
Cauldron’s process allows frequent, larger-volume harvesting, increasing productivity while lowering costs. It reduces electricity, water, sterilization, and labor needs to enhance capital efficiency, eliminate large-scale bioreactor requirements, and reduce capital expenditure.
7. Quantum Technology
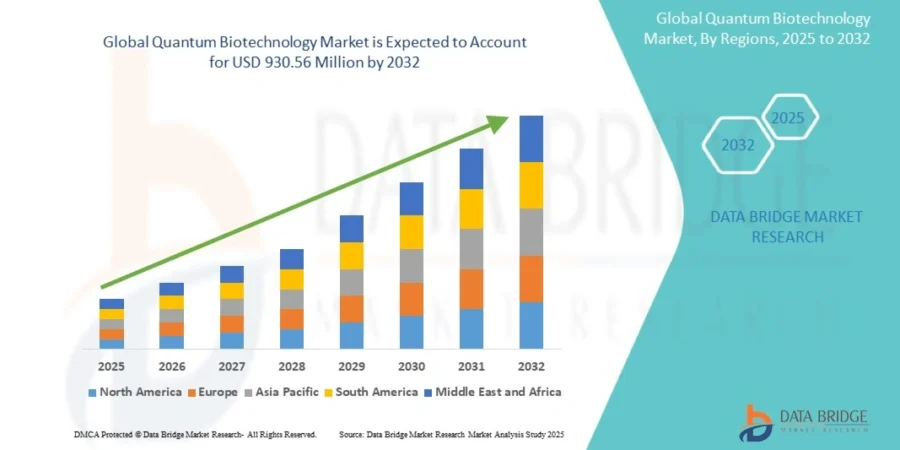
The global quantum biotechnology market was valued at USD 321 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 930.56 million by 2032, with a CAGR of 14.23% from 2025 to 2032.
Credit: Data Bridge Market Research
The University of Queensland launched the AUD 45 million (approximately USD 30.2 million) ARC Centre of Excellence in Quantum Biotechnology (QUBIC) to apply quantum technologies in addressing challenges in health, energy, and agriculture.
Quantum computing is transforming drug discovery and molecular design by enabling accurate simulations of protein-ligand interactions.
Researchers recently introduced a quantum-classical generative model for small-molecule drug design that led to the synthesis of 15 new KRAS inhibitor molecules for cancer therapy.
In protein analysis, quantum computing is providing deeper insights into molecular interactions. For example, Pasqal and Qubit Pharmaceuticals developed a hybrid quantum-classical method for analyzing protein hydration, successfully tested on Orion, a neutral-atom quantum computer.
Beyond drug discovery, quantum computing is enhancing genomic sequencing and personalized medicine by enabling faster and more precise analysis of complex genetic data.
Besides, quantum algorithms processing large-scale genomic datasets are advancing precision medicine tailored to individual genetic profiles.
Moreover, researchers are using quantum algorithms to determine Gibbs free energy profiles for prodrug activation and simulate covalent bond interactions to enable more accurate predictions of drug stability and efficacy.
QDX builds a Computational Drug Discovery Platform
Singaporean startup QDX creates a computational drug discovery platform that combines molecular dynamics, quantum mechanical calculations, and AI. The platform uses large-scale, long-range molecular dynamics simulations to study the behavior of biological macromolecules.
The startup’s quantum technology stack performs rapid ab initio energy calculations and molecular simulations to provide detailed insights into molecular interactions.
It integrates these capabilities with AI systems trained on extensive quantum data to improve molecule optimization and design, which enhances predictions of binding affinities and molecular behaviors. QDX provides pharmaceutical companies and researchers with tools to accelerate drug discovery and develop therapeutics efficiently.
PolarisQB facilitates Quantum-aided Drug Design
US-based startup PolarisQB develops the Quantum-Aided Drug Design (QuADD) platform to accelerate drug discovery using quantum computing. It employs quantum annealing, in collaboration with D-Wave, to solve large-scale optimization problems faster than traditional computational methods.
By accessing a chemical space of 10³⁰ compounds, it allows researchers to explore de novo combinatorial spaces and on-demand chemical libraries. This identifies optimized drug candidates within days instead of months. QuADD uses physics-based calculations to design molecules for various protein targets, including protein-protein interactions, GPCRs, kinases, and metallo-proteins.
The startup’s platform optimizes molecular structures, objectives, and constraints in minutes to generate candidates tailored for drug-likeness, synthetic accessibility, and blood-brain barrier permeability. QuADD also offers real-time data-driven collaboration tools to ensure transparency and actionable insights for researchers.
8. Tissue Engineering
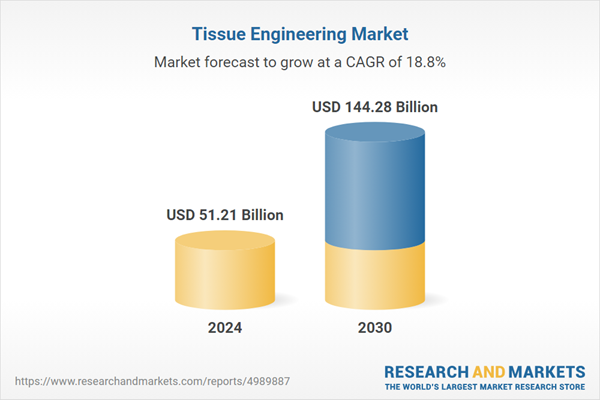
The global tissue engineering market was valued at USD 51.21 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.82%, reaching USD 144.28 billion by 2030.
Credit: Research and Markets
The rising prevalence of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, and orthopedic disorders, has created a need for advanced tissue engineering solutions. Besides, the shortage of organs and tissues for transplantation is increasing the demand for bioengineered alternatives.
In August 2024, Dr. Josephine Wu from Trinity College Dublin secured USD 882 604 (EUR 800 000) in Wellcome Trust funding for OPTO-BIOPRINTING. This tissue engineering platform uses light to control protein production within cells, showcasing the potential of biofabrication techniques in developing functional tissues for transplantation and research.
Supporting progress in this field, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) launched the Cancer Tissue Engineering Collaborative (TEC) Research Program in 2025 to advance biomimetic tissue-engineered models for cancer research.
Further, AI-driven scaffold design is advancing biocompatible materials and improving their integration with biological tissues. Machine learning models are being used to predict viable tissue engineering technologies and streamline commercialization timelines for speeding up the clinical application of bioengineered tissues.
In addition, AI integrated with advanced imaging techniques is enhancing diagnostic capabilities to enable real-time monitoring of engineered tissue structures and functions.
Researchers are further developing genetically modified stem cells to improve regenerative capabilities to increase their use in treating degenerative diseases and tissue damage.
Injectable biomimetic hydrogels are being designed as matrices to support stem cell growth and differentiation to improve cell viability and tissue regeneration. Moreover, gene editing and mRNA technologies are also modifying stem cells at the genetic level to enable targeted tissue regeneration with precision and efficiency.
Amodera Lab makes Betulin Nanofiber Technology
Latvian startup Amodera Lab builds betulin nanofiber technology, a bio-based material for skincare, medicine, and veterinary use. This technology extracts betulin from birch bark using a proprietary, eco-friendly method that increases efficiency compared to traditional processes.
The extracted betulin is incorporated into nanofibers through a needle-free electrospinning process. It enables applications in skin anti-aging, wound healing, and pet paw protection.
The startup’s technology also supports cosmeceutical uses, including dermal fillers and post-surgical treatments, as well as medical applications such as drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and anti-inflammatory therapies.
The material’s adaptability allows its use in formats such as facial sheet masks, eye patches, and lip treatments. Further, veterinary applications include wound healing and inflammation management.
Cell AgriTech produces Cultivated Meat
Malaysian startup Cell AgriTech creates cultivated meat products using biotechnology to avoid traditional livestock farming. The process begins with a simple biopsy to select and screen healthy animal cells to provide a foundation for meat production.
These cells are placed in a bioreactor and supplied with nutrients, vitamins, and controlled environmental conditions, which allows them to grow and multiply naturally. As the cells mature, they move through progressively larger bioreactors to form muscle and fat similar to natural growth inside an animal.
After several weeks, the cultivated meat is harvested to offer a sustainable alternative to conventional meat. Cell AgriTech eliminates the need for antibiotics, growth hormones, and large-scale farming, reducing environmental impact while preserving the taste and texture of traditional meat.
9. Bioprinting
The 3D bioprinting market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 23.3%, reaching USD 5.11 billion by 2029.
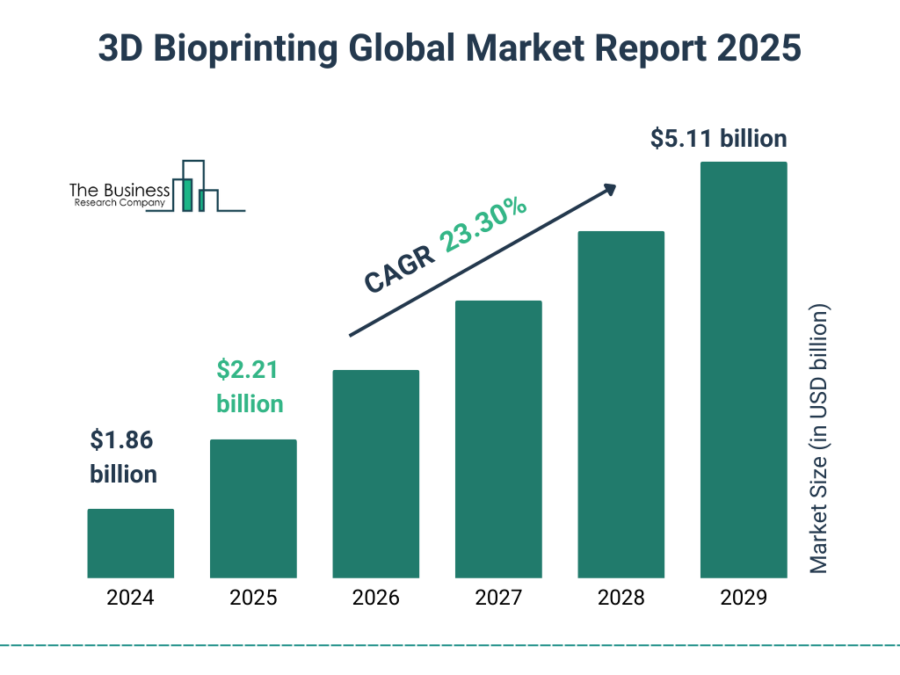
Credit: The Business Research Company
Europe accounts for 40% of bioprinting companies, which makes it the leading hub, while North America represents 38% of the industry. Asia holds 17% of the global share and is supported by increasing investments in regenerative medicine, bioprinting infrastructure, and biofabrication technologies.
AI and machine learning are enhancing bioprinting by optimizing cell placement, refining material selection, and reducing fabrication errors. These tools improve the structural integrity of bioprinted constructs to ensure medical compatibility and long-term functionality.
Computational models also provide real-time predictive insights to advance the mechanical and biological properties of bioprinted tissues.
Further, peptide self-assembly technology combined with 3D printing enables the development of complex biological structures with improved functional biomimicry.
Advances in cellular reprogramming are driving the creation of superior bioinks, enabling more functional bioprinted tissues. In addition, scalable fabrication of vascularized tissue constructs addresses challenges in tissue engineering to improve the viability of bioprinted organs.
Organ transplantation remains a key application for 3D bioprinting, addressing global organ shortages. As of now, 103 223 people are on the US national transplant waiting list, with 17 deaths reported daily due to organ scarcity.
Bioprinting offers a solution by creating bioengineered tissues and organs to reduce reliance on donor-based transplants. The commercialization of bioprinted organs is expected to shorten waiting times and improve accessibility, potentially saving many lives.
Biomotion builds a 3D Bioprinting System
Austrian startup Biomotion develops the ExplorerONE 3D bioprinting platform that uses various printheads and printing modes to combine multiple materials and cell types within a single construct. It supports a wide range of biomaterials, including custom formulations, to broaden experimental possibilities.
Its drag-and-drop software simplifies the process, which allows researchers to turn concepts into bioprints without requiring extensive expertise.
The platform also includes an open hardware expansion kit to enable the development of custom innovations to suit specific research requirements. Biomotion allows researchers to produce consistent and reproducible biofabrication of human tissues.
CompagOs produces 3D In-Vitro Bone Models
Swiss startup CompagOs builds Bon3OID, a 3D in vitro bone model derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. It uses 3D bioprinting to create hydrogel scaffolds embedded with cells from both healthy and diseased donors.
These scaffolds undergo cyclic mechanical loading in bioreactors to mimic the mechanical stresses experienced by bone cells during daily activities, which promotes cell-mediated mineralization.
The organotypic bone models include osteoblasts and osteocytes, and also allow customization with additional cell types, such as osteoclasts and cancer cells, to meet specific research or clinical needs. This adaptability enables the replication of conditions like osteogenesis imperfecta, osteosarcoma, and bone metastases.
10. Lab Automation
The global lab automation market is expected to grow from USD 6.5 billion in 2025 to USD 16 billion by 2035, with a CAGR of 9.4% during this period.
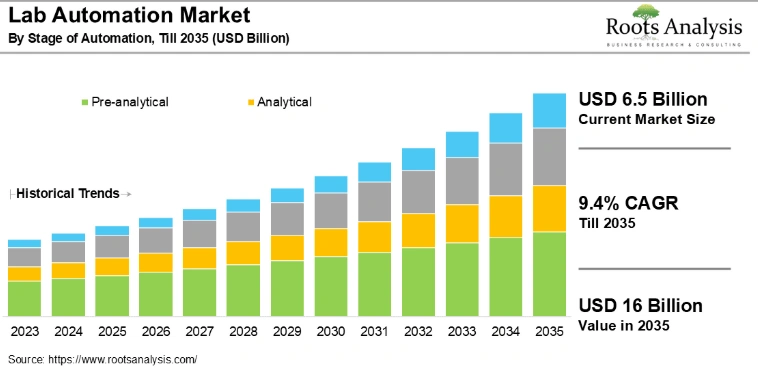
Credit: Root Analysis
Monomer Bio secured USD 5.6 billion in seed funding to develop an AI-powered lab automation platform to accelerate treatment development in February 2024.
According to the DDW Research & Consultancy 2025 report, over 50% of laboratories plan to invest in new automation equipment within the next two years.
Also, AI-driven automation is streamlining research, drug development, and manufacturing by enabling faster, more precise, and scalable lab processes.
Autonomous lab (ANL) systems, which integrate robotics and AI, independently conduct biotechnology experiments and optimize medium conditions for recombinant bacterial strains.
Automated predictive analytics are further enhancing workflows, improving research throughput, and reducing experimental timelines. Miniaturized and fully automated labs are becoming more common, supported by technologies like high-throughput screening, microplate readers, and liquid-handling robots.
In the US, diagnostic inaccuracies are estimated to cause 40 000 – 80 000 deaths annually. Automated diagnostic systems streamline ordering, testing, and reporting processes, reducing human error and improving turnaround times.
Moreover, clinical laboratories widely adopt automation to enhance accuracy, lower costs, and improve patient outcomes. Automated systems provide higher throughput, better reagent efficiency, and standardized diagnostic testing.
Aradon builds a Biotech Operating System
Dutch startup Aradon creates Aradon Studio, an operating system to streamline research and development workflows for biotech organizations. It includes process canvas, a graphical interface that allows teams to map and discuss processes collaboratively. This feature identifies inefficiencies and highlights optimization opportunities.
Its improvement autopilot suggests software and hardware integrations with high potential returns, while the integration wizard connects software and scripts. This tool generates integration plans, allowing new technologies to be deployed within 24 hours.
The startup’s platform operates on secure infrastructure to ensure that critical biotech data stays within the user’s system while retaining full functionality. Aradon enables biotech teams to enhance innovation, strengthen operational oversight, and allocate resources effectively.
ABLE Labs manufactures Liquid Handling Robot
South Korean startup ABLE Labs develops a compact liquid handling robot NOTABLE to automate repetitive laboratory tasks with flexibility and ease.
The system includes 12 ANSI/SLAS microplate slots and supports modular add-ons like a magnetic shaker, temperature shaker, and an optional ULPA fan filter for controlled environments. Its frameless design integrates with analytical instruments, while the framed version provides environmental control when needed.
The startup’s Windy software interface simplifies operation, which allows researchers to use the system without extensive training. Further, its continuous software updates and customer-driven improvements support evolving laboratory needs.
Discover all Biotechnology Trends, Technologies & Startups
Biotechnology is evolving through AI-driven research, advanced gene therapies, and innovations in biomanufacturing. Nanobiotechnology plays an important role in targeted drug delivery, while CRISPR-based diagnostics expand early disease detection capabilities. These advancements are driving progress in healthcare and personalized medicine.
The Biotechnology Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.










